About your snaptricity, Parts – Elenco Snaptricity® User Manual
Page 6
About Your Snaptricity
®
Parts
How does electricity turn the shaft in the motor?
The answer is magnetism. Electricity is closely
related to magnetism, and an electric current
flowing in a wire has a magnetic field similar to
that of a very, very tiny magnet. Inside the motor
is a coil of wire with many loops wrapped around
metal plates. This is called an electromagnet. If
a large electric current flows through the loops, it
will turn ordinary metal into a magnet. The motor
shell also has a magnet on it. When electricity
flows through the electromagnet, it repels from
the magnet on the motor shell and the shaft
spins. If the fan is on the motor shaft, then its
blades will create airflow.
-5-
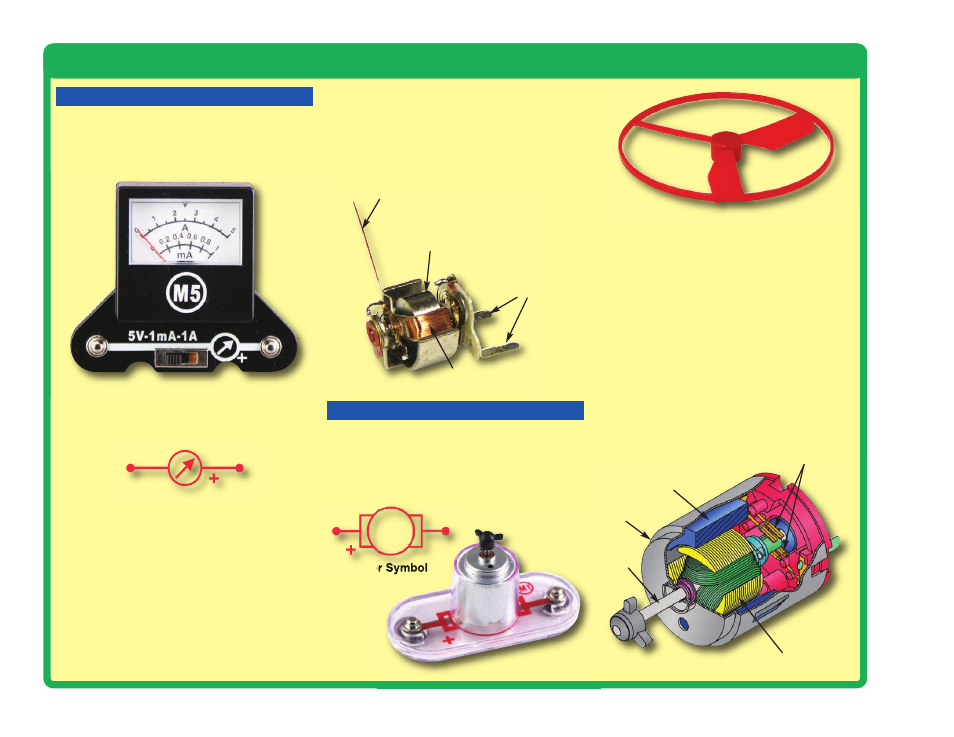
The meter (M5) is an important measuring
device. You will use it to measure the voltage
(electrical pressure) and
current
(how fast
electricity is flowing) in a circuit.
The electrical symbol for a meter is shown below.
The meter measures voltage when connected in
parallel to a circuit and measures the current
when connected in series in a circuit.
This meter has one voltage scale (5V) and two
current scales (1mA and 1A). These use the
same meter but with internal components that
scale the measurement into the desired range.
This will be explained more later. Note: Your M5
meter is a simple meter. Don’t expect it to be as
accurate as normal electronic test instruments.
The motor (M1)
converts electricity into
mechanical motion. An electric current in the
motor will turn the shaft and the motor blades,
and the fan blade if it is on the motor. The
electrical symbol for a motor is also shown here.
METER
MOTOR
Meter Symbol
Magnet
Coil
Pointer
Contacts
Motor Symbol
Magnet
Electromagnet
Shaft
Power Contacts
Shell
Meter (M5)
Motor (M1)
Fan
Inside the meter there is a fixed magnet and a
moveable coil around it. As current flows through
the coil, it creates a magnetic field. The
interaction of the two magnetic fields causes the
coil (connected to the pointer) to move (deflect).
