Gk013 p14_15, Gears, belts, & chains, Mechanism of machines master class – Elenco Tumbling Robot User Manual
Page 8: Mini quiz, Gears, belts, and chains - importance
Driving wheel
Driven wheel
MECHANISM OF MACHINES MASTER CLASS
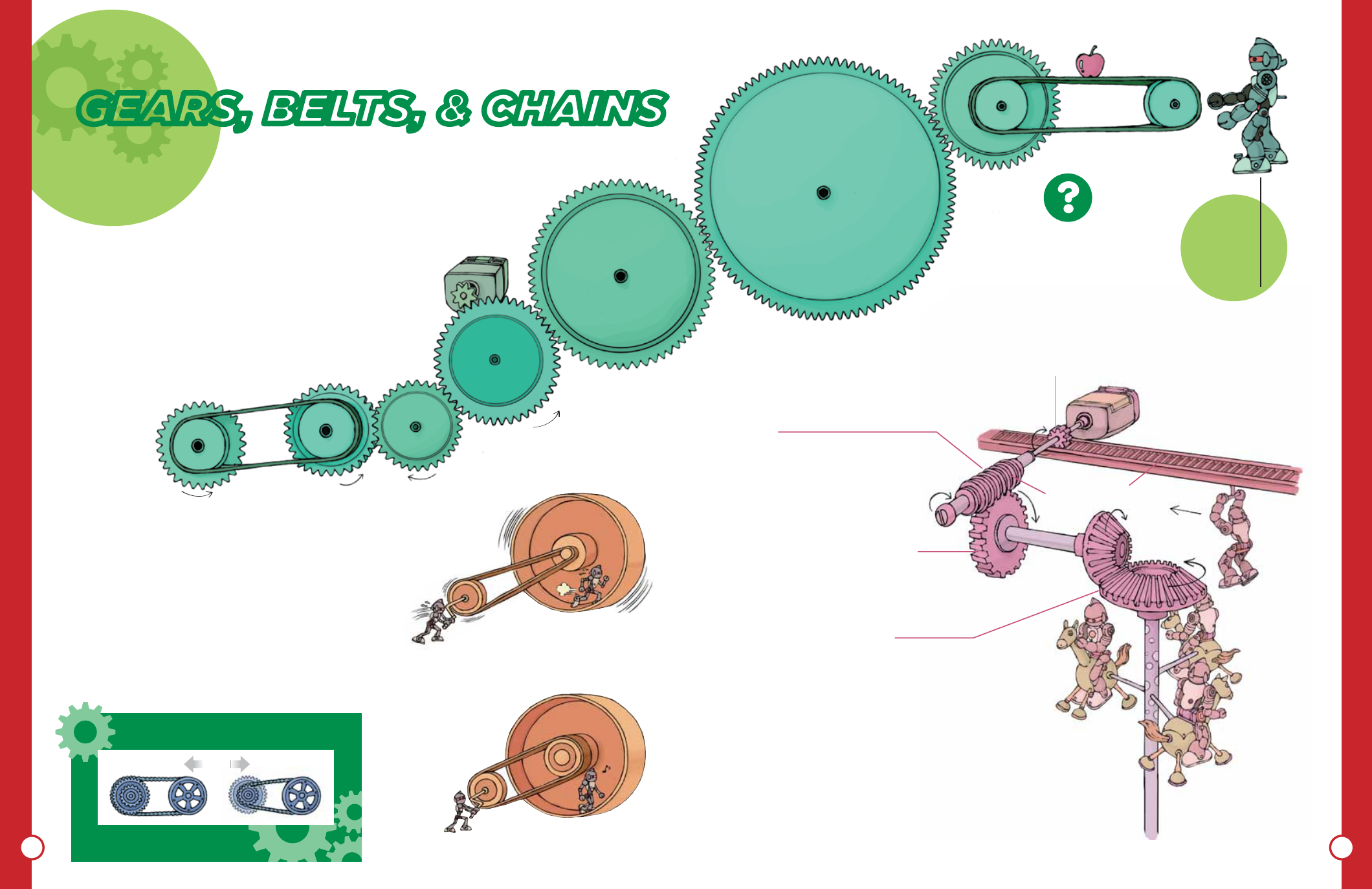
GEARS, BELTS, & CHAINS
-TRANSFER ROTATION, CHANGE SPEED AND DIRECTION
OF ROTATION-
GEARS, BELTS, & CHAINS
Gears, belts, and chains transfer rotational
motion. They are used in many mechanisms
of everyday devices such as bicycles and cars.
•Transfer rotational motion
When a gear rotates, it rotates adjacent gear. The direction
of the rotation of the second gear becomes opposite to the
first gear. Contrary, the two gears attached by belts or
chains will rotate in the same direction.
•Rack and Pinion
A rack is a linear gear bar. A
circular gear is called pinion.
A pinion rotates on a rack.
This mechanism is used to
transfer a rotational motion
(pinion) to a linear sliding
motion (rack) or vise versa.
•Worm Gear
Worm gear is an assembly consists of a
worm and a worm wheel. Worm's screw
like thread rotates the worm wheel. Worm
gear can shift the direction of the rotation
by 90 degree. It is useful to reduce the
rotational speed by large amount.
•Bevel Gear
Bevel gears can change the
direction of rotation by 90
degree.
Mini quiz
Gears joined by
belts rotate in the
same directions
When the driving wheel
has a fixed diameter, the
larger the driven wheels
becomes, the slower it
rotates and requires less
force.
Gears attached by
teeth rotate
opposite directions
Technical consultation: Masahiro Mori, Professor Emeritus, Tokyo University
illustration: Kasyu
01
Gears, belts, and
chains - Importance
•Change rotational directions
Adjacent gears usually rotate opposite directions to each
other. However, choosing right types of gears, the
rotational directions can be changed by 90 degree. By
arranging special gears, one motor's rotation can produce
motion in a variety of directions.
03
Gears, belts, and
chains - Importance
•Change the rotational speed
When two gears have same diameter, the rotational speed
of the two gears is the same. On the contrary, when two
gears have different diameters, the two gears have different
rotational speeds. The larger the diameter becomes, the
slower it rotates. The smaller the diameter becomes, the
faster it rotates. Geared bicycles use this mechanism of
gears. The same rules apply to the number of teeth. The
more teeth a gear has, the slower it rotates.
02
Gears, belts, and
chains - Importance
Gear Change of Bicycle
The smaller the gear becomes, the faster the
wheels rotates. The pedals require greater force.
Can the robot receive the apple?
Let's trace the direction of the belt!
Answer is at the lower right corner.
Answ
er of the mini quiz:
Y es, the r
obot will rec
eive the apple
Pinion
Rack
Worm
Worm wheel
14
15
JR. SCIENTIS
T
TUMBLING ROBO
T
