Overview – Hitachi SJ 300 User Manual
Page 3
SJ100/L100 / PID / 3
1. OVERVIEW
SJ100/L100 series inverters have an integrated PID control function as standard. They can be used for
controls, such as constant flow control for fan & pump applications, and they have the following features.
l Target signal can be given not only by the digital operator but also by an external digital signal, which can
be set to 16 different targets. Furthermore, it can also be given by an analog input signal (0 - 10V or 4 -
20mA).
l Feedback signal can be given to SJ100/L100 by analog voltage input (10V max.)or by analog current
input (20mA max.).
l For the feedback signal, the performance area can be defined individually. For example 0 - 5V, 4 - 20mA
or others.
l Using a scale conversion function, you can get actual values of target value and/or feedback value for air
flows, water flows or temperature on the display.
Please read this guide book to use the convenient PID function of the SJ100/L100 series inverters correctly
and without any trouble.
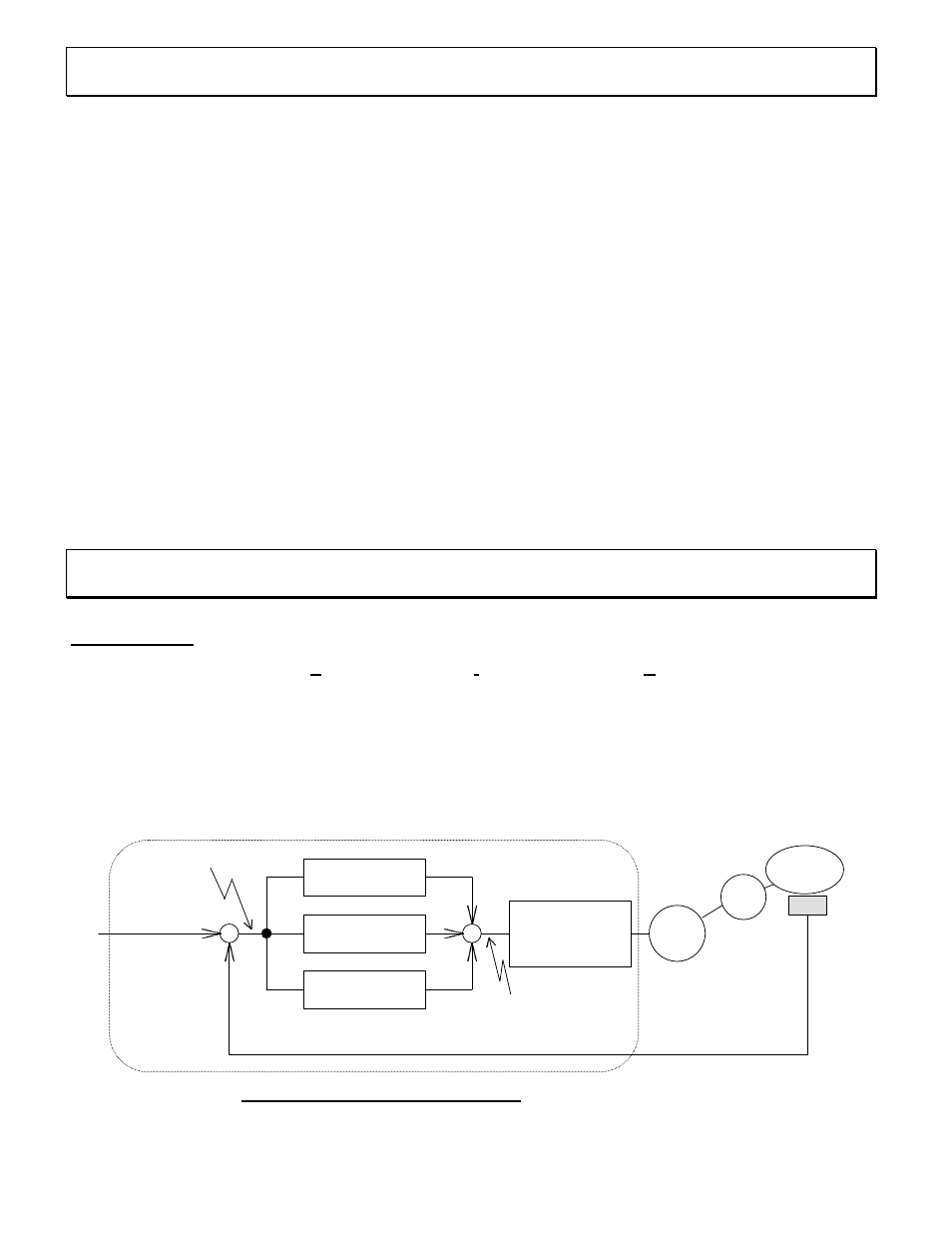
2. PID CONTROL ON SJ100/L100
2-1 PID Control
“P” in PID stands for
P
roportional, “I” for
I
ntegral, and “D” for
D
ifferential. The combination of
these controls is called PID control. PID control is widely used in various fields, such as the process
control of air flow, water flow, pressure, temperature and others. It controls the output frequency of the
inverter according to PID calculation, which is based on the deviation between target and feedback. The
inverter adjusts its output frequency to correct the deviation. This control block diagram is shown in Fig. 2-
1 below.
P : Proportional
operation
I : Integral
operation
D : Differential
operation
Integrated into SJ100/L100
Fan, pump, etc.
deviation
ε
Target
Sensor &
Transducer
Frequency
command
Feedback
(Flow, Pressure or temperature etc.)
Fig. 2-1 PID Control block diagram
Motor
Target
of
control
Load
Inverter
