Routing configuration, Ip route, Outing – D-Link DSL-500G User Manual
Page 41: Onfiguration, Figure 19. ip route table
DSL-500G ADSL Router User’s Guide
Routing Configuration
Links to the IP Route and IP Address tables are found within the Routing folder. The remaining links are
duplicate links to menus that have been previously described.
IP Route
IP Routes are used to define gateways and hops used to route data traffic. Most users will not need to use this
feature as the previously configured default gateway and LAN IP settings on your host computers should be
sufficient.
You may need to define routes if your LAN includes two or more networks or subnets, if you connect to two or
more ISP services, or if you connect to a remote corporate LAN. Use the IP Route Table to Add new IP routes.
The new IP routes are in effect additional rules used by the Router for routing data. See the next section, Adding
IP Routes for instructions.
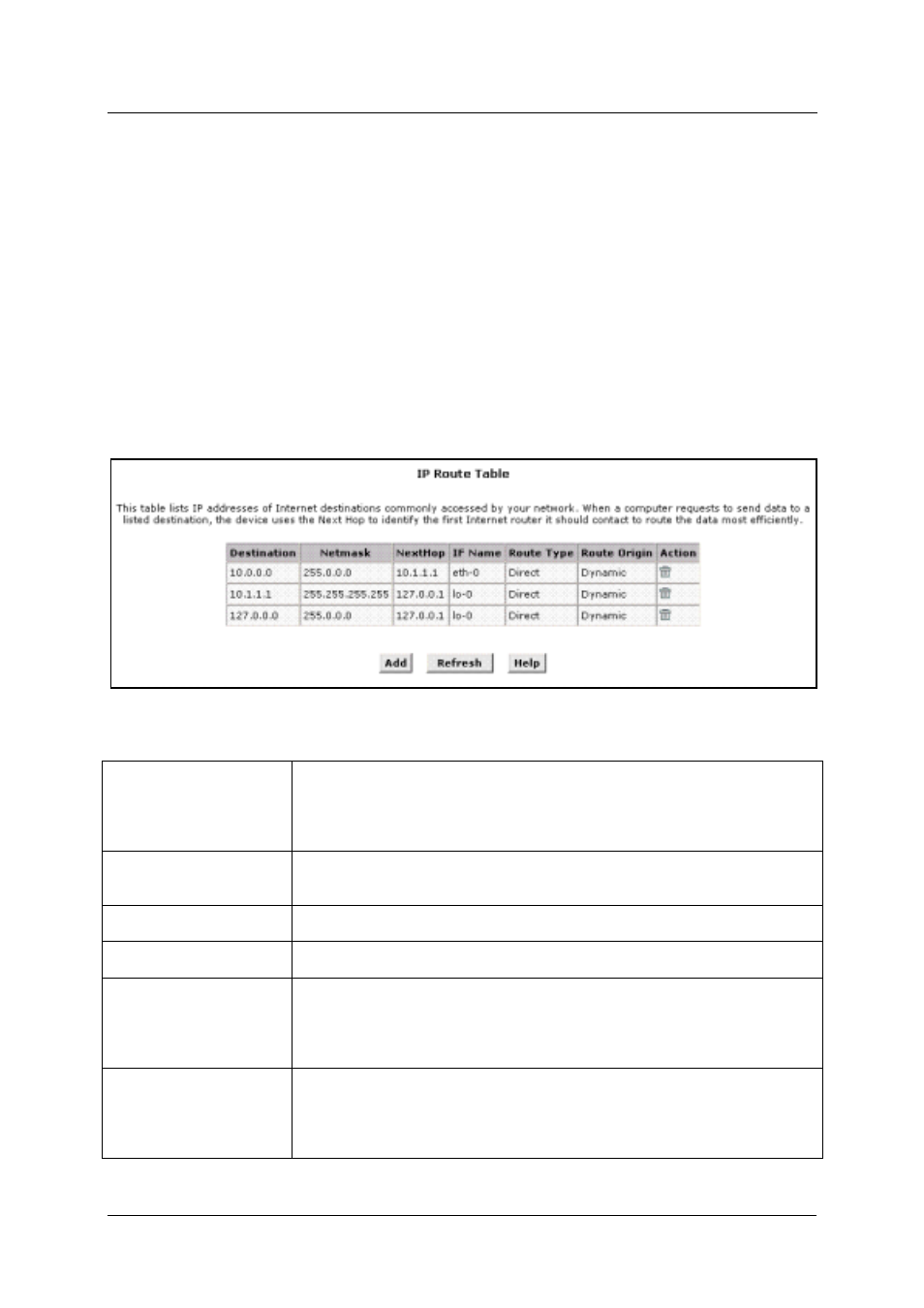
Figure 18. IP Route Table
Information displayed in the IP Route Table is summarized below:
Destination
Specifies the IP address of the destination computer. The destination can
specified as the IP address of a specific computer or an entire network. It
can also be specified as all zeros to indicate that this route should be used
for all destinations for which no other route is defined (this is the route that
creates the default gateway).
Netmask
Indicates which parts of the destination address refer to the network and
which parts refer to a computer on the network. The default gateway uses
a netmask of 0.0.0.0.
Next Hop
Specifies the next IP address to send data to when its final destination is
that shown in the destination column.
IF Name
Displays the name of the interface through which to data is forwarded to
the specified next hop.
Route Type
Displays whether the route is direct or indirect. In a direct route, the source
and destination computers are on the same network, and the router
attempts to directly deliver the data to the computer. In an indirect route,
the source and destination computers are on different networks, and the
router forwards data to a device on another network for further handling.
Route Origin
Displays how the route was defined. Dynamic indicates that the route was
predefined on the system by your ISP or the manufacturer. Routes you
create are labeled Local. Other routes can be created automatically, or
defined remotely through various network management protocols (LCL or
ICMP).
31
