Measurement Computing CIO-CTRxxHD User Manual
Page 16
The cut-off frequency is that frequency above which no variation of voltage with
respect to time may enter the circuit. For example, if a low-pass filter had a cut-off
frequency of 30 Hz, interference associated with line voltage (60 Hz) would be mostly
filtered out but a signal of 25 Hz would pass with less attenuation.
Also, in a digital circuit, a low-pass filter is often used to remove contact bounce noise
signals from a switch or a relay contacts. Also, in a digital circuit, a low pass filter
might be used to “de-bounce” (filter) an input from a switch or external relay. (Unless
switch/relay contacts are mercury-whetted, they tend to bounce briefly on closure,
generating a pulsating noise signal. This can easily lead to erroneous counts unless
filtered out.)
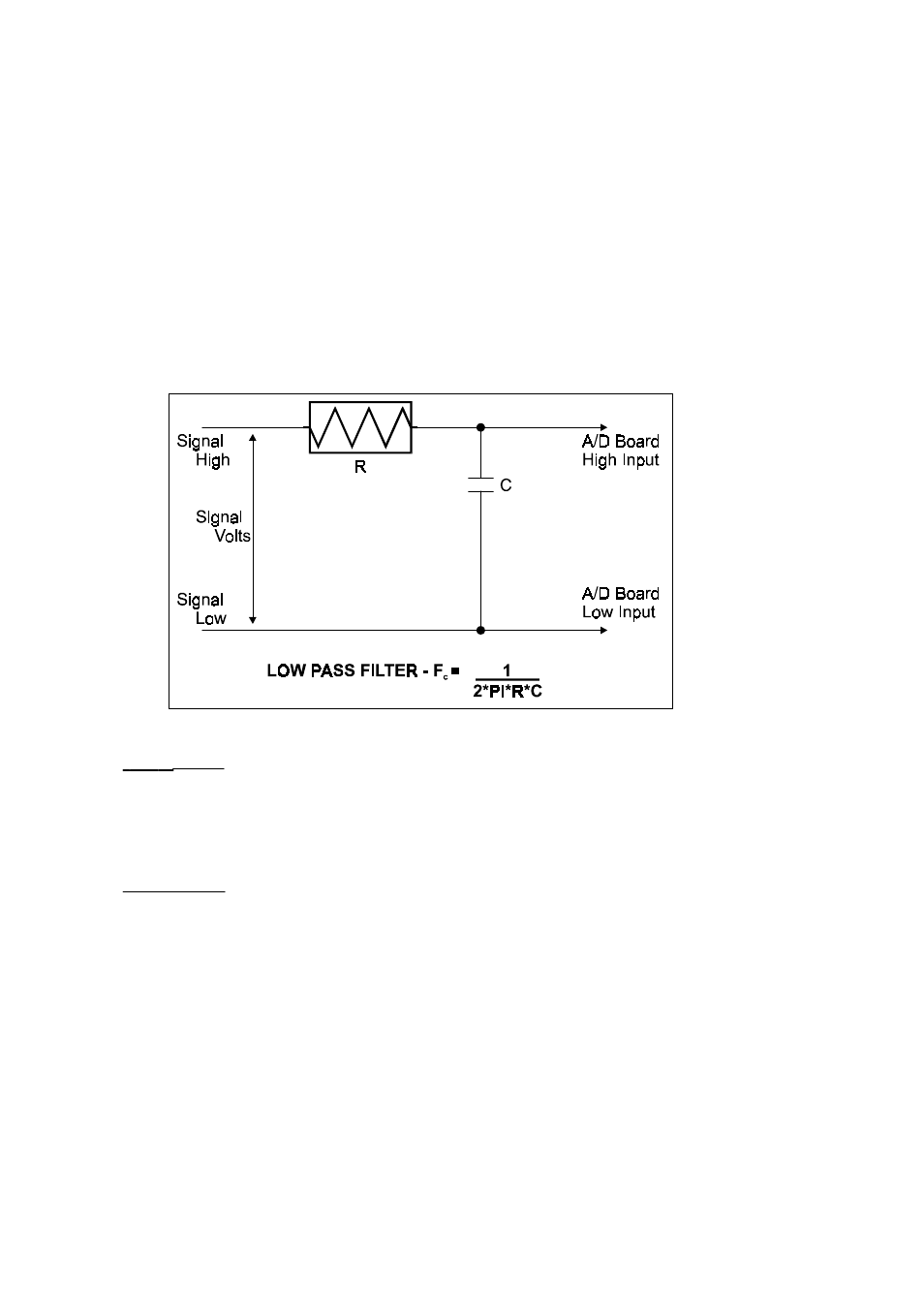
A simple low-pass filter can be constructed from one resistor (R) and one capacitor
(C). The cut-off frequency is determined according to the formula:
Fc =
1
Where
π
= 3.14...
2
π
R C
R = ohms
C = farads
Fc = cut-off frequency in cycles/second
R =
1
.
2
π
C Fc
12
