6 excitation and remote-sensing, Excitation and remote-sensing, Figure 4-3: sinc filter power line noise rejection – ADLINK PCI-9524 User Manual
Page 70: At 60 hz multiples
54
Operation
Theory
ADLINK Technology Inc.
Copyright 2008
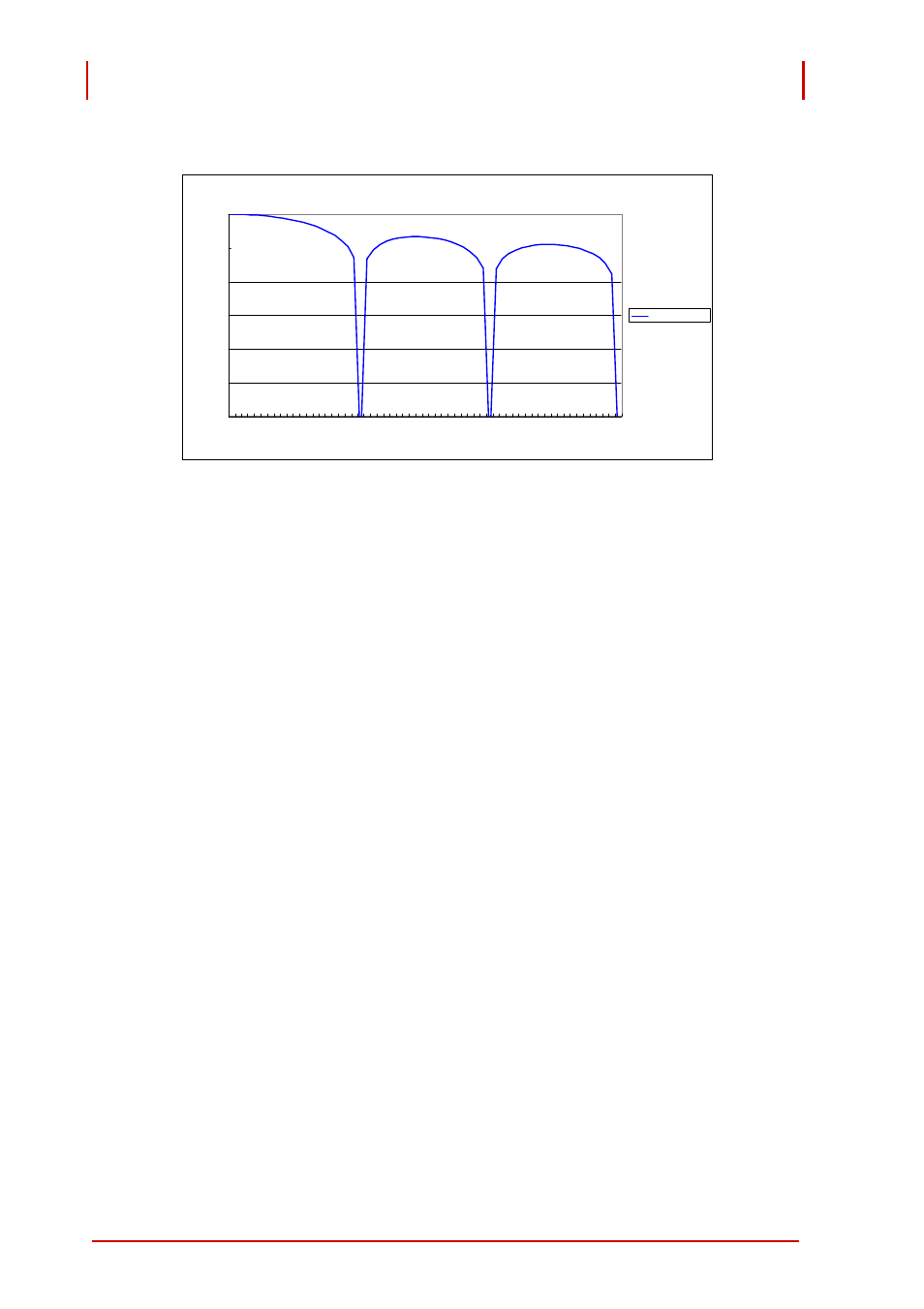
Figure 4-3: SINC Filter Power Line Noise Rejection
at 60 Hz Multiples
Sinc Response
-120
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0.00
30.00
60.00
90.00
120.00
150.00
180.00
Frequency (Hz)
A
tt
enu
at
ion (
d
B
)
Sinc Response
The power line frequency is either 50 or 60-HZ in most countries.
For sampling rates supporting power line noise rejection, please
refer to the notes after Table 4-1 for your reference.
The SINC filter cannot suppress power line noise for a sampling
rate above 60 SPS (or 100 SPS with auto-zero). Under such con-
ditions, power line noise rejection relies on the inherent common-
mode rejection ability of the input amplifier. Under this circum-
stance, using the post-processing IIR digital filter can attenuate
power line noise somewhat, at the cost of increased signal settling
time. See Section 4.2.9 for details.
4.2.6
Excitation and Remote-sensing
Users can select excitation voltages from either 2.5V or 10V
sources. For most load-cell transducers, 10V is recommended.
The higher the excitation, the higher the resolution will generally
be; since the signal is larger at the beginning of the signal chain
and hence a better overall 'signal-to-noise ratio' (SNR).
The remote-sensing function requires users to connect all the
excitation voltage driving pins to the corresponding remote-sens-
