Flexible resolution mode, How flexible resolution works, Flexible resolution mode -6 – National Instruments NI PCI-5911 User Manual
Page 20: How flexible resolution works -6
Chapter 2
Hardware Overview
2-6
ni.com
Flexible Resolution Mode
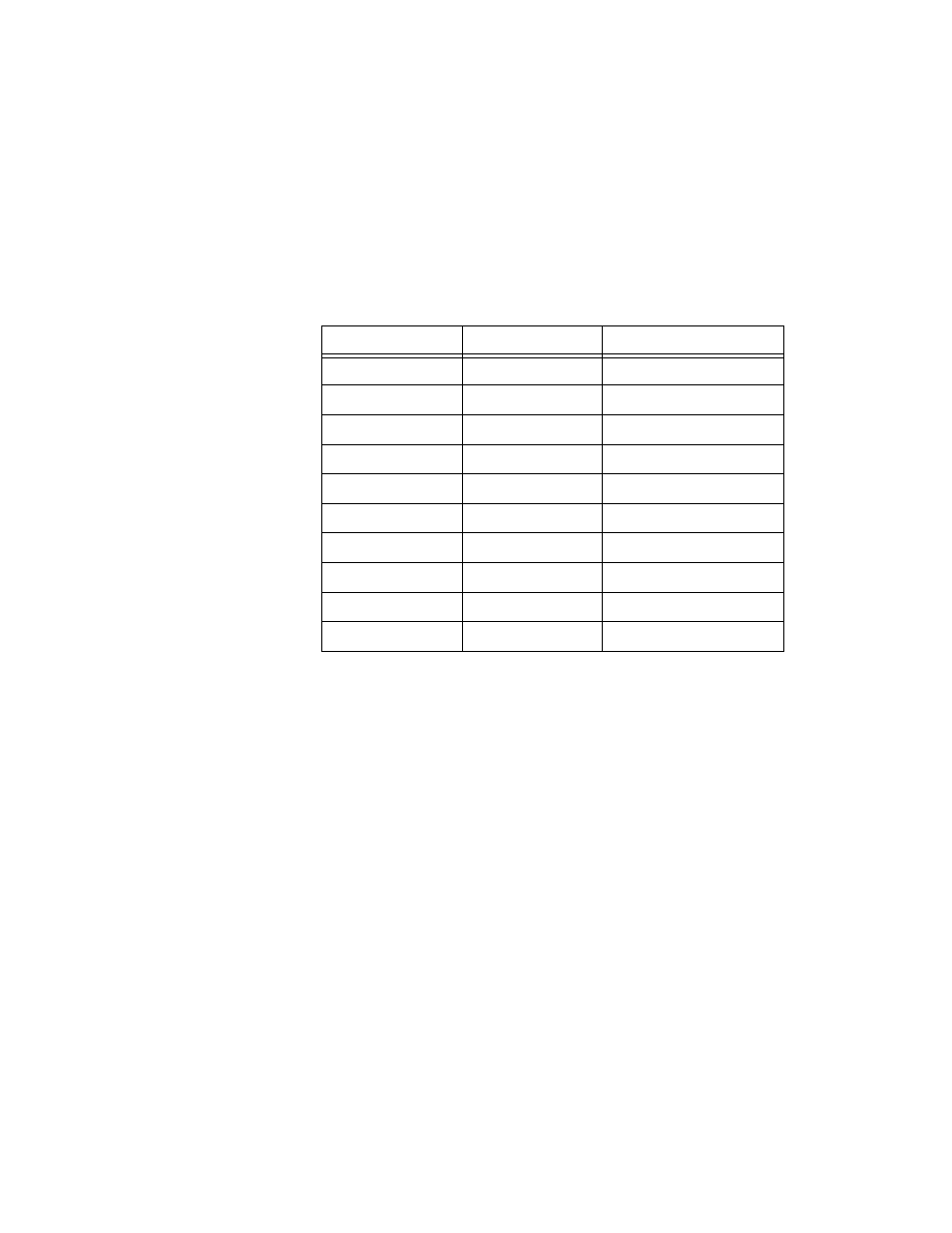
Table 2-2 shows the relationship between the available sampling rates,
resolution, and the corresponding bandwidth for flexible resolution mode.
Like any other type of converter that uses noise shaping to enhance
resolution, the frequency response of the converter is only flat to its
maximum useful bandwidth. The NI 5911 has a bandwidth of 4 MHz.
Beyond this frequency, there is a span where the converter acts resonant
and where a signal is amplified before being converted. These signals are
attenuated in the subsequent digital filter to prevent aliasing. However,
if the applied signal contains major signal components in this frequency
range, such as harmonics or noise, the converter may overload and signal
data will be invalid. In this case, you receive an overload warning. You must
then either select a higher input range or attenuate the signal.
How Flexible Resolution Works
The ADC can be sourced through a noise shaping circuit that moves
quantization noise on the output of the ADC from lower frequencies to
higher frequencies. A digital lowpass filter applied to the data removes all
but a fraction of the original shaped quantization noise. The signal is then
resampled to a lower sampling frequency and a higher resolution. Flexible
resolution provides antialiasing protection due to the digital lowpass filter.
Table 2-2. Available Sampling Rates and Corresponding Bandwidth
in Flexible Resolution Mode
Sampling Rate
Resolution
Bandwidth
12.5 MS/s
11 bits
3.75 MHz
5 MS/s
14 bits
2 MHz
2.5 MS/s
15.5 bits
1 MHz
1 MS/s
17.5 bits
400 kHz
500 kS/s
18 bits
200 kHz
200 kS/s
18.5 bits
80 kHz
100 kS/s
19 bits
40 kHz
50 kS/s
19.5 bits
20 kHz
20 kS/s
20.5 bits
8 kHz
10 kS/s
21 bits
4 kHz
