Lumagen Radiance XE-3D User Manual
Page 12
Section 2 – Overview
RadianceXE
rev 091211
6
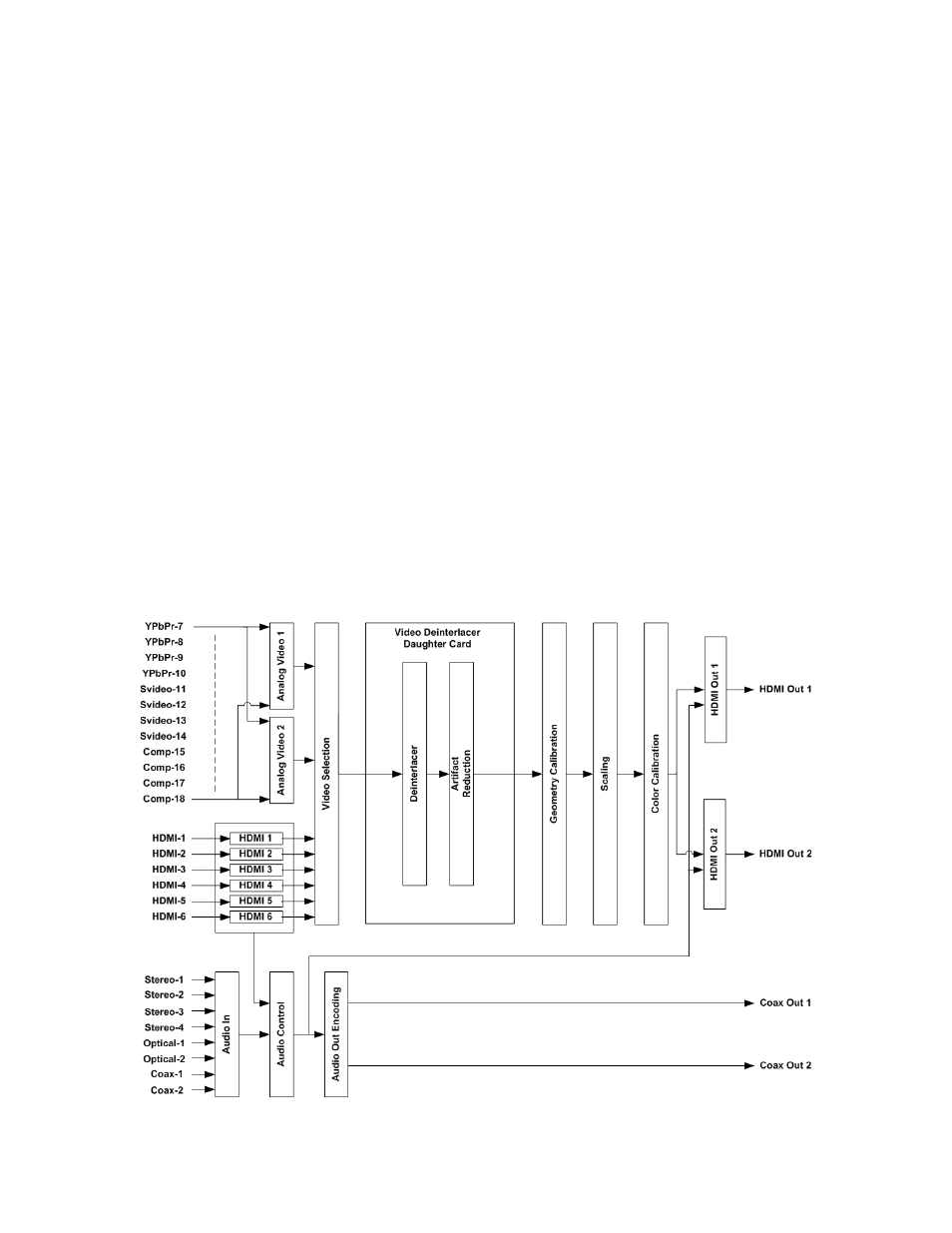
Block Diagram
The function of the Radiance is to act as a video switch, process the selected video source and then output
video in the appropriate format and resolution. Standard definition (SD), enhanced-definition (ED), high-
definition (HD) video inputs, plus a number of PC formats are supported. Video inputs are converted to
progressive video (if necessary) and are then scaled to the video output resolution.
Interlaced video has been in use for more than 50 years and is still the most common video format. It
displays half of the lines of picture information each sixtieth (or fiftieth) of a second. Each half of the image
is called a field and displays either all the even lines, or all the odd lines. So, an entire image, called a
frame, takes a thirtieth (or twenty-fifth) of a second to display on the screen. An “i” suffix on the resolution
specification is used to indicate interlaced formats.
In contrast, progressive video presents each frame as a whole. A “p” suffix on the resolution specification is
used to indicate progressive formats. Converting interlaced video to progressive video is referred to as
“deinterlacing.”
The Radiance is comprised the following major functional sections:
•
Video input selection with conversion to digital (if needed) and video decoding
•
Video deinterlacing
•
Video filtering and scaling
•
Video output of HDMI digital video
•
Audio input selection
•
Audio control
•
Audio output encoding
The functional blocks are shown below.
