Communications setup, Pid loop setup, Step 8 – complete configurator – Super Systems 9120 User Manual
Page 17: Menu option, Step 9 – complete configurator
4574 - SSi 9120 Manual Rev A
Page 17
Super Systems Inc
options are either no or yes.
Step 8 – Complete Configurator
Communications Setup
Menu option
Note: This menu item is also located later in the manual under the
Section 1 – 9120 Configurator Menus
section
.
Communications Setup
is the communications definitions for the controller. Please contact Super Systems Inc. at 800-
666-4330 for more information regarding port setup. It is
strongly recommended
that none of the settings be modified
without technical support from Super Systems Inc. Clicking on any of the values will display an input box that will allow
the user to modify the current settings.
Step 9 – Complete Configurator
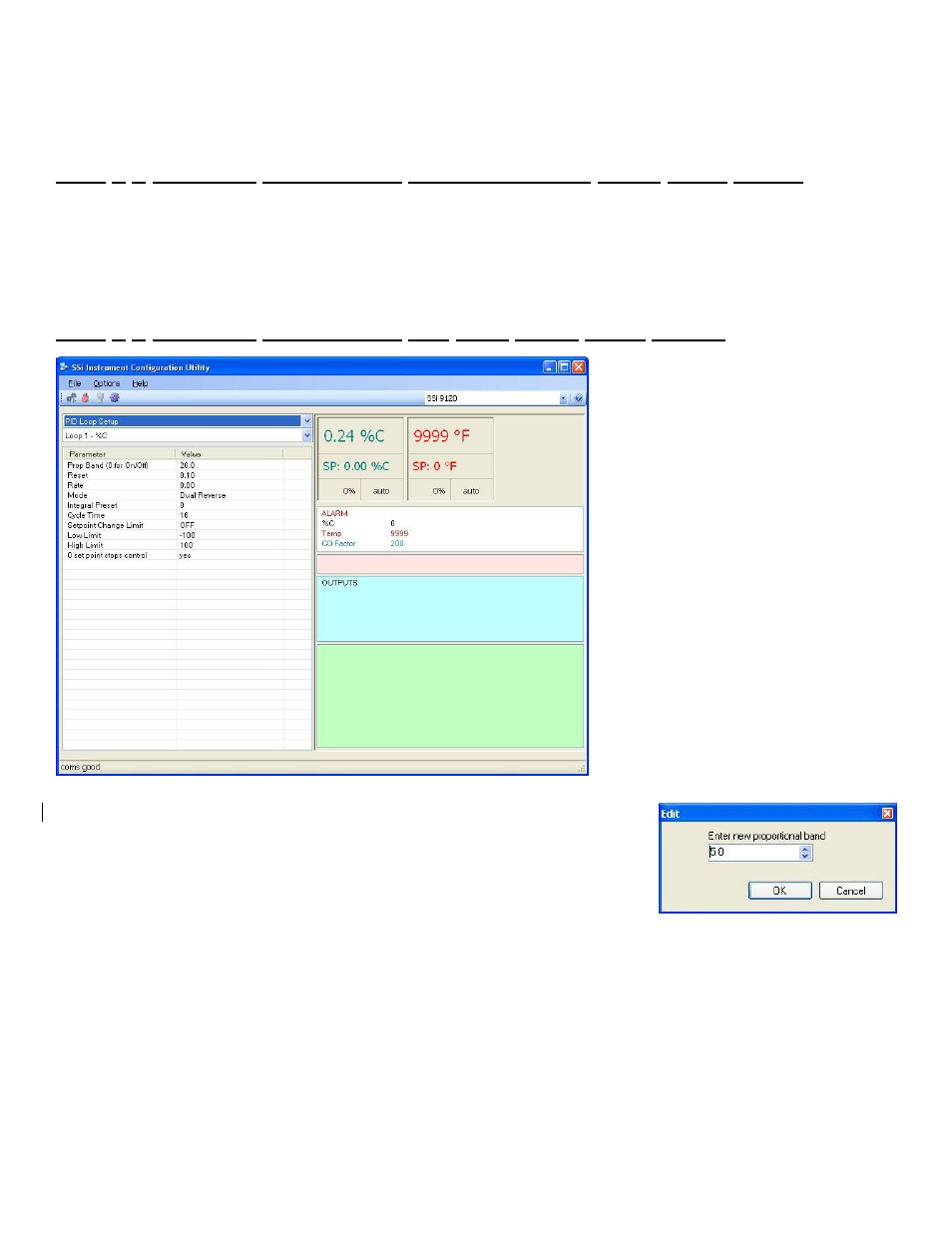
PID Loop Setup
Menu Option
Note: This menu item is also located later
in the manual under the
Section 1 – 9120
Configurator Menus
section
.
PID is the tuning parameters entered for
each Process Variable loop. The loop
value can be either Loop 1, or Loop 2.
Prop Band (0 for On/Off)
This is the proportional band field. This represents the P in PID. P = Proportional.
This is a field in which you want the process variable to stay around the setpoint.
Clicking on the value will allow the user to change the value. The range for the
proportional band value is 0 – 999.0.
Reset
This is the reset field. This represents the I in PID. I = Integral. This is the actual temperature being monitored over a
period of time and then averaged to keep within the Proportional band. The reset is in repeats per minute. This helps to
eliminate offset. Clicking on the value will allow the user to change the value. The reset range 0 – 100.00
Rate
This is the rate field. This represents the D in PID. D = Derivative. This is the sudden change or rate in the temperature.
This rate is in minutes. This affects the controller output which is proportional to the rate of change of the measurement
and will control the amount of output by time restraints. Thus derivative takes action to inhibit more rapid changes of the
measurement than proportional action. Derivative is often used to avoid overshoot. Clicking on the value will allow the
user to change the value. The range for the rate is 0 – 100.00. The rate is not typically used for heating/carbon
