Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX9755 User Manual
Page 20
MAX9750/MAX9751/MAX9755
2.6W Stereo Audio Power Amplifiers and
DirectDrive Headphone Amplifiers
20
______________________________________________________________________________________
Applications Information
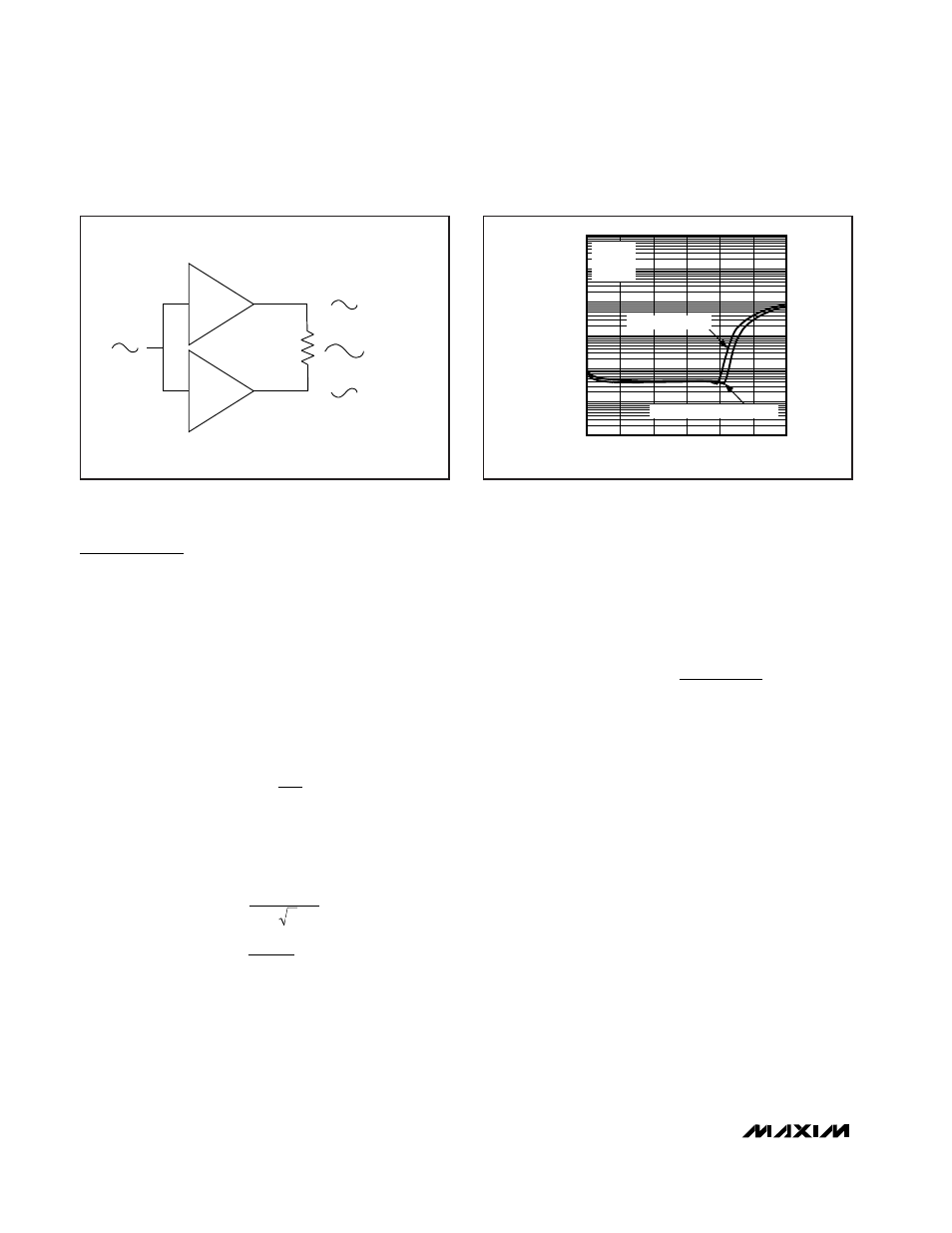
BTL Speaker Amplifiers
The MAX9750/MAX9751/MAX9755 feature speaker
amplifiers designed to drive a load differentially, a con-
figuration referred to as bridge-tied load (BTL). The BTL
configuration (Figure 9) offers advantages over the sin-
gle-ended configuration, where one side of the load is
connected to ground. Driving the load differentially
doubles the output voltage compared to a single-
ended amplifier under similar conditions. Thus, the
device’s differential gain is twice the closed-loop gain
of the input amplifier. The effective gain is given by:
Substituting 2 X V
OUT(P-P)
into the following equation
yields four times the output power due to double the
output voltage:
Since the differential outputs are biased at midsupply,
there is no net DC voltage across the load. This elimi-
nates the need for DC-blocking capacitors required for
single-ended amplifiers. These capacitors can be large
and expensive, can consume board space, and can
degrade low-frequency performance.
Power Dissipation and Heat Sinking
Under normal operating conditions, the MAX9750/
MAX9751/MAX9755 can dissipate a significant amount
of power. The maximum power dissipation for each
package is given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings
under Continuous Power Dissipation, or can be calcu-
lated by the following equation:
where T
J(MAX)
is +150°C, T
A
is the ambient tempera-
ture, and θ
JA
is the reciprocal of the derating factor in
°C/W as specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings
section. For example, θ
JA
of the thin QFN package is
+42°C/W. For optimum power dissipation, the exposed
paddle of the package should be connected to the
ground plane (see the Layout and Grounding section).
For 8Ω applications, the worst-case power dissipation
occurs when the output power is 1.1W/channel, resulting
in a power dissipation of about 1W. In this case, both the
TSSOP and TQFN packages can be used without violat-
ing the maximum power dissipation or exceeding the
thermal protection threshold. For 4Ω applications, the
TSSOP package may require heat-sinking or forced air
cooling to prevent the device from reaching its thermal
limit. The more thermally efficient TQFN package is sug-
gested for speaker loads less than 8Ω.
Output Power (Speaker Amplifier)
The increase in power delivered by the BTL configura-
tion directly results in an increase in internal power dis-
sipation over the single-ended configuration. The
P
T
T
DISSPKG MAX
J MAX
A
JA
(
)
(
)
=
−
θ
V
V
P
V
R
RMS
OUT P P
OUT
RMS
L
=
=
−
(
)
2 2
2
A
R
R
VD
F
IN
= ×
2
+1
V
OUT(P-P)
2 x V
OUT(P-P)
V
OUT(P-P)
-1
Figure 9. Bridge-Tied Load Configuration
OUTPUT POWER (mW)
THD+N (%)
125
100
75
50
25
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
0.001
0
150
V
DD
= 5V
R
L
= 16Ω
A
V
= 3dB
OUTPUTS IN PHASE
OUTPUTS 180° OUT OF PHASE
Figure 10. Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise vs. Output Power
with Inputs In/Out of Phase (Headphone Mode)
