Specifying scaling factors, Choosing a region of interest, Choosing a learning algorithm – National Instruments IMAQ Vision for Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 81: Figure 6-5. types of image distortion
Chapter 6
IMAQ Vision for LabWindows/CVI User Manual
6-6
ni.com
Specifying Scaling Factors
Scaling factors are the real-world distances between the dots in the
calibration grid in the x and y directions and the units in which the distances
are measured. Use the
GridDescriptor
structure to specify the scaling
factors.
Choosing a Region of Interest
Define a learning region of interest (ROI) during the learning process to
define a region of the calibration grid you want to learn. The software
ignores dot centers outside this region when it estimates the transformation.
Creating a user-defined ROI is an effective way to increase correction
speeds depending on the other calibration options selected. Set the
user-defined ROI using the ROI parameter of either
imaqLearnCalibrationGrid()
or
imaqLearnCalibrationPoints()
.
Choosing a Learning Algorithm
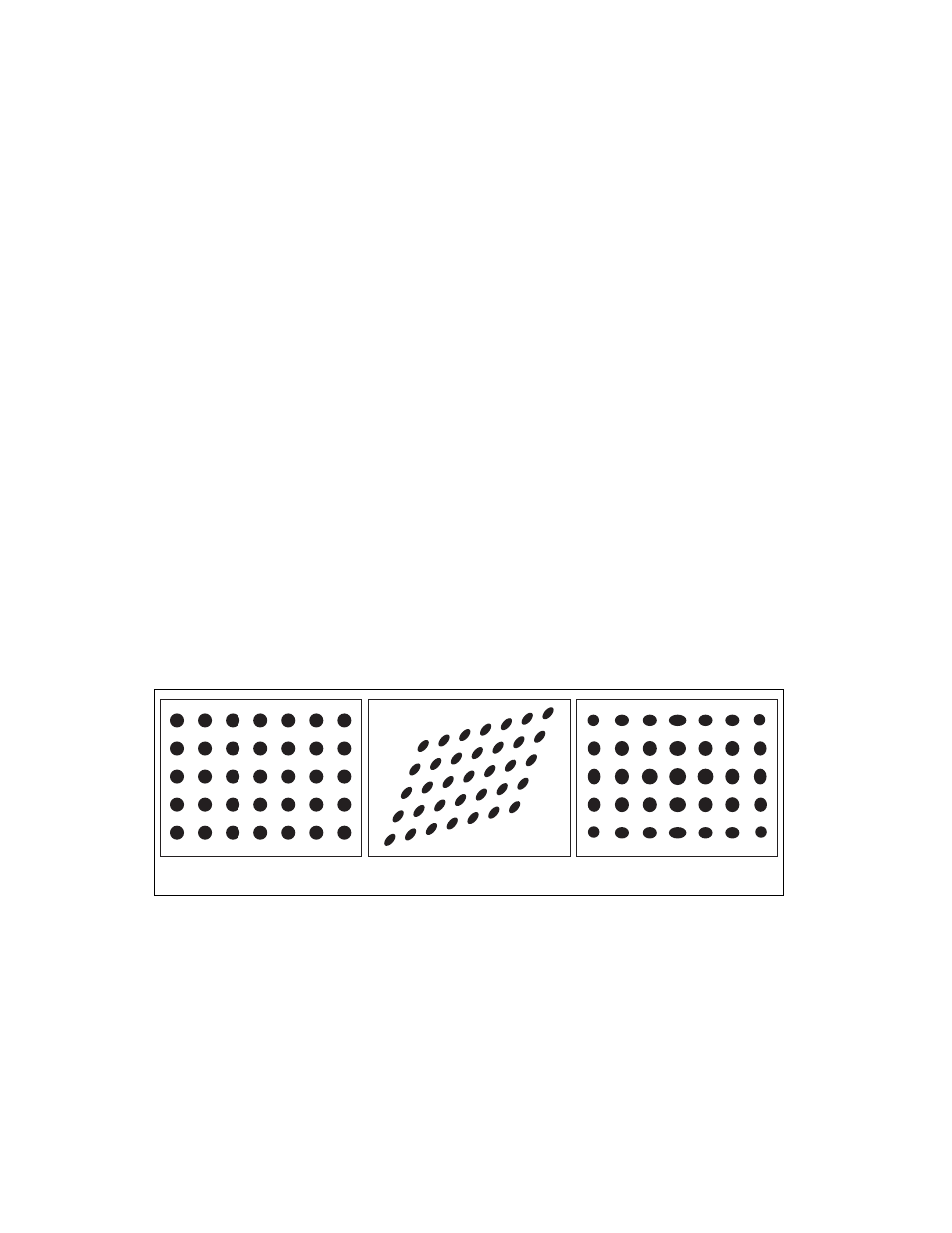
Select a method in which to learn the calibration information: perspective
projection or nonlinear. Figure 6-5 illustrates the types of errors your image
can exhibit. Figure 6-5a shows an image of a calibration grid with no
errors. Figure 6-5b shows an image of a calibration grid with perspective
projection. Figure 6-5c shows an image of a calibration grid with nonlinear
distortion.
Figure 6-5. Types of Image Distortion
Choose the perspective projection algorithm when your system exhibits
perspective errors only. A perspective projection calibration has an accurate
transformation even in areas not covered by the calibration grid, as shown
in Figure 6-6. Set the
mode
element of the options parameter to
a.
c.
b.
