Dc output wiring sizing, Figure 1: individual ac feed wiring architecture, Figure 1: individual ac feed wiring architecture ) – Panduit PN380 User Manual
Page 9: Rectifiers
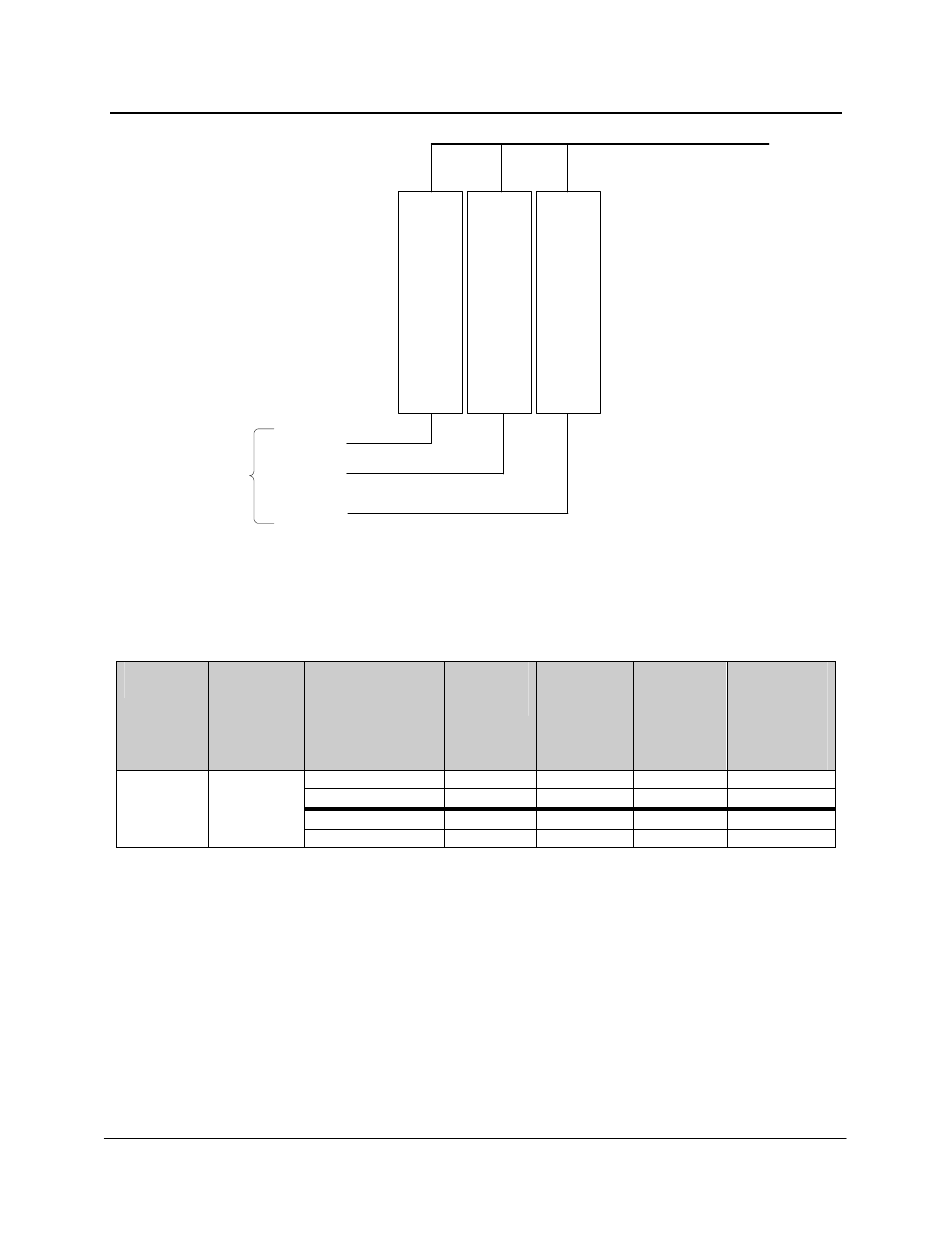
PANDUIT DPoE Power System User’s Guide
Issue 1.0
Part Number: PN380
Rectifiers
1
2
3
Feed 1
Feed 2
AC In
N+1 DC Out
Feed 3
Figure 1: Individual AC Feed Wiring Architecture
Each individual AC feed should be protected using a circuit breaker as listed in Table 4: Recommended
AC Circuit Breaker and Wire Sizes.
Table 4: Recommended AC Circuit Breaker and Wire Sizes
Type of
Feed
Number of
Rectifiers
on an AC
Feed
Part Number
Maximum
Input
Voltage
Maximum
Rated AC
Current (A)
Circuit
Breaker
Minimum
value (A)
90° C
Minimum
Wire Gauge
(AWG) to
use at 30° C
ambient
DPoEPWRR500 90
7
15
14
DPoEPWRR500 180
3.5
15
14
DPoEPWRR1250
90 17.6 20 12
Individual
AC
Feed
1
DPoEPWRR1250
180 8.8 15 14
DC Output Wiring Sizing
There are two main considerations for sizing DC wire: ampacity and voltage drop. Ampacity refers to the
safe current-carrying level as specified by U.S.-based organizations such as Underwriters Laboratories
and the National Fire Prevention Association, which publishes the National Electric Code (NEC). Voltage
drop is simply the amount of voltage loss in a length of wire due to ohmic resistance of the conductor. DC
wire may be sized for either ampacity or voltage drop depending on branch load loop length and
conductor heating. In general, ampacity considerations will drive wire selection for short loop lengths
(less than 50 feet) and voltage drop will drive wire selection for long loop lengths (greater than 50 feet).
The National Electric Code table 310.16 provides ampacity values for various sizes, bundles, and
insulation temperature rated wire.
4
