9301 functional description, Audio down mixer and mono mixer function – Cobalt Digital COMPASS 9301 AES Audio Delay User Manual
Page 12
1
9301 Functional Description
1-8
9301 PRODUCT MANUAL
9301-OM (V4.2)
Output audio rates are always 48 kHz locked to the selected reference, but
discrete AES inputs can be set to bypass the sample rate converters to align
these inputs with the output timing (AES must be nominally 48 kHz input).
The sample rate converters are enabled (bypass turned off) by default. Output
AES is always precisely synchronized with the selected reference.
As set with the default settings, the routing between AES input channels and
AES output channels is basic 1-to-1 (AES Ch 1 input is routed to AES Ch 1
output, and so on). Other sources and/or destinations for each channel are
selected (from the choices listed above) using the card edge controls or a
remote control system.
Note:
As shown in Figure 1-1, the 9301 is equipped with eight discrete AES input
pair ports and eight discrete AES output pair ports. On Rear I/O Modules hav-
ing limited AES I/O capabilities, switches S11 thru S14 allow available rear
module BNC connectors to be allotted between AES inputs and outputs as
desired. Buffered copies of
AES OUT (1-4)
are available as dedicated outputs
and as respective outputs fed through S11 – S14 on the 9301 card.
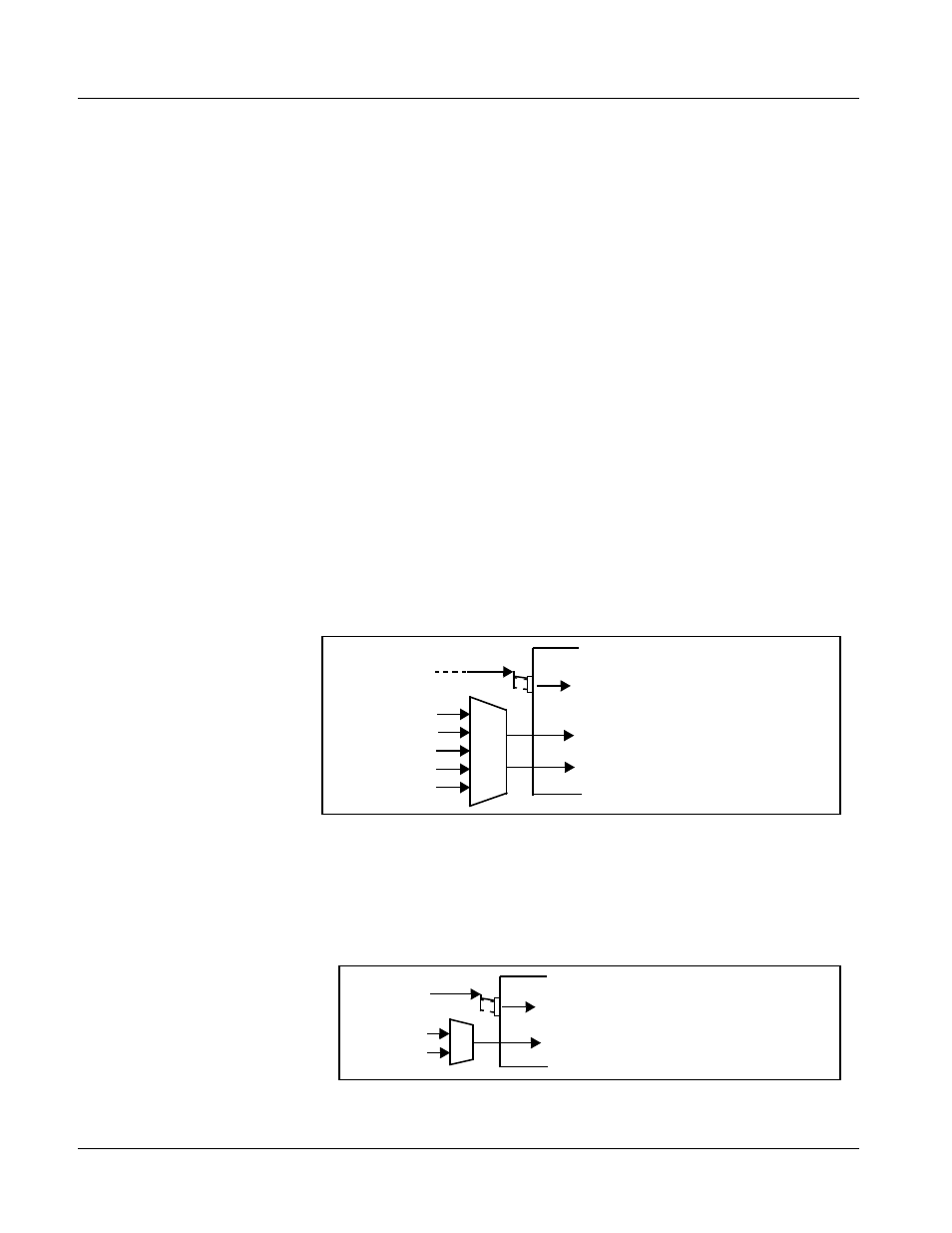
Audio Down Mixer and Mono Mixer Function
(See Figure 1-2.) The Audio Down Mixer function provides for the selection
of any five AES audio sources serving as Left (
L
), Right (
R
), Center (
C
), Left
Surround (
Ls
), and Right Surround (
Rs
) individual signals to be multiplexed
into a stereo pair (Down Mix Left (
DM-L
) and Down Mix Right (
DM-R
)). The
resulting stereo pair
DM-L
and
DM-R
can in turn be routed and processed just
like any of the other audio sources described earlier.
Figure 1-2 Audio Mixing Functional Block Diagram with Example Sources
The Mono Mixer function (Figure 1-3) generates an additional mono-mixed
channel from two selected AES input channels serving as left and right inputs.
The resulting mono mix channel
MONO
can in turn be routed and processed
just like any of the other audio sources described earlier.
Figure 1-3 Audio Mono Mix Functional Block Diagram with Example Sources
DM-L
Ls
L
C
R
Rs
DM-R
AES Ch 1
AES Ch 2
AES Ch 6
AES Ch 4
AES Ch 5
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
MONO
L
Σ
R
AES Ch 12
AES Ch 16
AES Ch 1 - Ch 16
