Connections – Harman-Kardon AVR 145 User Manual
Page 16
16
CONNECTIONS
Audio Connections
There are two formats for audio connections: digital and analog. Digital
audio signals are of higher quality, and are required for listening to
sources encoded with digital surround modes, such as Dolby Digital and
DTS. There are two types of digital audio connections commonly used:
coaxial and optical. Either type of digital audio connection may be used
for each source device, but never both simultaneously for the same
source. However, it’s okay to make both analog and digital audio con-
nections at the same time to the same source.
Digital Audio
Coaxial digital audio jacks are usually color-coded in orange. Although
they look similar to analog jacks, they should not be confused, and you
should not connect coaxial digital audio outputs to analog inputs or
vice versa.
Figure 4 – Coaxial Digital Audio
Optical digital audio connectors are normally covered by a shutter to
protect them from dust. The shutter opens as the cable is inserted. Input
connectors are color-coded using a black shutter, while outputs use a
gray shutter.
Figure 5 – Optical Digital Audio
Due to the nature of digital signals as binary bits, they aren’t subject
to signal degradation the way analog signals are. Therefore, the quality
of coaxial and optical digital audio connections should be the same,
although it is important to limit the length of the cable. Whichever type of
connection you choose, Harman Kardon recommends that you always
select the highest quality cables available within your budget.
Analog Audio
Analog connections require two cables, one for the left channel (white)
and one for the right channel (red). These two cables are often attached
to each other for most of their length. Most sources that have digital
audio jacks also have analog audio jacks, although some older types of
sources, such as tape decks, have only analog jacks. For sources that
are capable of both digital and analog audio, you may wish to make
both connections. If you wish to record materials from DVDs or other
copy-protected sources, you may only be able to do so using analog
connections. Remember to comply with all laws regarding copyright if
you choose to make a copy for your own personal use.
Figure 6 – Analog Audio
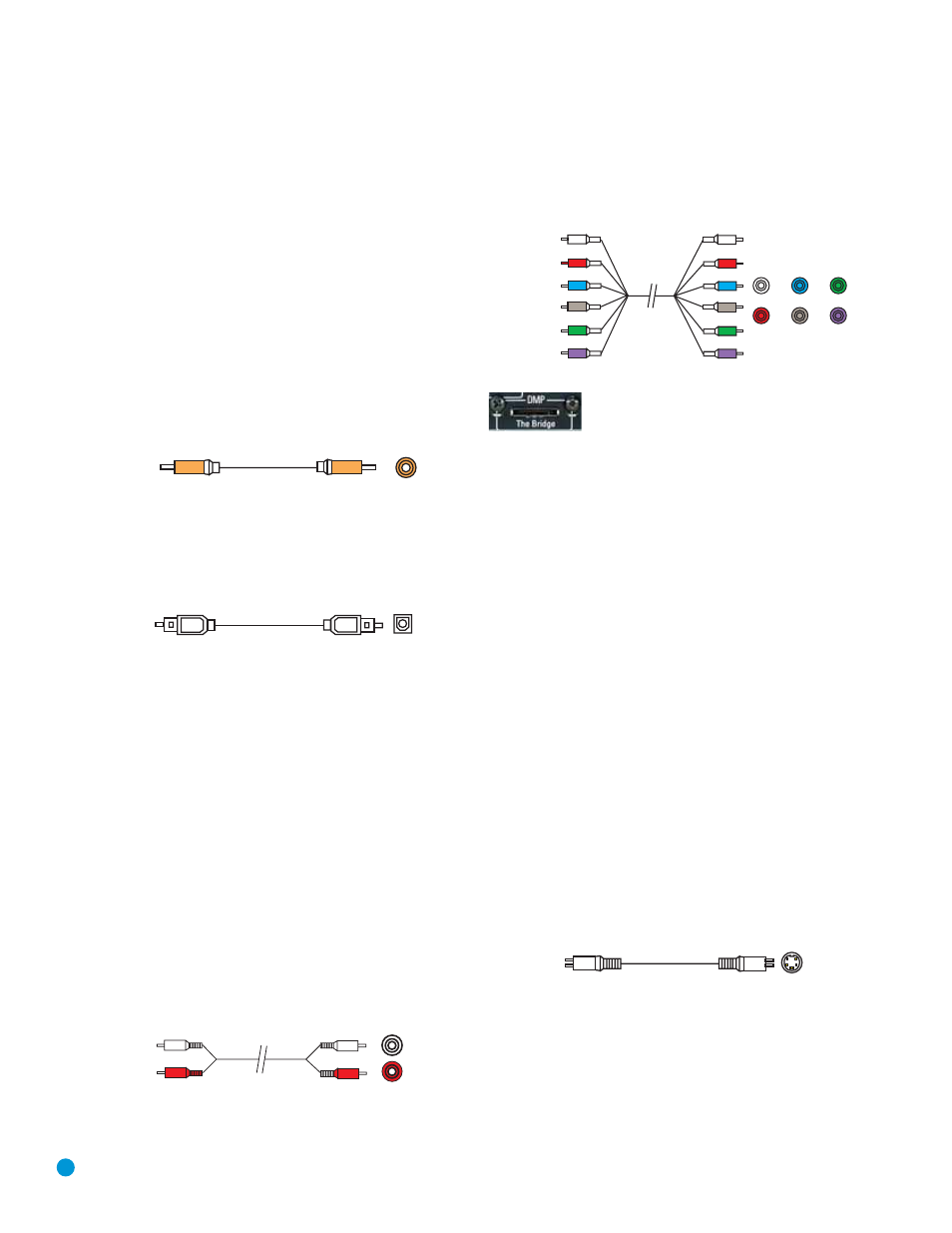
Multichannel analog connections are used with advanced sources where
the digital content is copy-protected and all surround processing is per-
formed inside the source. These types of connections are usually used
with DVD-Audio, SACD, Blu-ray Disc, HD-DVD and other advanced
players.
Figure 7 – Multichannel Analog Audio
Figure 8 – The Bridge
Harman Kardon receivers also include a proprietary, dedicated audio
connection called “The Bridge/DMP”. If you own an iPod with a dock
connector, you may separately purchase The Bridge and connect it to
The Bridge/DMP port on the receiver. Dock your iPod (not included) in
The Bridge, and you may listen to your materials through your high-per-
formance audio system. You may even use the AVR 145 remote to
control the iPod, with navigation messages displayed on the front panel
and on the screen of a video display connected to the AVR.
Video Connections
Although some sources produce an audio signal only (e.g., CD player,
tape deck), many sources output both audio and video signals (e.g.,
DVD player, cable television box, HDTV tuner, satellite box, VCR, DVR).
In addition to the audio connection, you will need to connect one type of
video connection for each source (never more than one at the same
time for any source).
There are three types of analog video connections: composite video,
S-video and component video.
Composite video is the basic connection most commonly available. The
jack is usually color-coded yellow, and looks like an analog audio jack,
although it is important never to confuse the two. Do not connect a
composite video jack to an analog or coaxial digital audio jack, and vice
versa. Both the chrominance (color) and luminance (intensity) compo-
nents of the video signal are transmitted using a single cable.
Figure 9 – Composite Video
Composite
video cable
Multichannel
analog audio
cable (RCA)
Front Surround Center
Subwoofer
L
R
Analog audio
cable (RCA)
Optical
Optical digital
audio cable
Coaxial
Coaxial digital
audio cable
