Hanna Instruments HI 83206-2008 User Manual
Page 25
48
49
Nitrite HR
NITRITE HIGH RANGE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range
0 to 150 mg/L
Resolution
1 mg/L
Accuracy
±4 mg/L ±4% of reading
Typical EMC
±1 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source
Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 575 nm
Method
Adaptation of the Ferrous Sulfate method. The reaction between nitrite and the
reagent causes a greenish-brown tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93708-0
Powder reagent
1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93708-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93708-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 73.
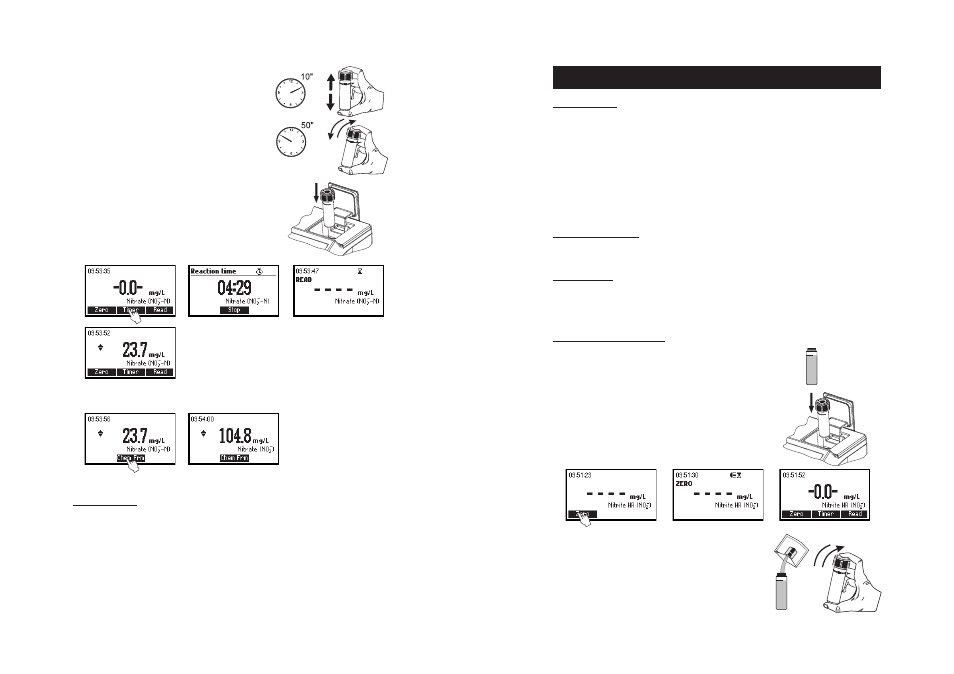
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Nitrite HR method using the procedure described
in the
Method Selection section (see page 12).
• Fill the cuvette up to the mark with 10 mL of unreacted
sample and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press ZERO key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the
meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add the content of one packet of HI 93708-0 reagent. Replace
the cap and shake gently until completely dissolved.
10 mL
Nitrate
• Replace the cap and immediately shake vigorously up
and down for exactly 10 seconds. Continue to mix by
inverting the cuvette gently for 50 seconds, while taking
care not to induce air bubbles. Powder will not com-
pletely dissolve. Time and way of shaking could sensitively
affect the measurement.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument, taking care
not to shake it.
• Press TIMER and the display will show the countdown prior
to the measurement or, alternatively, wait for 4 minutes
and 30 seconds and press READ. When the timer ends
the meter will perform the reading. The instrument
displays the results in mg/L of nitrate-nitrogen.
• Press the or to access the second level of functions.
• Press the Chem Frm functional key to convert the result in mg/L of nitrate (NO
3
-
).
• Press the or to go back to the measurement screen.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by:
Ammonia and amines, as urea and primary aliphatic amines
Chloride above 100 ppm
Chlorine above 2 ppm
Copper
Iron(III)
Strong oxidizing and reducing substances
Sulfide must be absent
