General, Be1-cds240 solution – Basler Electric BE1-CDS240 General Information User Manual
Page 15
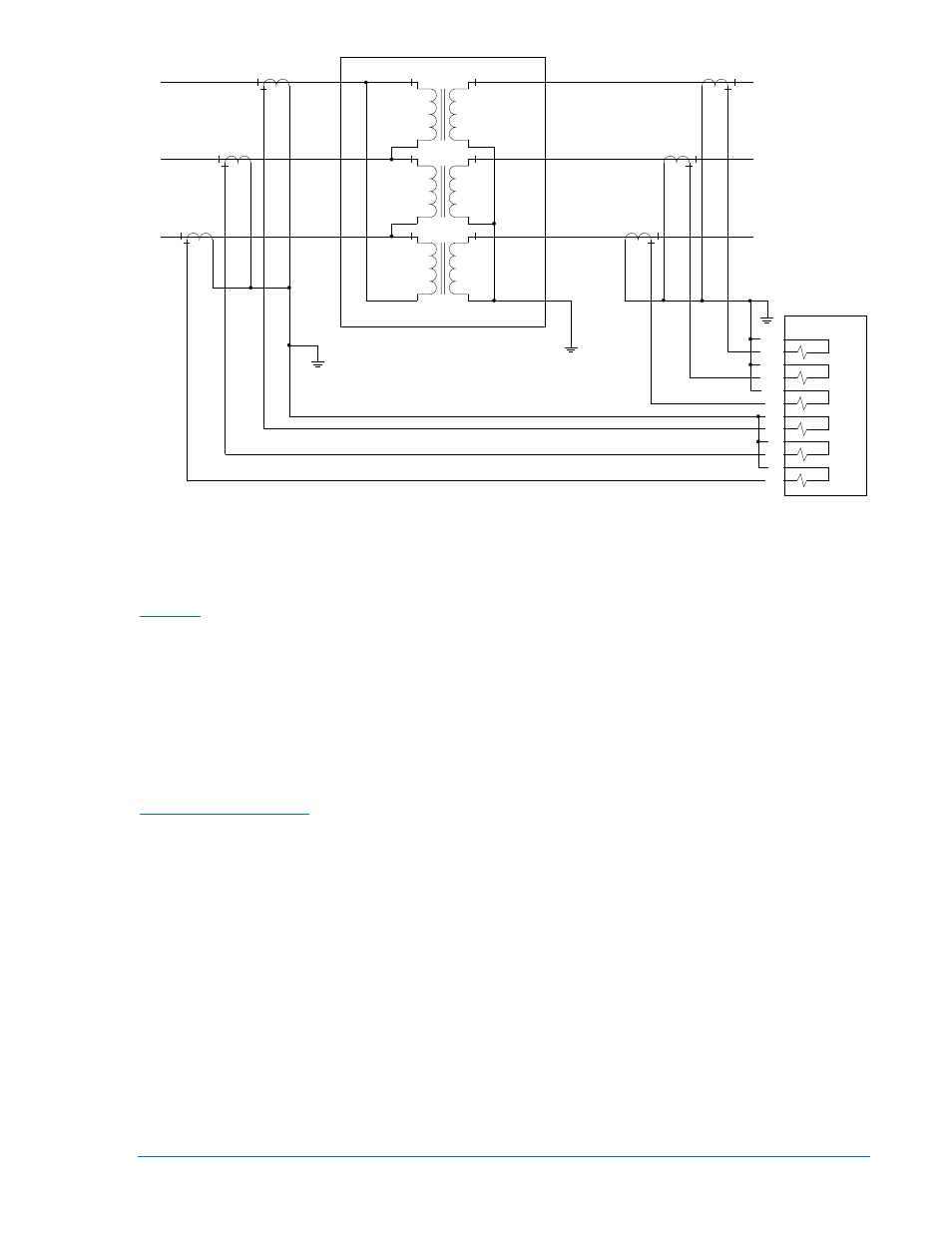
Figure 1-6. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration, Internal Phase Compensation
Problem 5: Zero-Sequence Current Sources Within the Zone of Protection
General
A ground source (grounded transformer winding or zigzag grounding bank) within the zone of protection
can result in differential current being measured during ground imbalances. The most common example
of this is when the zone of protection is around a delta/grounded, wye transformer. If a ground fault or
neutral imbalance occurs on the power system external to the wye side zone of protection, the zero-
sequence components of the current flow through the grounded neutral and are a component of the
current flowing out of the zone of protection. On the delta side, there is no path for the zero-sequence
components to flow and they circulate inside the delta winding. The result is that this component of the
current is not seen entering the zone of protection on the delta side resulting in a differential current that
can cause the relay to operate.
BE1-CDS240 Solution
There are two traditional solutions to this problem. The first is using delta phase-shift compensation on
the grounded side of the zone of protection to block the zero-sequence components from getting to the
differential protection. The second is removing the zero-sequence components from the currents using a
zero-sequence trap to prevent them from getting to the differential protection. The BE1-CDS240 provides
both solutions.
In the previous discussion on compensating for the phase shift on the primary system, the solution is to
combine the currents such that the currents seen by the differential are made up of the same components
at all terminals of the zone of protection. This solution has the added benefit of causing the currents to
match (after magnitude mismatch is eliminated by tap adjustment) under all situations of imbalance
including ground faults. That is, by using delta compensation on the wye side of the power transformer to
mimic the power transformer's delta connection, the zero-sequence currents are blocked from flowing to
the differential protection and circulate in the CT delta just as they circulate in the delta of the power
transformer on the delta side.
The BE1-CDS240 selects the proper phase shift compensation settings to not only provide the correct
phase shift but also to block zero-sequence currents as appropriate.
The second solution of inserting a zero-sequence trap is used in applications where there is a grounding
bank within the zone of protection that is not predicted by the transformer connection information
H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
X
2
X
1
X
0
X
3
C
B
A
P0017-04
02-28-03
A13
A14
A9
A11
A7
A8
A5
A6
BE1-CDS240
A4
A3
A12
A10
9365200990 Rev M
BE1-CDS240 General Information
1-13
