Choice of blade and speed, Basic saw operations – Sears 113.244530 User Manual
Page 16
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
CHOICE OF BLADE AND SPEED
Your
band
saw
will
cut
a
wide
variety
of
material-wood, wood like products, non-ferrous met
als (brass, aluminum, copper) and ferrous metals
(steel, iron). In order to obtain satisfactory results fol
low these general guide lines:
1. Use the correct type of blade for the material being
cut. For example if cutting ferrous metal make sure
to use a steel cutting blade.
2. Use a finer tooth blade for cutting thin workpieces
when a smoother cut is required, for hard materi
als, or when using lower speeds.
3. Use a coarser tooth blade for cutting thicker work
pieces, when making straight cuts, for medium to
soft materials or when using higher speeds.
4. Use a blade that will have at least 2 teeth in the
material at all times.
5. Use thin, narrow blades for tight radius work, and
thick, wide blades for large curves and straight
cuts.
6
. Match the approximate blade speed (FPM) to the
material being cut. See chart below;
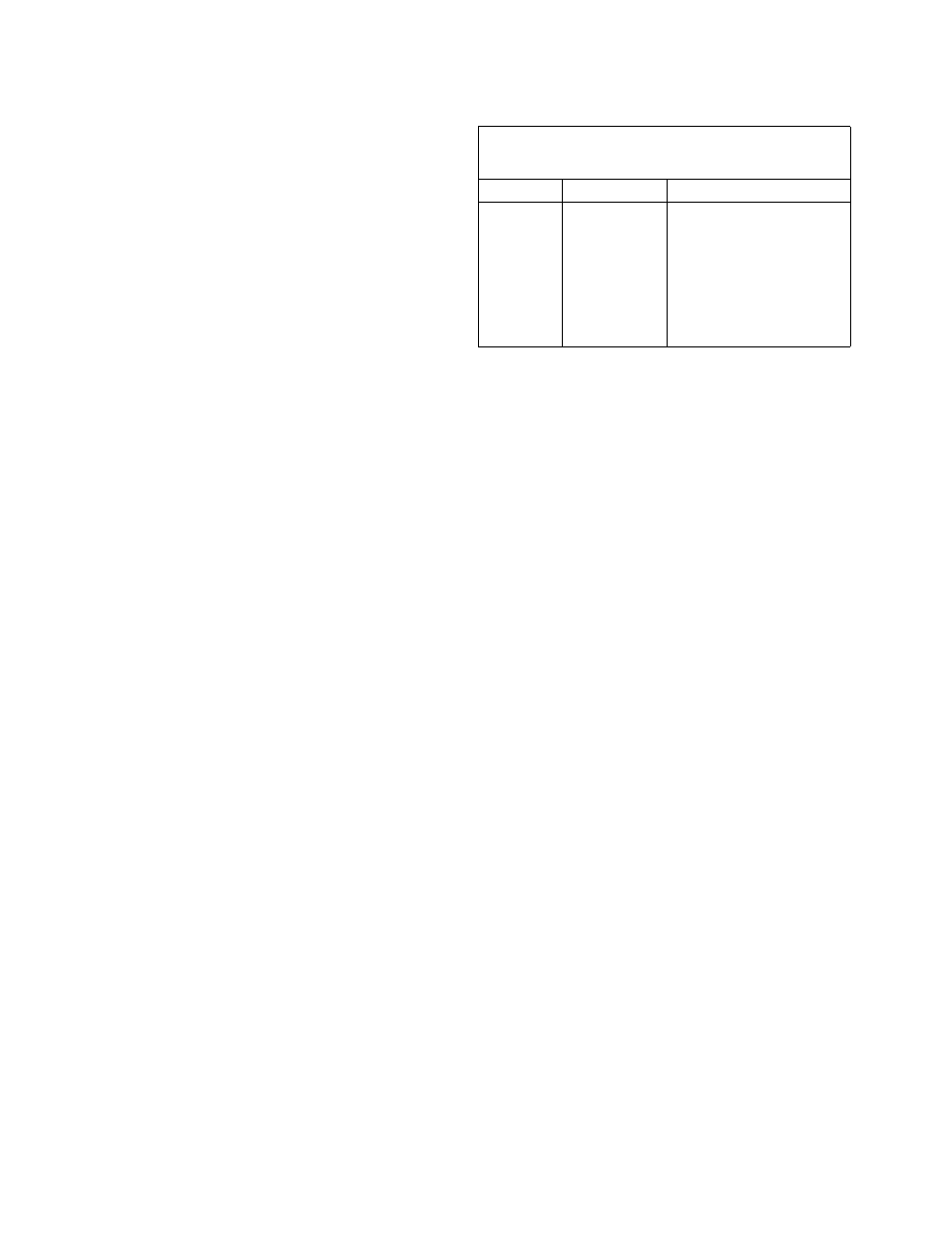
BLADE TYPE AND APPROXIMATE
SPEED FOR CUTTING
Material
Speed
Blade
Wood
Plastic
Aluminum
Brass
Copper
Steel
2460 FPM
1230 FPM
1130 FPM
840 FPM
400 FPM
300 FPM
General Purpose Blade
General Purpose Blade
Metal Cutting Blade
Metal Cutting Blade
Metal Cutting Blade
Metal Cutting Blade
CAUTION: Do not cut hardened steel.
Basic Saw Operations
BEFORE EACH USE:
Inspect your saw.
Make sure the blade guides and thrust bearings
are properly adjusted.
DISCONNECT THE SAW. To avoid injury from acci
dental starting, unplug the saw, push the knob off and
lock with a padlock before changing the setup, open
ing covers, removing guards, or blade.
CHECK FOR DAMAGED PARTS. Check for:
• alignment of moving parts,
• binding of moving parts,
• broken parts,
• stable mounting, and
• any other conditions that may affect the way the
saw works.
If any part is missing, bent, or broken in any way, or
any electrical part doesn’t work properly, turn the saw
off and unplug the saw. REPLACE damaged, miss
ing, or failed parts before using the saw again.
MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep the saw clean
for best and safest performance.
REMOVE
ADJUSTING
KEYS
AND
WRENCHES
from tool before turning it on.
To avoid injury from jams, slips or thrown pieces:
• Choose the right size and style blade for the
material and the type of cutting you plan to do.
•
USE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES.
(See page 19). Consult this owner’s manual for
recommended accessories. Follow the instruc
tions that come with the accessories. The use of
improper accessories may cause risk of injury to
persons.
•
• Make sure the blade teeth point downward,
toward the table.
• Make sure the blade tension is properly
adjusted.
• Make sure the table lock knob is tight and no parts
have excessive play.
• To avoid accidental blade contact, minimize blade
breakage and provide maximum blade support,
always adjust the upper blade guide and blade
guard to just clear the workpiece.
• KEEP WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents. Floor must not be slip
pery.
To avoid burns or other fire damage, never use the saw
near flammable liquids, vapors or gases.
Plan ahead to protect your eyes, hands,
face, ears.
KNOW YOUR SAW. Read and understand the owner’s
manual and labels affixed to the tool. Learn its applica
tion and limitations as well as the specific potential haz
ards peculiar to this tool.
To avoid injury from accidental contact with moving
parts, don’t do layout, assembly, or setup work on the
saw while any parts are moving.
AVOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING. Make sure switch is
“OFF” before plugging saw into a power outlet.
Plan your work.
• USE THE RIGHT TOOL. Don’t force tool or attach
ment to do a job it was not designed to do.
• Use this band saw to cut only wood, wood like
products, plastics, non-ferrous and ferrous metals
(ferrous metals 1/16 inch thick or less).
16
