Checking system charge, Refrigerant charging, Air coil fan motor removal – Carrier 50RTG User Manual
Page 22: Thermistor, Control sensors
22
Checking System Charge —
Units are shipped with
full operating charge. If recharging is necessary:
1. Insert thermometer bulb in insulating rubber sleeve on
liquid line near filter drier. Use a digital thermometer for
all temperature measurements. DO NOT use a mercury
or dial-type thermometer.
2. Connect pressure gage to discharge line near compressor.
3. After unit conditions have stabilized, read head pressure
on discharge line gage.
NOTE: Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes before
checking charge.
4. From standard field-supplied Pressure-Temperature chart
for R-22, find equivalent saturated condensing
temperature.
5. Read liquid line temperature on thermometer; then
subtract from saturated condensing temperature. The dif-
ference equals subcooling temperature.
6. ADD refrigerant to raise the temperature or REMOVE
refrigerant (using standard practices) to lower the temper-
ature (allow a tolerance of ± 3° F), as required.
Refrigerant Charging
NOTE: Do not vent or depressurize unit refrigerant to atmo-
sphere. Remove and reclaim refrigerant following accepted
practices.
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal
Motor power wires need to be disconnected from motor
terminals before motor is removed from unit.
1. Shut off unit main power supply.
2. Loosen bolts on mounting bracket so that fan belt can be
removed.
3. Loosen and remove the 2 motor mounting bracket bolts
on left side of bracket.
4. Slide motor/bracket assembly to extreme right and lift out
through space between fan scroll and side frame. Rest
motor on a high platform such as a step ladder. Do not
allow motor to hang by its power wires.
TROUBLESHOOTING
(Fig. 10 and 11, and Table 22)
When troubleshooting problems with a WSHP, consider the
following.
Thermistor —
A thermistor may be required for single-
phase units where starting the unit is a problem due to low
voltage. See Fig. 10 for thermistor nominal resistance.
Control Sensors —
The control system employs 2 nom-
inal 10,000 ohm thermistors (FP1 and FP2) that are used for
freeze protection. Be sure FP1 is located in the discharge fluid
and FP2 is located in the air discharge. See Fig. 11.
To prevent personal injury, wear safety glasses and gloves
when handling refrigerant. Do not overcharge system —
this can cause compressor flooding.
Before attempting to remove fan motors or motor mounts,
place a piece of plywood over evaporator coils to prevent
coil damage.
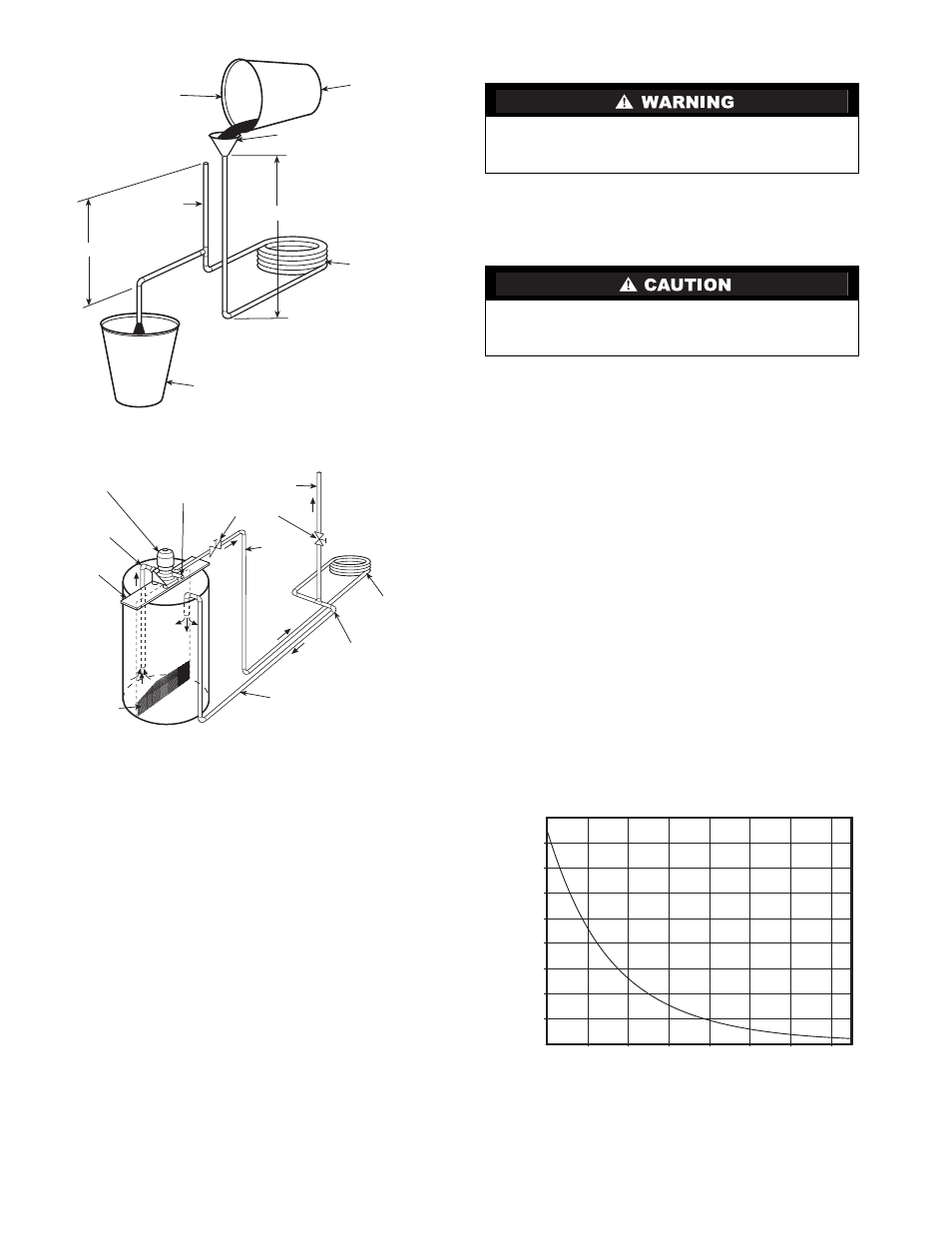
FILL CONDENSER WITH
CLEANING SOLUTION. DO
NOT ADD SOLUTION
MORE RAPIDLY THAN
VENT CAN EXHAUST
GASES CAUSED BY
CHEMICAL ACTION.
PAIL
FUNNEL
CONDENSER
PAIL
3’ TO 4’
VENT
PIPE
5’ APPROX
1”
PIPE
SUCTION
PUMP
SUPPORT
TANK
FINE MESH
SCREEN
RETURN
GAS VENT
PUMP
PRIMING
CONN.
GLOBE
VALVES
SUPPLY
1” PIPE
CONDENSER
REMOVE WATER
REGULATING VALVE
Fig. 8 — Gravity Flow Method
Fig. 9 — Forced Circulation Method
0.0
10.0
20.0
30.0
40.0
50.0
60.0
70.0
80.0
90.0
0.0
20.0
40.0
60.0
80.0
100.0
120.0
140.0
Temperature (F)
Resistance (kOhm)
Fig. 10 — Thermistor Nominal Resistance
