Signamax Managed Hardened PoE Industrial DIN-rail Mount Switch User Manual
Page 36
7 Forwarding
31
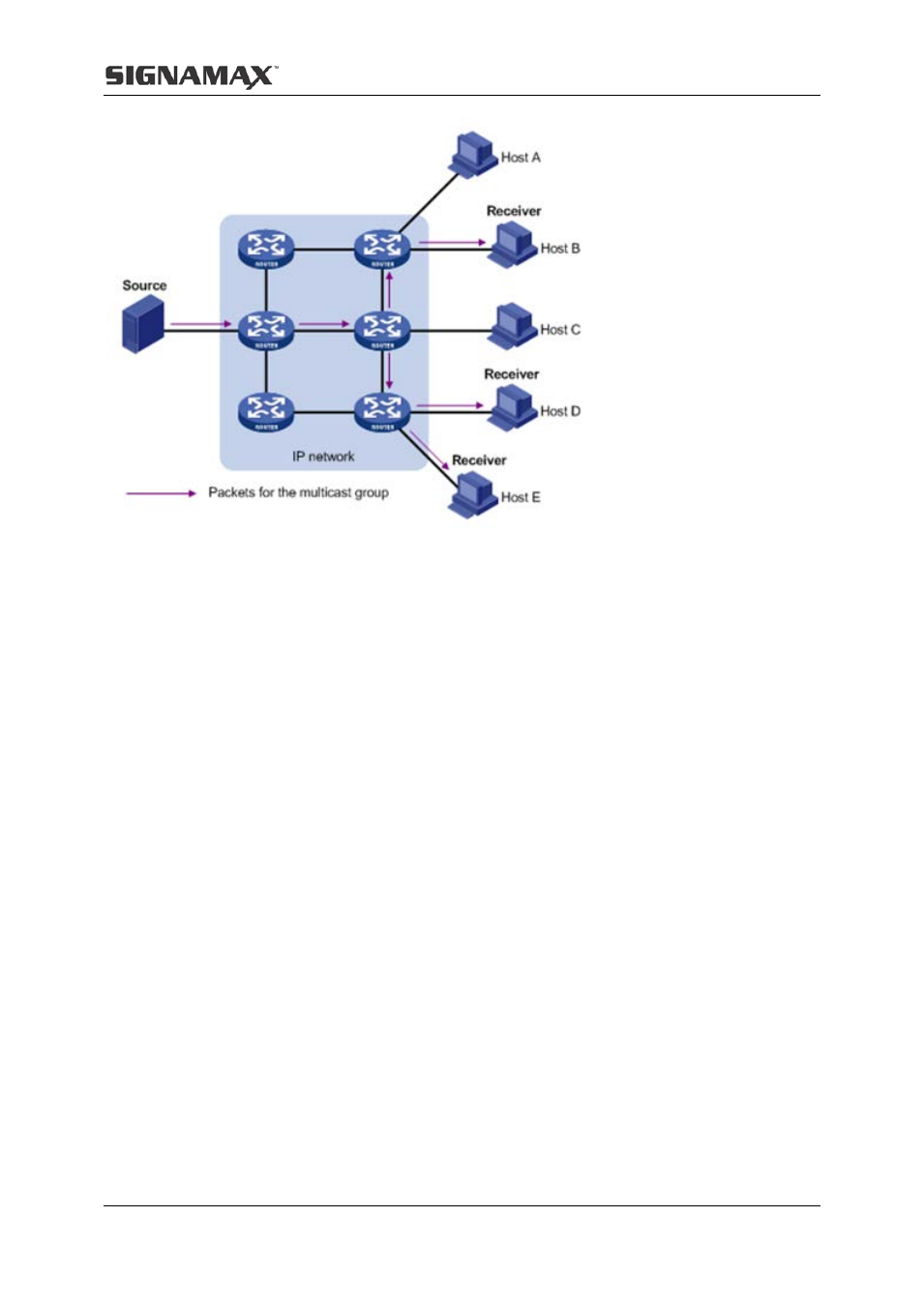
The advantages of multicast are summarized as follows:
Over unicast: As multicast traffic flows to the node the farthest possible from the source
before it is replicated and distributed, an increase of the number of hosts will not increase
the load of the source and will not remarkably add to network resource usage.
Over broadcast: As multicast data is sent only to the receivers that need it, multicast uses
the network bandwidth reasonably and enhances network security. In addition, data
broadcast is confined to the same subnet, while multicast is not.
A multicast group is a multicast receiver set identified by an IP multicast address. Hosts join a
multicast group to become members of the multicast group, before they can receive the
multicast data addressed to that multicast group. Typically, a multicast source does not need
to join a multicast group. An information sender is referred to as a multicast source. A
multicast source can send data to multiple multicast groups at the same time, and multiple
multicast sources can send data to the same multicast group at the same time. All hosts that
have joined a multicast group become members of the multicast group.
This page sets multicast MAC address entries. Each multicast MAC address entry contains
multicast address, forward ports, and VID.
VID:Specifies the VLAN group of which the forwarding ports are members.
Multicast MAC Address:Multicast MAC address, in the form of xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
Member:Specifies forwarding ports for the specified multicast MAC group address. One or
more ports can be added as the member.
The lower part of this page lists all existing multicast MAC addresses, as well as the
information of each multicast MAC address. The user can also modify or delete an existing
multicast MAC address.
