Unicast flow – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 11
5
NOTE:
The mac-address max-mac-count command and the mac-address mac-learning enable command
take effect only on local MAC addresses, which are learned in the data plane. They do not take effect on
remote MAC addresses, which are learned in the control plane.
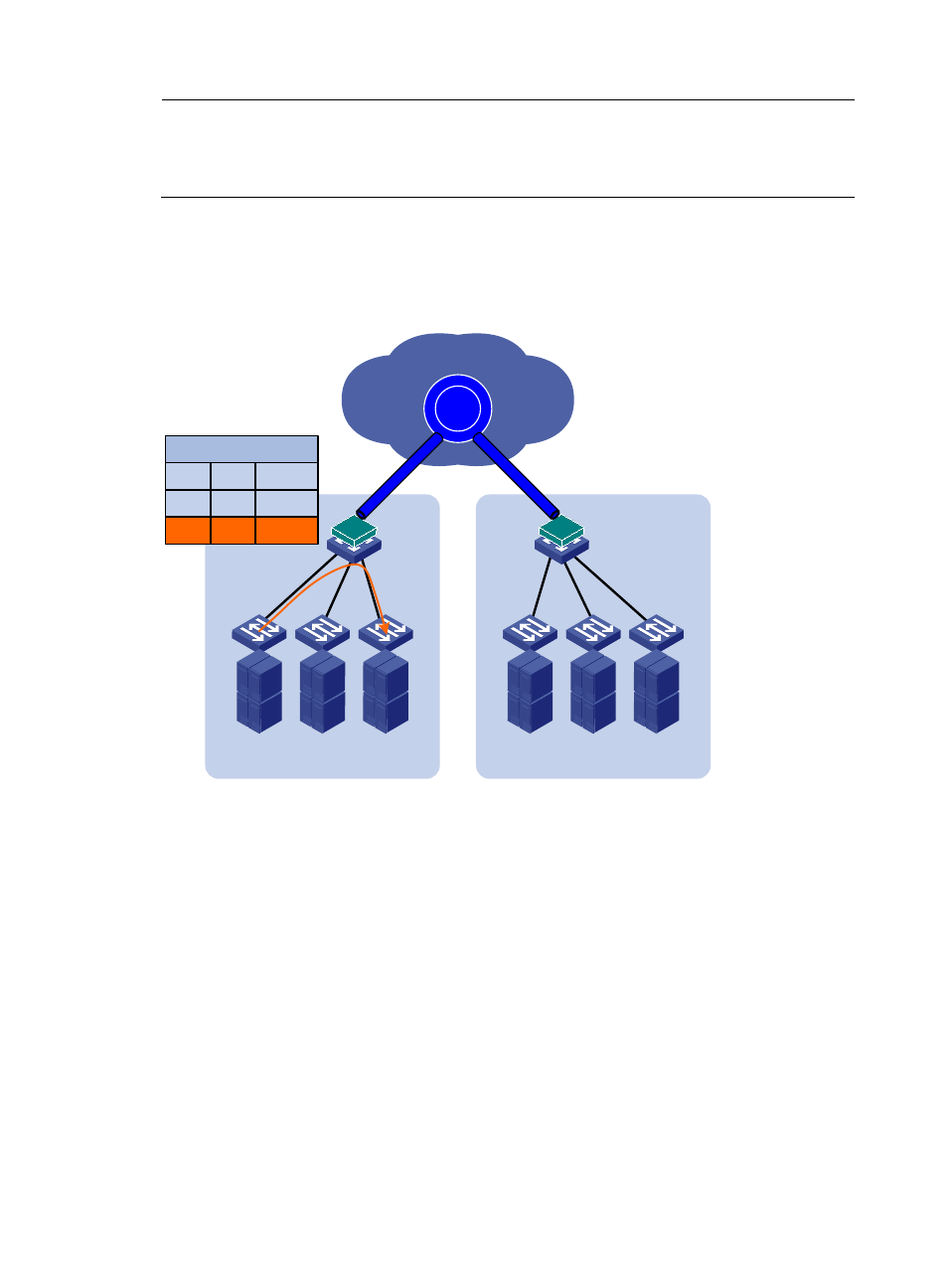
Unicast flow
For intra-site unicast flows, an edge device performs the typical MAC address table lookup, as shown
in
.
Figure 4 Layer 2 forwarding in a site
The following forwarding process (see
) takes place for unicast flows between sites:
1.
The source edge device learns the source MAC address of the incoming Ethernet frame, and looks
up the destination MAC address in its MAC table for the outgoing interface.
2.
If the outgoing interface is an EVI-Link interface instead of a physical port, the source edge device
encapsulates the frame in a GRE header, and then adds an IP header and a link layer protocol
header.
In the outer IP header, the source IP address is the source edge device's tunnel source IP address,
and the destination IP address is the destination edge device's tunnel source IP address.
3.
The source edge device forwards the encapsulated packet out of the EVI link to the destination
edge device across the IP transport network.
4.
The destination edge device removes the headers of the original Ethernet frame, looks up the
destination MAC address in the MAC address table, and sends the frame out of the matching
outgoing interface.
EVI
Site 1
EVI
Site 2
MAC table
VLAN
MAC
Interface
200
MAC1
XGE1/0/1
200
MAC2
XGE1/0/2
MAC1
MAC2
EVI
Transport network
XGE1/0/1
XGE1/0/2
Host A
Host B
