2 standard error of calibration, 3 standard error of prediction, 4 the f-statistic – Metrohm Vision – Theory User Manual
Page 10: 5 bias, Standard error of calibration, Standard error of prediction, The f-statistic, Bias
8
▪▪▪▪▪▪▪
equal to zero (0). Formally R² indicates the fraction of total variance in the data set modeled by the
equation.
1.4.2
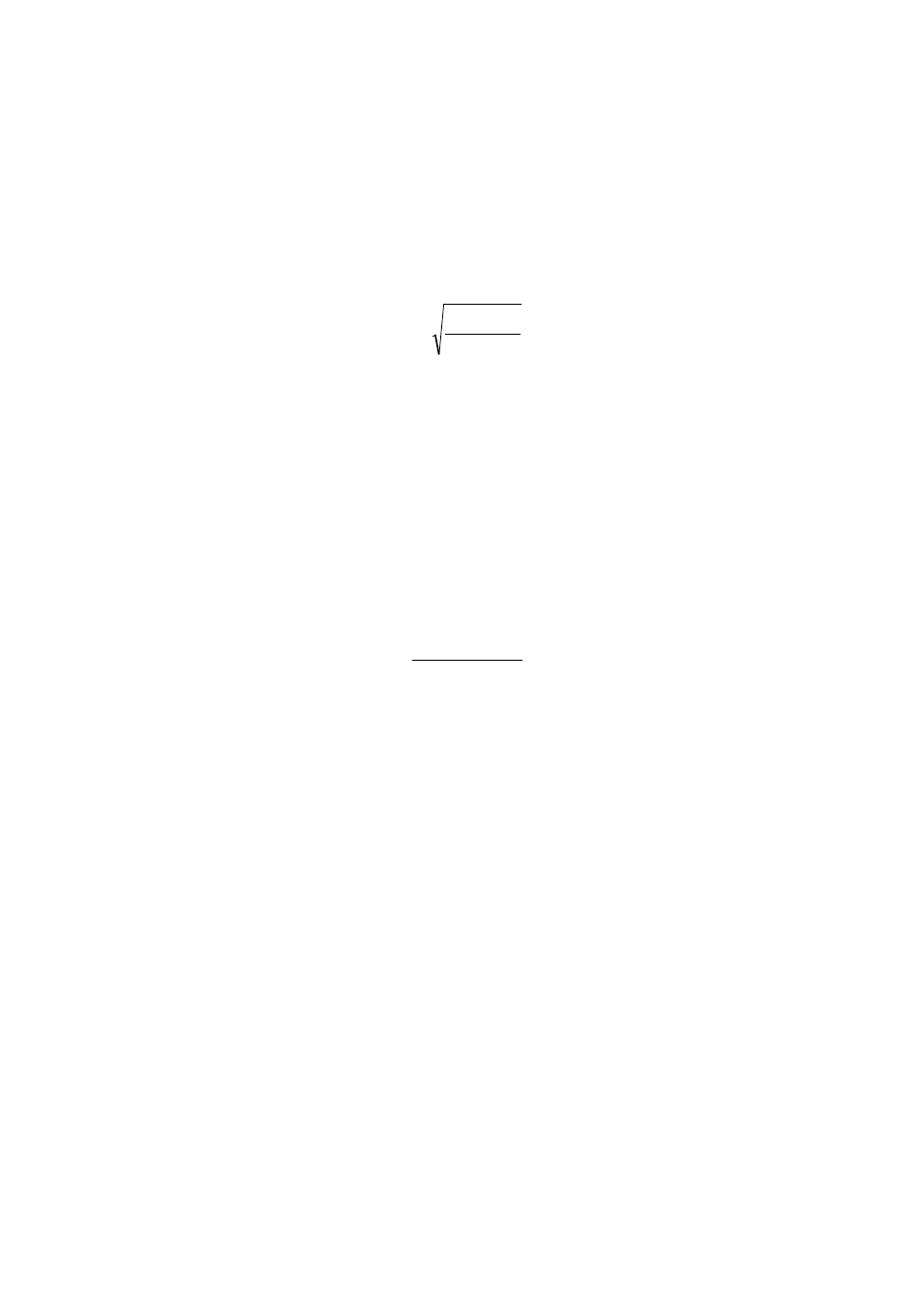
Standard Error of Calibration
Standard Error of Calibration (SEC) is a statistical parameter that indicates the upper limit of accuracy
in future predictions. When the calibration equation is applied to the training set itself, the SEC is
calculated from residuals f as:
SEC
f
N K
i
=
− −
∑
2
1
where N is the number of samples and K number of wavelengths or factors.
1.4.3
Standard Error of Prediction
The calculation for Standard Error of Prediction (SEP) is similar in form to that for SEC, except that f
now denotes residuals obtained from the prediction of the samples not used in the calibration, i.e. a
validation sample set. Also, the denominator of the expression does not include K. Usually SEP is
larger than SEC.
1.4.4
The F-Statistic
F value (or the F-test statistic) is defined is
F
R N K
K
R
=
− −
−
2
2
1
1
(
)
(
)
where N is the number of samples, K is the number of wavelengths or factors, and R² is the multiple
correlation coefficient. The F value is a useful estimate of goodness of fit of spectral and constituent
data. It can be also used as a tool for evaluation of how many wavelengths or factors should be used
in an equation, and for determining which samples to eliminate as outliers from the calibration set.
1.4.5
Bias
Bias is the average value of residuals calculated from constituent values of a prediction set. Bias value
close to zero (0) indicates that the deviations are distributed randomly. A bias value (either positive or
negative) that is large compared with typical constituent values indicates systematic error, e.g.
changes in the instrument, the condition of samples or the system being analyzed, or in the reference
analysis. In some cases, simple bias correction can be used to address this problem.
