14 ip control basics – Hall Research VSM-I-A-16-16 User Manual
Page 36
34
Hall Research Technologies, Inc.
Matrix
Command
Processing
Port 1001
Port 23
IP Setup
Serial
Control
IP
Control
RS-232
Port
The matrix stores the last 64 bytes received from the target in a receive FIFO,
then upon receipt of this command it sends whatever it has (as binary) out to the
user. Nothing if the buffer is empty.
Response:
Any characters in the receive FIFO buffer.
4. Command:
XB,n
If n is not specified it reports the current baud rate (1-8).
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Baud = 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2k, 38.4k, 57.6k, 115.2k respectively
Response:
XB,n
5. Command:
XP,n
n = 0 1 2
Tranmit Parity to target = None, Odd, Even respectively
Response:
XP,n
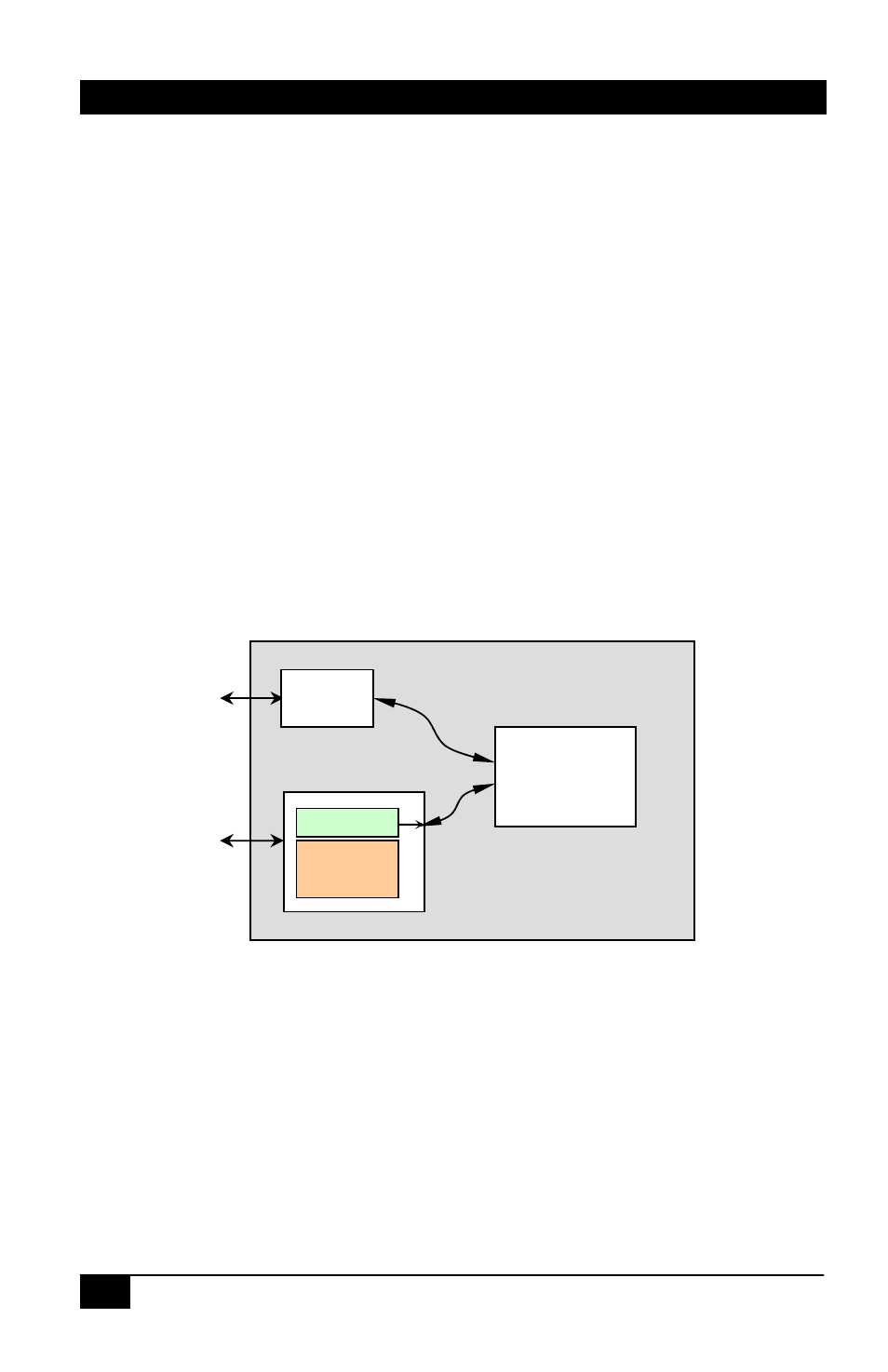
3.2.14 IP Control Basics
Figure 18 – Control Block Diagram
As shown in the figure above, the matrix can be controlled via RS232 Serial port
or through an IP (Ethernet) port if equipped. If the unit is missing the IP port, then
in its place, there is an auxiliary 2
nd
serial control port (see section 2.4.1.2).
The IP port of the matrix can be accessed via Telnet (interactive TCP connection).
Two ports are available, one for controlling the matrix and the other to configure
the IP parameters.
Though not recommended, using port 23 you can change the Ethernet interface’s
IP parameters such as IP address, gateway, port number, etc. The IP settings can
also be accessed through the unit’s primary RS232 serial port (recommended).
