Behringer SRC2000 User Manual
Page 8
8
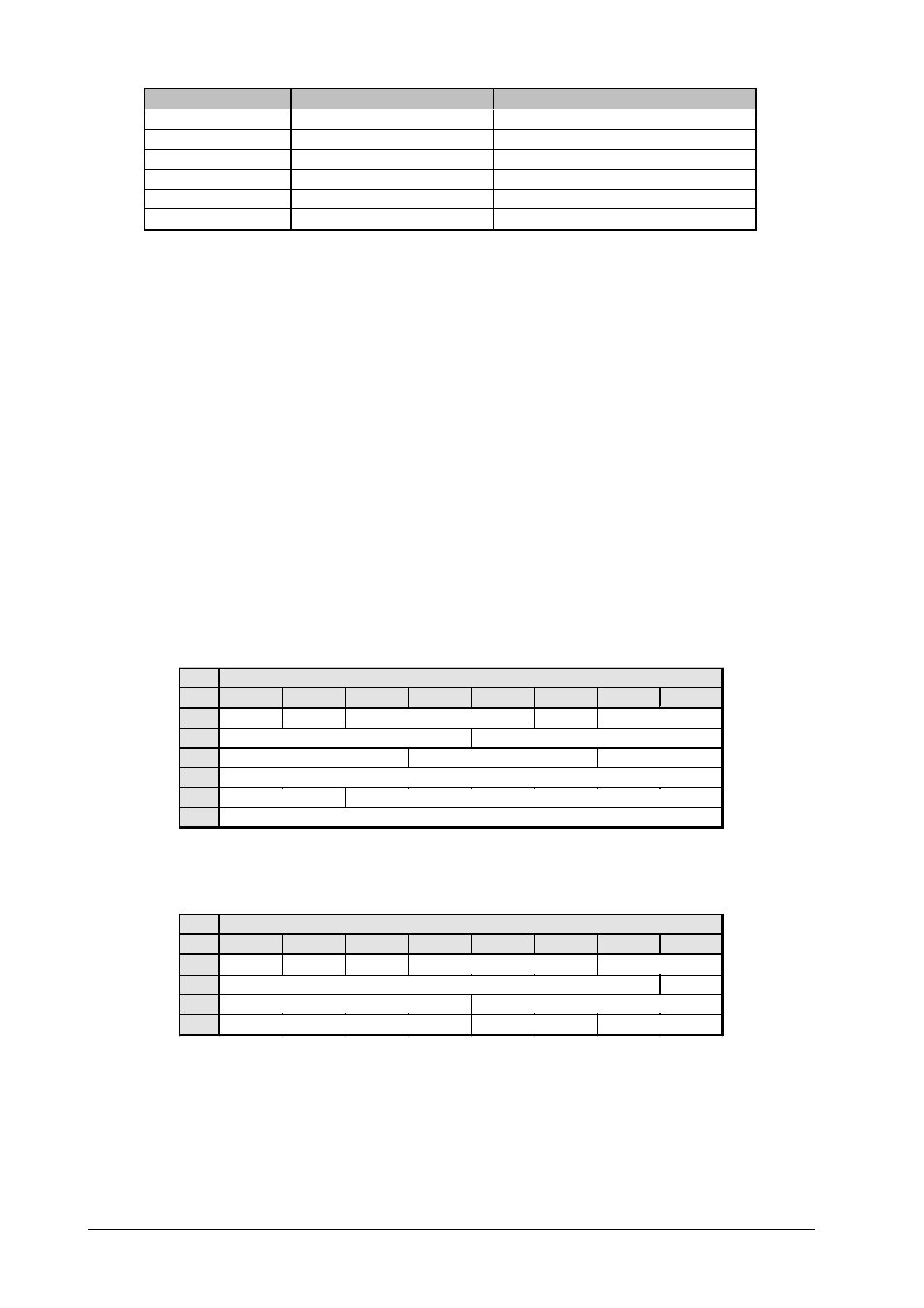
Type
AES / EBU
IEC 958 (SPDIF)
Connection
XLR
RCA / Optical
Mode of operation
Balanced
Unbalanced
Impedance
110 Ohms
75 Ohms
Level
0.2 V to 5 V pp
0.2 V to 0.5 V pp
Clock Accuracy
not defined
I: ± 50 ppm II: 0,1 % III: Variable Pitch
Jitter
± 20 ns
not defined
Tab. 1.1: Important characteristics of the AES/EBU and IEC 958 standards.
Unfortunately, these standards soon became watered-down, since a lot of devices simply did not provide
enough space for XLR jacks. In these units, either TRS jacks, mini jacks, or special adapters for Sub-D
connectors were employed.
Besides the electrical differences, the physical realizations of the interface concepts are slightly different.
The audio information is transmitted identically, meaning that in principle both formats are compatible. How-
ever, there are varying data blocks depending on which format is used. Table 1.2 represents an extract from
the data structure of the AES/EBU standard, table 1.3 shows the corresponding data in SPDIF format. It is
just the first bit that defines the following ones as a professional-type or consumer-type data stream.
It is obvious how the following bits differ in meaning. If a device such as a conventional DAT recorder features
only an SPDIF input, it will accept only SPDIF data. When receiving professional-type data, the data reception
is usually terminated since AES/EBU signals would lead to malfunctions in copy protection and emphasis if
processed by a consumer-type device.
The problem is common to many plug-in connections. A lot of devices do not switch off transmission, others
process both formats though equipped with just one interface type, and finally there are some that are simply
faulty, refusing to operate correctly though the correct identification is received. The ULTRAMATCH is able to
solve any of these problems. Whatever is received by the unit is transmitted from its output as a signal with
correct identification in the selected format.
Byte
Bit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
P/C
Audio?
Emphasis
Locked
Sampl. Freq.
1
Channel Mode
Use of User bits
2
Use of AUX bits
Length of audio sample
Reserved
3
Reserved for description of multichannel recording
4
Audio reference
Reserved
5
Reserved
Tab. 1.2: Identifying Information in Professional Format
Byte
Bit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
P/C
Audio?
Copy
Emphasis
Mode
1
Category code
Gen.St.
2
Source number
Channel number
3
Sampling frequency
Clock accuracy
Reserved
Tab. 1.3: Identifying Information in Consumer Format
1. INTRODUCTION
