HP Reliable Transaction Router User Manual
Page 26
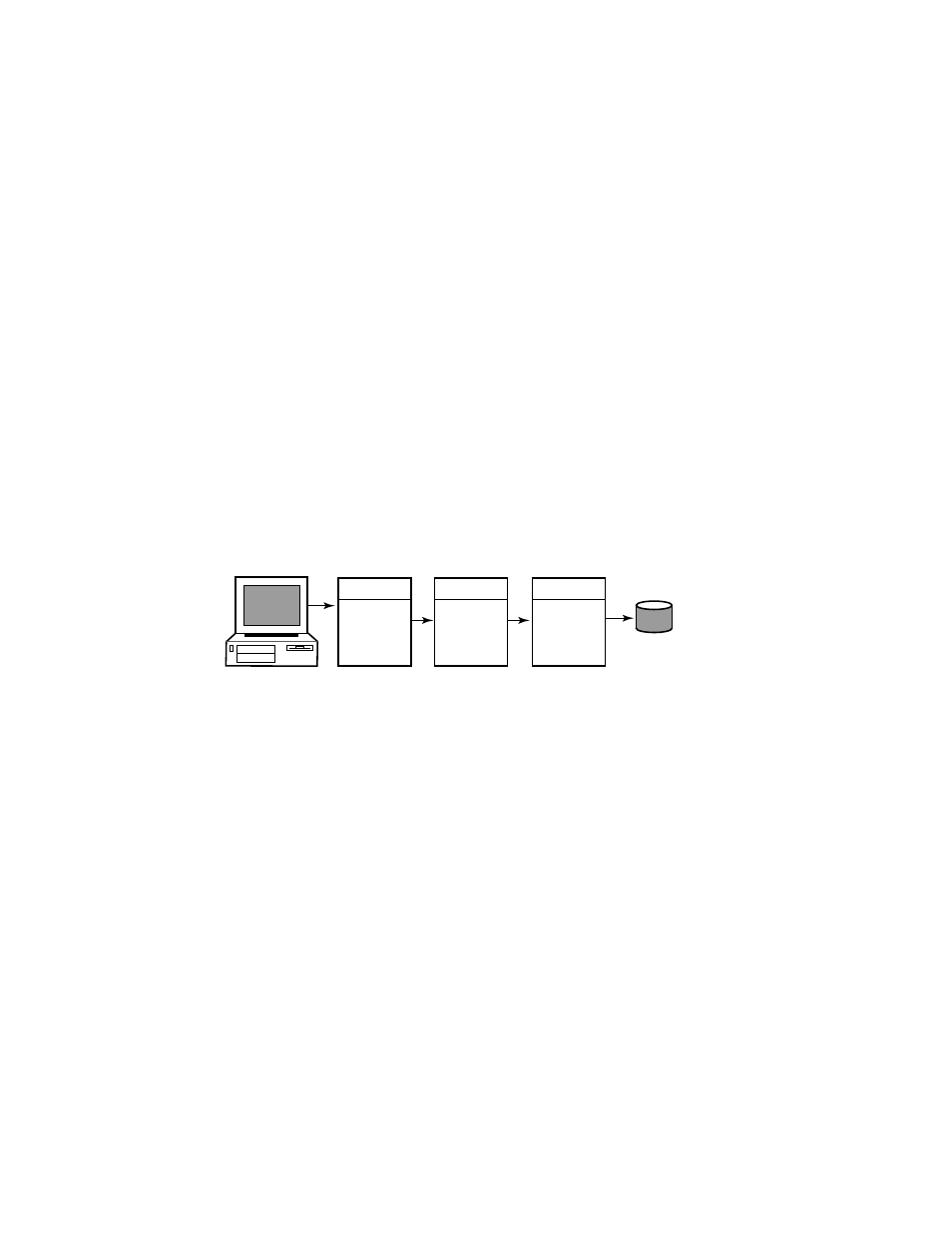
RTR Terminology
In this example, the frontend with the client application resides
on one node, and the router with the server application reside
a node that has both the router and backend roles. This is
a typical configuration where routers are placed on backends
rather than on frontends. A further separation of workload
onto three nodes is shown in Figure 1–11. However, in this
configuration, there remain several single points of failure where
one node/role or a network outage can disrupt processing of
transactions.
Figure 1–11 RTR Deployed on Three Nodes
Database
VM-0829A-AI
TR
FE
BE
Browser
While this three-node configuration separates transaction load
onto three nodes, it does not provide for continuing work if one
of the nodes fails or becomes disconnected from the others. In
many applications, there is a need to ensure that there is a
server always available to access the database.
Standby server
In this case, a standby server will do the job. A standby server
(see Figure 1–12) is a process or application that can take over
when the primary server is not available, due to hardware
failure, application software failure or network outage.
Both the primary and the standby server have the capability
to access the same database, but the primary processes all
transactions unless it is unavailable. On the other hand, the
standby processes transactions only when the primary becomes
unavailable. When not being used to process transactions, the
standby CPU can do other work.
1–14 Introduction
