Hanna Instruments HI 4009 User Manual
Page 13
13
XII.
XII.
XII.
XII.
XII. Other Measurement T
Other Measurement T
Other Measurement T
Other Measurement T
Other Measurement Techniques
echniques
echniques
echniques
echniques
Known Addition (for CN
-
)
An unknown concentration can be determined by adding a
known amount (volume and concentration) of measured
ion to a known volume of the sample. This technique is
called Known Addition. The method can use an ideal
sensor slope, but actual determined slopes at the tempera-
ture of measurement should be used if known. The volume
and concentration of the added standard must cause a mV
change of at least 30 mV. This method is preprogrammed
in the Hanna HI 4222 pH/ISE/mV meter, which simplifies
the method greatly. The method is recommended for
samples with higher ionic strengths.
Example: Cyanide ion determination in samples with con-
centrations less than 5 X 10
-4
M using known addition.
1. A 50 mL sample of unknown (Vsample) is placed in
a clean plastic beaker with a cyanide sensor. 500 uL
(0.5 mL) of HI 4001-00 ISA (V
ISA
) is added to the 50
mL sample and allowed to mix. The stable mV value
(mV 1) is recorded.
2. 10 mL (Vstd) of 10
-2
M (Cstd) stock standard is added
to the beaker and the mV value decreases. The un-
known cyanide concentration in the original sample
(Csample) can then be determined by the following
equation.
3. The procedure can be repeated with a second stan-
dard addition to verify slope and operation of the
method.
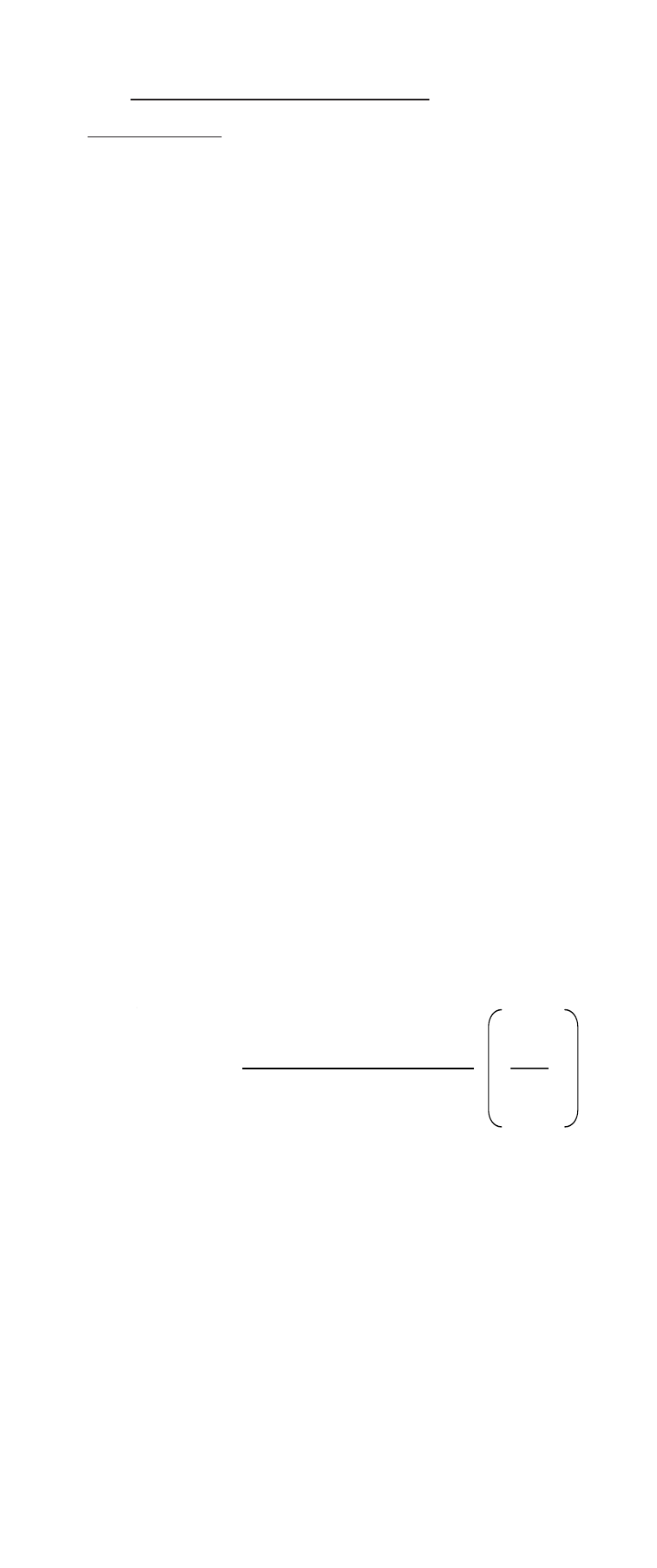
C
sample
=
(V
T
)10
∆E/S
- (V
S’
)
C
standard
V
standard
V
sample
V
S’
(V
sample
+V
standard
+V
ISA
)= V
T
(V
sample
+V
ISA
)= V
S’
