1 precedence and tos, Introduction, First generation – RCA THOMSON SpeedTouchTM (Wireless) Business DSL Router User Manual
Page 18: Precedence and tos, Chapter 3
Chapter 3
Basic QoS Concepts
E-NIT-CTC-20041213-0013 v0.5
16
3.1 Precedence and TOS
Introduction
There are two generations of quality of service architectures in the Internet Protocol.
The interpretation of the
Type of Service Octet
in the Internet Protocol header varies
between these two generations.
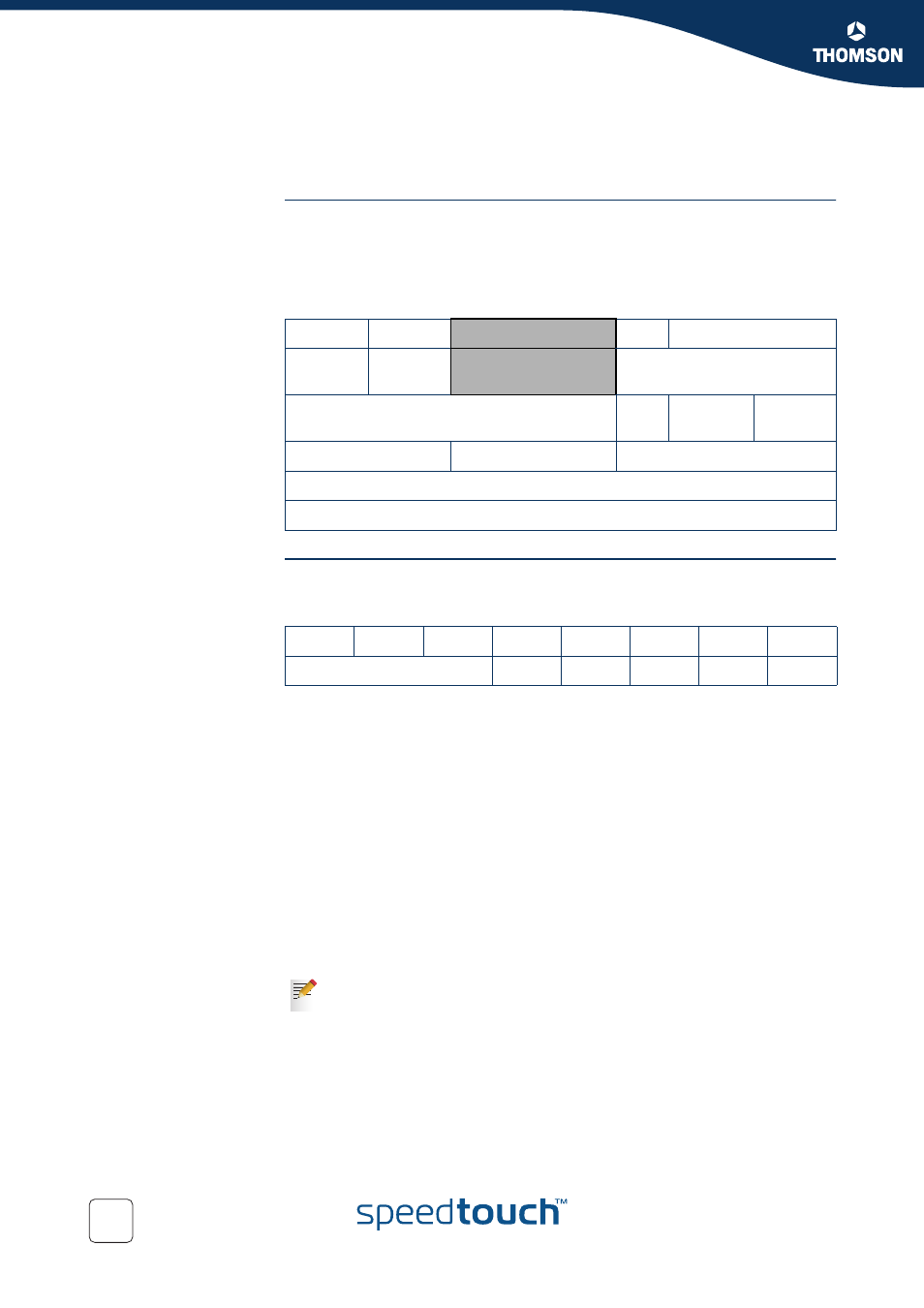
The figure below shows the Internet Protocol header.
The Type of Service Octet is the second 8-bit octet of the Internet Protocol header.
First generation
Precedence and Type of Service bits.
The initial definition of the
Type of Service Octet
looked like this:
Most
Precedence
descriptions are obscure: they relate to message handling priorities
of US military communications in the 1960s. The essence is that higher values of
Precedence lead to higher levels of network service.
To prevent high link utilisation causing routing traffic to be lost, it is traditional to use
Precedence = 7 for interior routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIP and to use
Precedence = 6 for exterior routing protocols such as BGP.
The
D
type of service bit can be a value of 0 to request normal delay, a value of 1 to
request a low delay service.
The
T
type of service bit can be a value of 0 to request normal throughput, a value of
1 to request a high throughput service.
The
R
type of service bit can be a value of 0 to request normal reliability, a value of 1
to request a high reliability service.
The
C
type of service bit can be a value of 0 to request normal costs, a value of 1 to
request a low cost service.
0
4
8
16
31
Version
Header
Length
Type of Service
Total Length
Identification
DM
OFF
Time to Live
Protocol
Header Chuckles
Source Address
Destination Address
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Precedence
D
T
R
C
The D,T,R and C type of service bit is defined in
RFC791
(Internet Protocol)
