Operating theory – Super Systems SuperOX User Manual
Page 4
Super Systems Inc. Page 4 of 14
SuperOX
TM
Operations Manual
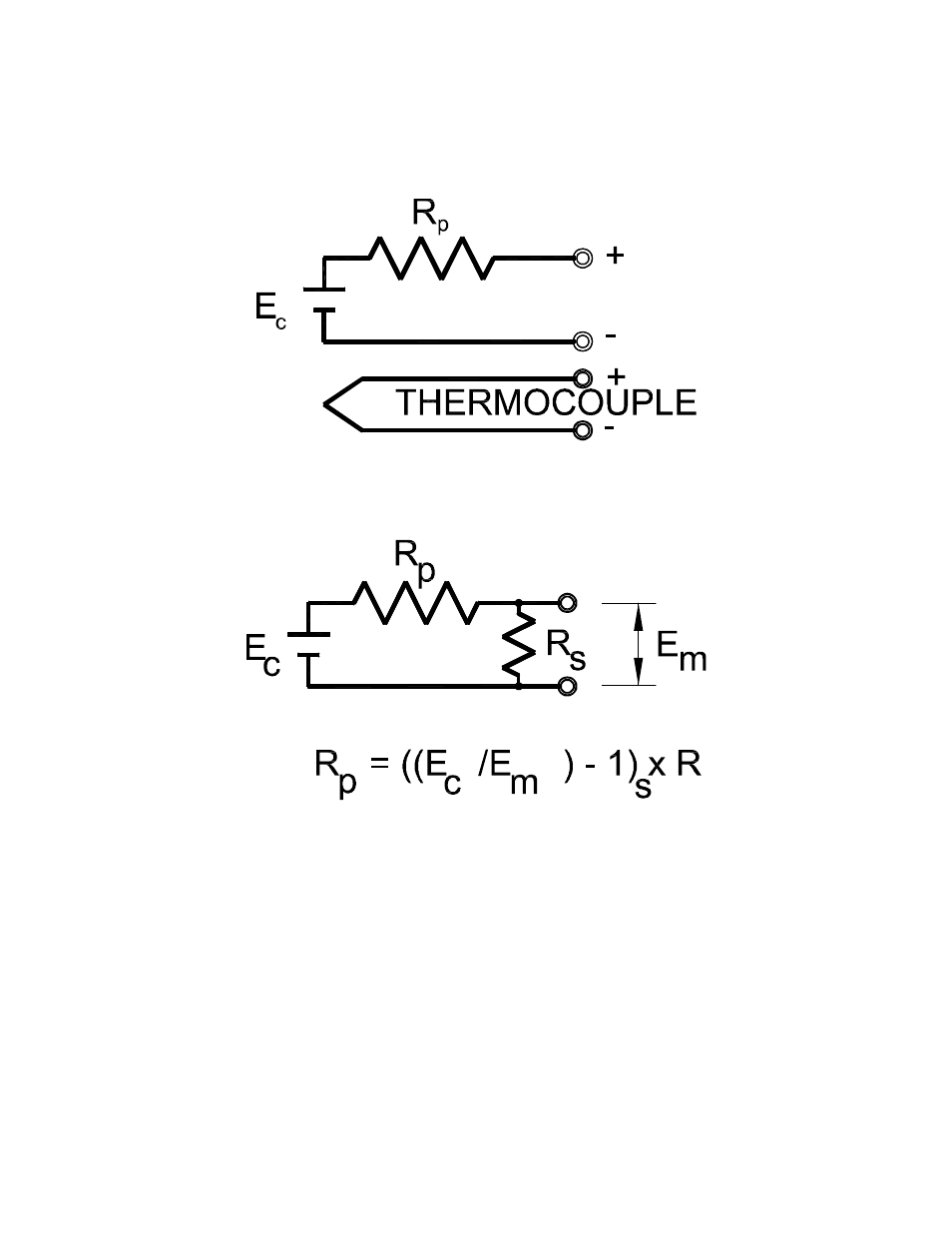
To the instrument technician, the sensor looks like a battery (see Figure 2). It displays a voltage,
EC, from which the carbon potential can be calculated. The probe thermocouple is shown next
to the sensing electrode.
Figure 2
The value of the internal resistance can be measured, as shown in Figure 3, by connecting a
shunt resistor across the sensor terminals, measuring the resultant voltage, Em, and carrying
out the simple calculation shown.
Figure 3
Operating Theory
Oxygen concentration of a conventional combustion atmosphere is measured by an in situ
zirconia sensor, which responds to oxygen according to the Nernst equation shown here.
Because the equation is logarithmic (to the base 10), the coefficient 0.0496TR is the number of
millivolts accompanying a tenfold change in concentration:
Ec= -0.02756TR log (PR /PF) millivolts
where TR is the temp in degrees Rankine and PF and PR are the % oxygen (O2) in the furnace
and the reference gas.
