Figure 1, Sandy bridge-ep architecture for a poweredge r620 – Dell PowerEdge 1655MC User Manual
Page 8
Optimal BIOS settings for HPC with Dell PowerEdge 12
th
generation servers
8
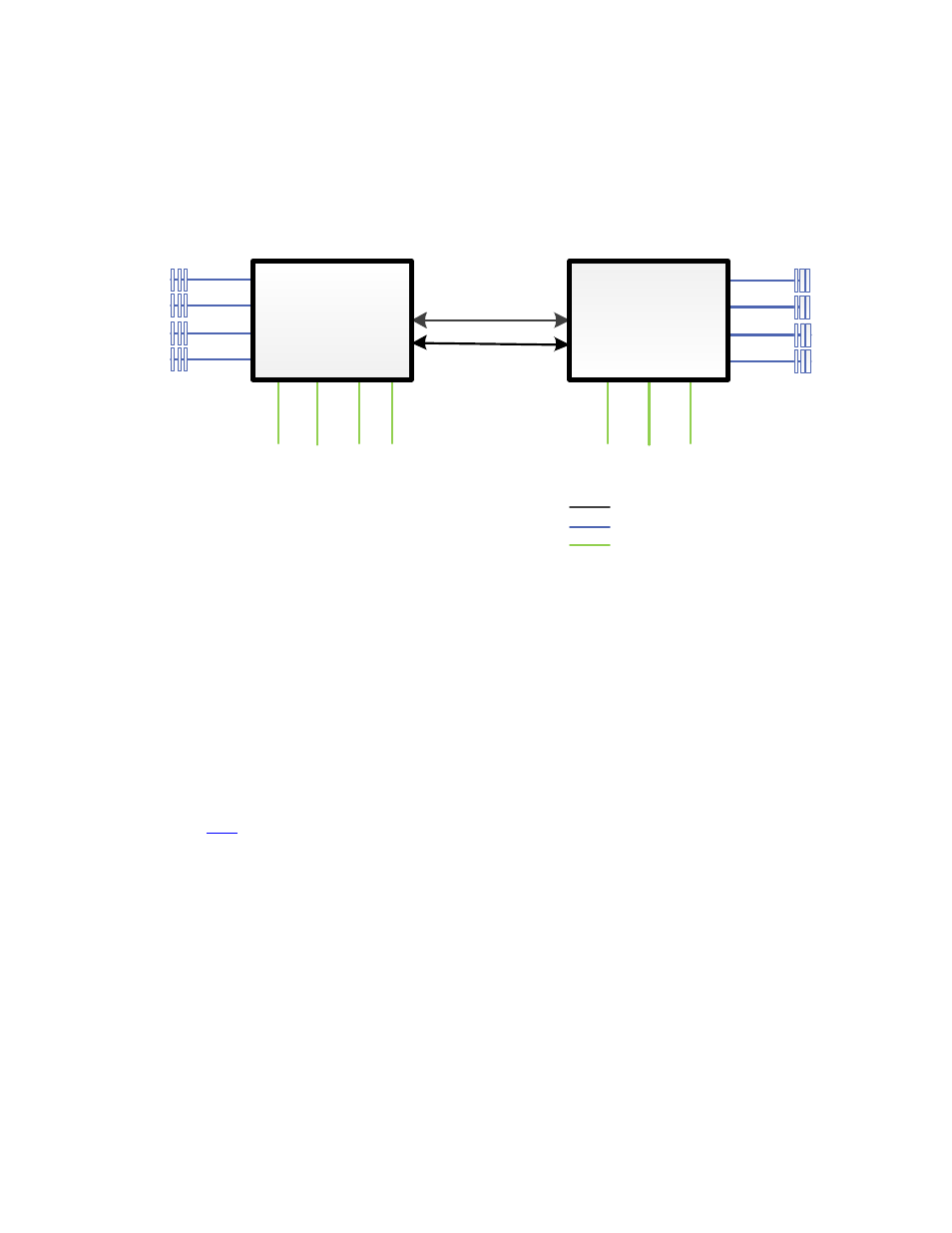
Like Westmere-EP, Sandy Bridge is also a NUMA-based architecture. Figure 1 shows a block diagram
of the Sandy Bridge-EP architecture. Each processor socket has an integrated memory controller. A
core’s access to the memory attached to its local memory controller is faster and has higher
bandwidth than access to the memory attached to the other, remote socket’s, memory controller.
Figure 1. Sandy Bridge-EP architecture for a PowerEdge R620
QPI links
8.0 GT/s
Four memory
channels
Four memory
channels
3 DIMMs
per
channel
3 DIMMs
per
channel
NDC
x8
Left
x16
Center
x8
Storage
x8
Right
x16
Right
x8
Center
x16
QPI
DDR3 memory channel
PCI-Gen3 lanes
Processor
Processor
With Westmere-EP, each memory controller had three DDR3 memory channels; Sandy Bridge-EP
increases that to four memory channels per controller. The maximum number of DIMMs per channel
remains three. Sandy Bridge supports up to eight cores per socket as opposed to the six cores per
socket on Westmere-EP.
The QPI links that connect the processors run at up to 8 GT/s with Sandy Bridge. The maximum
speed with Westmere was 6.4 GT/s. Sandy Bridge supports up to two QPI links whereas Westmere
supported only one. Additionally, Sandy Bridge-based processors can support DIMMs at speeds up to
1600 MT/s; Westmere’s limit was 1333MT/s. Sandy Bridge-EP also has a larger L3 cache of up to
20MB compared to Westmere-EP’s 12MB L3 cache. Intel introduced Advanced Vector Extensions
(AVX)
6
with its Sandy Bridge lineup. AVX provides a huge performance boost when compared to
Westmere or Nehalem, as it doubles the number of FLOPS/cycle. A detailed explanation of AVX can
be foun
Unlike Westmere, Sandy-Bridge-based processors also include an integrated PCI controller. This
makes access to the PCI slots non-uniform. Access to slots that are directly connected to the
socket’s PCI controller will be faster than to slots connected to the remote socket’s PCI controller.
Also new to Sandy-Bridge-based systems is PCI-Gen3 support. This is good news for HPC, as the
Mellanox FDR InfiniBand HCA can utilize this technology enhancement and run at Gen3 speeds.
Sandy Bridge-based servers come in three architectures: Sandy Bridge-EP, Sandy Bridge-EN and
Sandy Bridge-EP 4S. These architectures are compared in Table 2. Additionally Sandy Bridge-EN
processors operate at a lower wattage, with maximum Thermal Design Power (TDP) ranging from
50W to 95W. Sandy Bridge-EP processors have a Maximum TDP of up to 135W
7
. Other differences
include the number of PCI lanes and number of QPI lanes.
