Chapter 7: digital output interface, 1 overview, 2 dout connector – Sensoray 2426 User Manual
Page 11: 1 load connections
2426 Instruction Manual
9
Digital Output Interface
Chapter 7: Digital Output Interface
7.1 Overview
Sixteen general purpose digital output (DOUT) channels are
available on the 2426 module. DOUT channels are numbered 0
to 15.
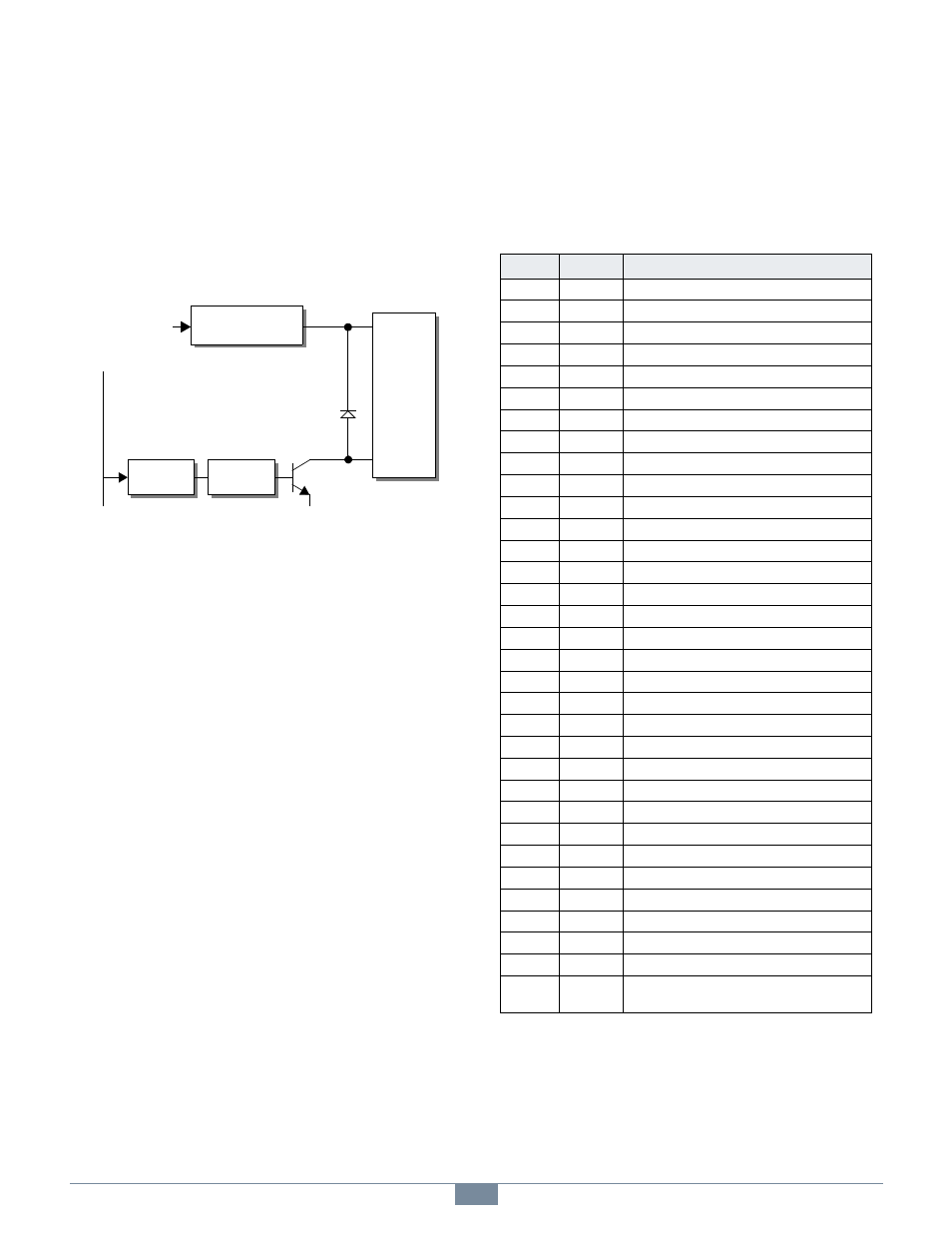
Figure 10: DOUT Channel Block Diagram
As shown in Figure 10, every DOUT channel has a control
circuit that includes a state register, optical isolator, and
active-low, open-collector output transistor. The transistor
applies the common GND signal to -DOUT when the channel
is turned on.
Under software control, each DOUT channel may be
configured to operate in either Standard or PWM mode. In the
Standard mode (default upon module reset), a channel is
programmed to explicit, static states by the network client.
When operating in PWM mode, a channel will output pulses
having period and duty cycle specified by the network client.
Integral support is provided for system interlock circuits and
multiple DIO power supply voltages. Each DIO channel may
be powered from any power source available on the module’s
internal power bus (see “Internal Power Bus” on page 4).
DOUT 0-15 - Each of these will light when its affiliated
channel is programmed to the “on” state, independent of
the channel’s operating mode. Note that these reflect the
programmed states of DOUT channels; a channel’s
physical and programmed states may differ if:
• The channel is connected in a “wired-or” topology and
its programmed state is off, but an external driver on the
same channel is turned on.
• The channel’s programmed state is on, but it is powered
from an interlock contact that is open.
Upon module reset, all channels switch to the off state and
default to the Standard operating mode.
7.2 DOUT Connector
All DOUT loads are connected to the module through the
female DB-37 connector labeled DOUT in Figure 2.
7.2.1 Load Connections
A channel’s output is, in effect, a differential pair consisting of
+DOUT and -DOUT. Whenever possible, the load should be
connected across these two signals as shown in Figure 11.
Interlock Power
Routing Matrix
Internal
Power Bus
DOUT
+DOUT
-DOUT
Optical
Isolator
I
n
t
e
r
n
a
l
D
a
t
a
B
u
s
State
Register
Connector
Power Bus
Common GND
Table 4: DOUT Connector Pin Assignments
Pin
Name
Function
1
+DOUT0
DOUT channel 0 positive output
20
-DOUT0
DOUT channel 0 negative output
2
+DOUT1
DOUT channel 1 positive output
21
-DOUT1
DOUT channel 1 negative output
3
+DOUT2
DOUT channel 2 positive output
22
-DOUT2
DOUT channel 2 negative output
4
+DOUT3
DOUT channel 3 positive output
23
-DOUT3
DOUT channel 3 negative output
5
+DOUT4
DOUT channel 4 positive output
24
-DOUT4
DOUT channel 4 negative output
6
+DOUT5
DOUT channel 5 positive output
25
-DOUT5
DOUT channel 5 negative output
7
+DOUT6
DOUT channel 6 positive output
26
-DOUT6
DOUT channel 6 negative output
8
+DOUT7
DOUT channel 7 positive output
27
-DOUT7
DOUT channel 7 negative output
9
+DOUT8
DOUT channel 8 positive output
28
-DOUT8
DOUT channel 8 negative output
10
+DOUT9
DOUT channel 9 positive output
29
-DOUT9
DOUT channel 9 negative output
11
+DOUT10 DOUT channel 10 positive output
30
-DOUT10
DOUT channel 10 negative output
12
+DOUT11 DOUT channel 11 positive output
31
-DOUT11
DOUT channel 11 negative output
13
+DOUT12 DOUT channel 12 positive output
32
-DOUT12
DOUT channel 12 negative output
14
+DOUT13 DOUT channel 13 positive output
33
-DOUT13
DOUT channel 13 negative output
15
+DOUT14 DOUT channel 14 positive output
34
-DOUT14
DOUT channel 14 negative output
16
+DOUT15 DOUT channel 15 positive output
35
-DOUT15
DOUT channel 15 negative output
17,18,19,
36,37
NC
Not connected. These are uncommitted pins,
reserved for future use.
