Function commands table 3, I/o signaling – Rainbow Electronics DS2770 User Manual
Page 21
DS2770
21 of 27
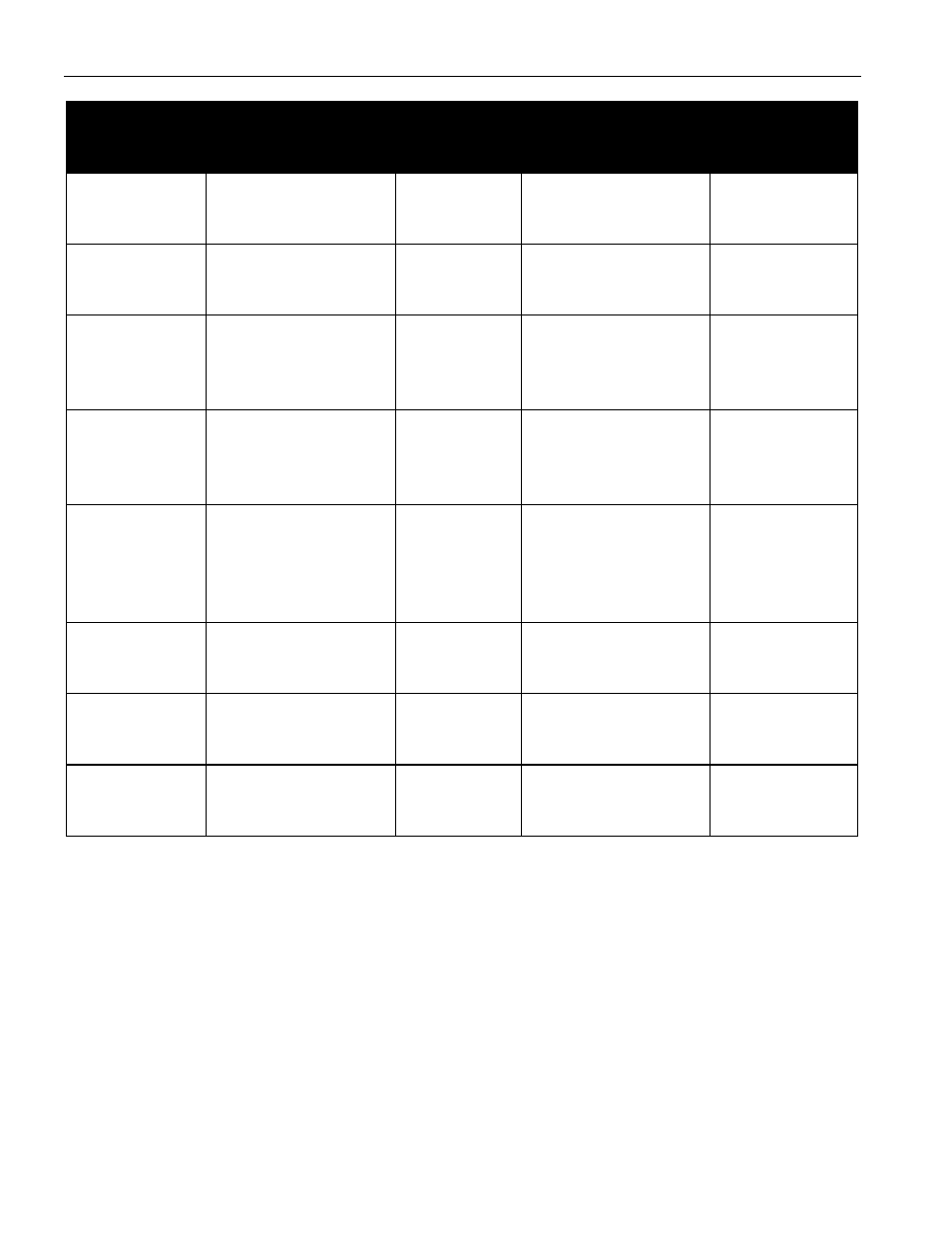
FUNCTION COMMANDS Table 3
COMMAND
DESCRIPTION
COMMAND
PROTOCOL
BUS STATE AFTER
COMMAND
PROTOCOL
BUS DATA
Read Data
Reads data from
memory map starting
at address XX
69h, XX
Master R
X
Unlimited
Write Data
Writes data to memory
starting at address XX
6Ch, XX
Master Tx
Unlimited
Copy Data
Copies shadow RAM
data to EEPROM
block that begins with
address location XX
48h, XX
Master Reset
None
Recall Data
Recalls EEPROM
block that begins with
address location XX to
shadow RAM
B8h, XX
Master Reset
None
Lock
Permanently locks the
block of lockable
EEPROM memory
that begins with
address location XX
6Ah, XX
Master Reset
None
Refresh
Restores Status
Register initialization
data
63h
Master Reset
None
Start Charge
Initiates charge
through the host
interface.
B5h
Master Reset
None
Stop Charge
Terminates charge
through the host
interface.
BEh
Master Reset
None
I/O SIGNALING
The 1-Wire bus requires strict signaling protocols to insure data integrity. The DS2770 uses the following
four protocols: the initiation sequence (reset pulse followed by presence pulse), Write 0, Write 1, and
Read Data. All of these types of signaling except the presence pulse are initiated by the bus master.
Figure 18 shows the initialization sequence required to begin any communication with the DS2770. A
presence pulse following a reset pulse indicates the DS2770 is ready to accept a Net Address command.
The bus master transmits (T
X
) a reset pulse for t
RSTL
. The bus master then releases the line and goes into
Receive Mode (R
X
). The 1-Wire bus line is then pulled high by the pull-up resistor. After detecting the
rising edge on the DQ pin, the DS2770 waits for the t
PDH
and then transmits the presence pulse for t
PDL
.
