I/f (interface) mode, Flow, Port number – Lantronix XPort User Manual
Page 30: I/f (interface) mode -6, Flow -6, Port number -6
Using Setup Mode for Configuration
I/F (Interface) Mode
The Interface (I/F) Mode is a bit-coded byte that you enter in hexadecimal notation.
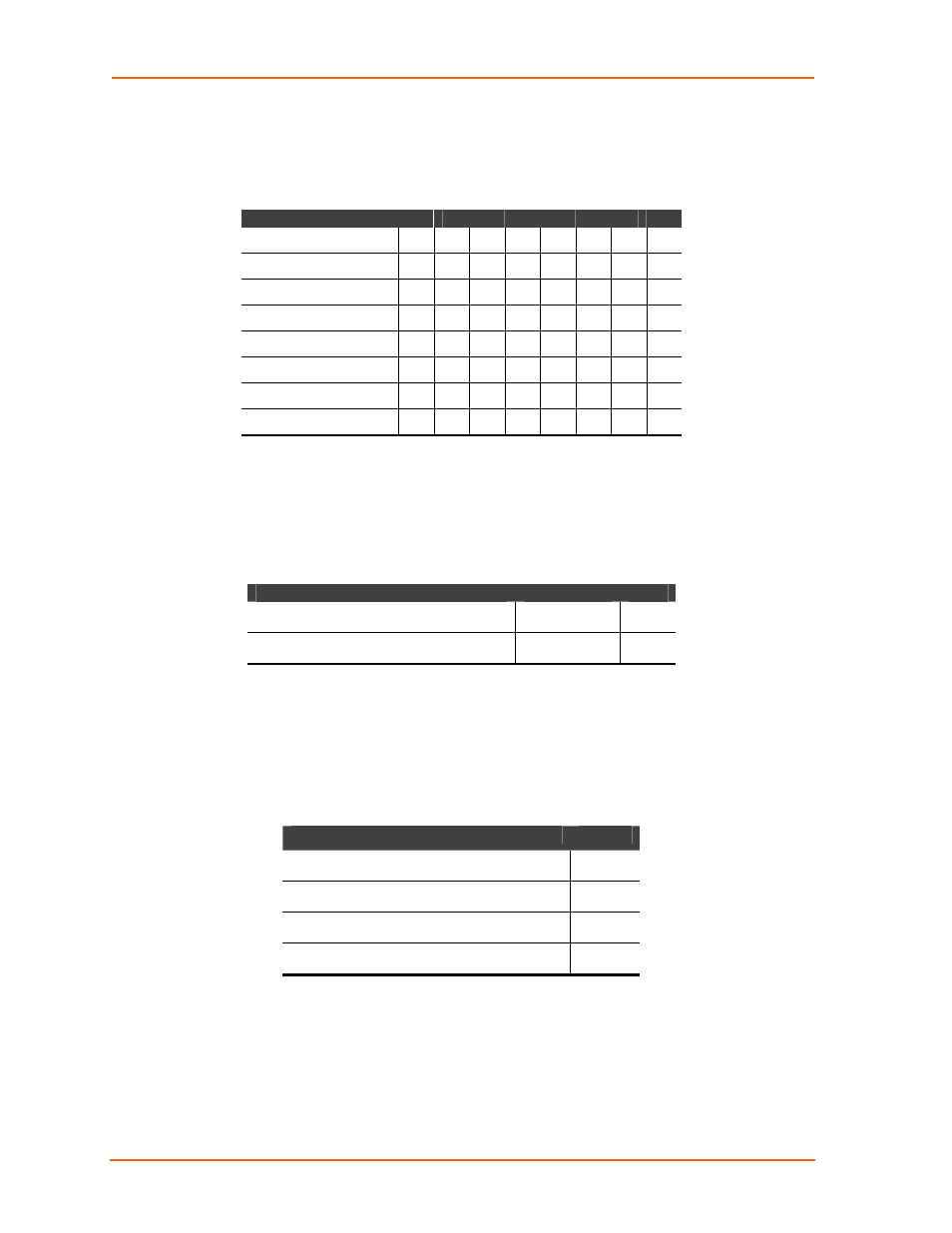
Table 4-5.
Interface Mode Options
I/F Mode Option
7 6
5
4
3
2
1
0
RS-232C
(1)
0
0
7 Bit
1
0
8 Bit
1
1
No
Parity
0 0
Even
Parity
1 1
Odd
Parity
0 1
1 stop bit
0
1
2 stop bits
(1)
1
1
(1) 2 stop bits are implemented by the software. This might influence performance.
Note:
If you attempt to select an I/F Mode bit that pertains to RS-422/485, a
WARNING: RS-422/485 I/F Modes not supported message displays.
The following table demonstrates how to build some common Interface Mode
settings:
Table 4-8. Common Interface Mode Settings
Common I/F Mode Setting
Binary
Hex
RS-232C, 8-bit, No Parity, 1 stop bit
0100 1100
4C
RS-232C, 7-bit, Even Parity, 1 stop bit
0111 1000
78
Flow
Flow control sets the local handshaking method for stopping serial input/output.
Generally, flow control is not required if the connection is used to pass a blocked
protocol with block sizes less than 1k (ACK/NAK) and/or speeds of 19200 or less.
Use the following table to select flow control options:
Table 4-11. Flow Control Options
Flow Control Option
Hex
No flow control
00
XON/XOFF flow control
01
Hardware handshake with RTS/CTS lines
02
XON/XOFF pass characters to host
05
Port Number
The setting represents the source port number in TCP connections. It is the number
that identifies the channel for remote initiating connections. The default setting for
Port 1 is 10001. The range is 1-65535, except for the following reserved port
numbers:
4-6
XPort™ User Guide
