Keeping the beat—pulse, Closing the connection—close, Movement commands – Pioneer 2 / PeopleBot User Manual
Page 42: Ovement, Ommands
Pioneer 2 Operating System
housekeeping functions, start its sonar and motor controllers (among other things), listen
for client commands, and begin transmitting server information to the client.
Note that once connected, Pioneer 2's and PeopleBot’s motors are disabled, regardless
of their state when last connected. After starting a connection, you must either enable
the motors manually (white MOTORS button) or send the P2OS motors ENABLE command
with the argument 1; sfRobotComInt(4,1), for example.
Keeping the Beat—PULSE
A P2OS safety watchdog expects that the controller receives at least one
communication packet from the client every watchdog seconds (default is two).
Otherwise, it assumes the client-server connection is broken and stops the robot.
It’s good practice to have the client send a PULSE command just after opening the P2OS
servers. And if your client application will be otherwise distracted for some time,
periodically issue the PULSE command to let P2OS know you are indeed alive and well.
If the robot shuts down due to lack of communications traffic, it will revive upon receipt
of a client command and automatically accelerate to the last-specified speed and
heading setpoints.
Closing the Connection—CLOSE
To close the client-server connection, disabling the motors and sonar, and resetting P2OS
to its wait state, simply issue the client CLOSE command.
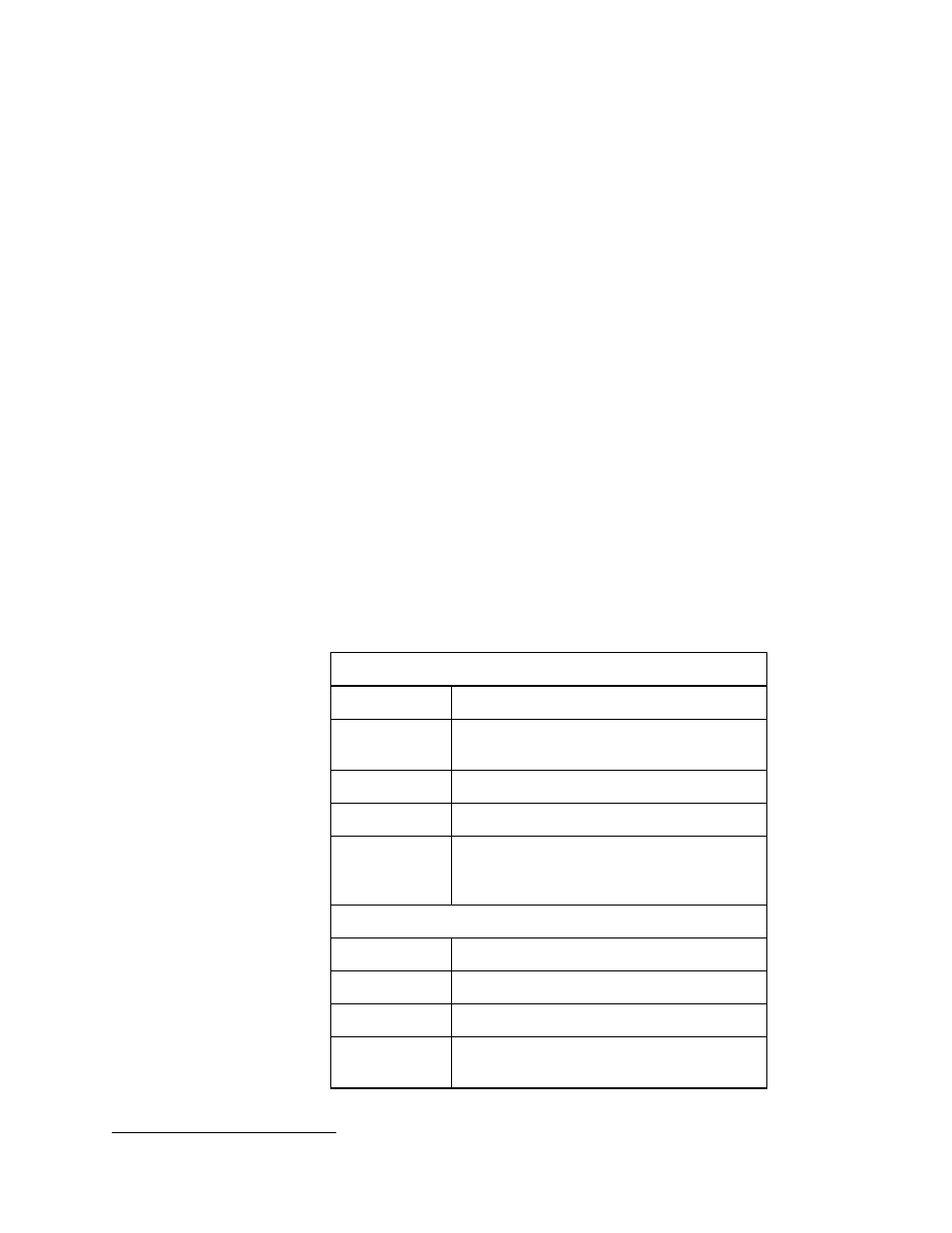
Movement Commands
Table 7. P2OS movement commands
Rotation
HEAD Absolute
heading
DHEAD,
DCHEAD
Differential heading from control point
ROTATE Rotational
speed
SETRA
Rotational (de)acceleration to achieve setpoint
SETRV
Sets maximum rotational velocity and is
velocity used for Colbert turn and turnto
command speeds.
Translation
VEL Forward/back
velocity
MOVE Forward/back
distance
SETA Translation
(de)acceleration to achieve setpoint
SETV
Sets maximum translational velocity and is
used for Colbert move command speed.
The P2OS motor-control
servers accept several
different motion com-
mands of two mutually
exclusive types: either
direct wheel-velocities or
translational/rotational
motor controls. The robot
servers automatically
abandon any P2OS
translational or rotational
setpoints and switch to
direct wheel-velocity
control mode when they
receive a VEL2 command.
Any other motion
command makes P2OS
abandon direct wheel-
velocity control.
For example, if P2OS is in
direct-wheel velocity
(VEL2) mode and is given
a HEAD command, it
disables that direct-wheel
velocity mode and starts
controlling the heading
36
19
Alternatively, disable the motors with the ENABLE command argument 0.
