Raid level descriptions – Dulce Systems PRO DQxc User Manual
Page 18
Page 35
PRO DQ
g2
Installation and User’s Manual
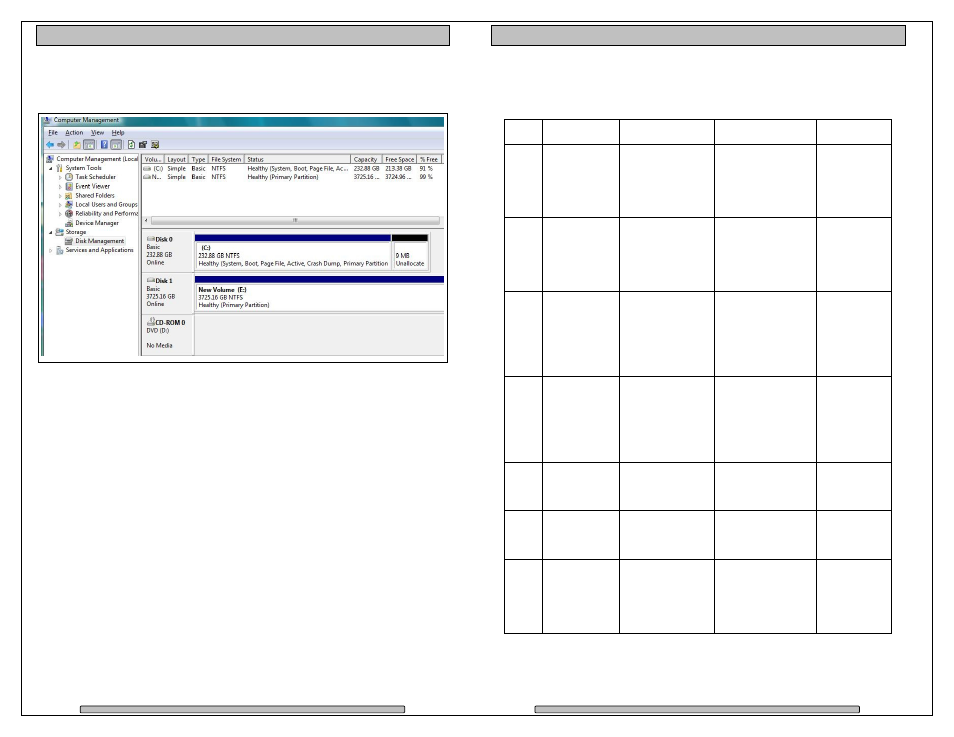
Right click the Unallocated segment and select New Simple Volume. Enter the
desired Volume Size, assign the desired Drive Letter or Path, check Perform a
Quick Format at the Format Partition screen.
Page 36
PRO DQ
g2
Installation and User’s Manual
8. RAID Level Descriptions
Although the RAID Controller supports a large variety of RAID Levels, RAID 0 or
RAID 3 are most commonly used for video and content creation purpose.
RAID
Level
Description
Advantage
Disadvantage
Ideal for
0
Striping.
Highest
performance.
No disk
redundancy, one
drive failure will
lose all data.
Highest
resolution
HD, 2K, and
maximum
multiple
streams.
1
Mirroring.
Highest
redundancy.
Less cost efficient
for redundancy,
loses ½ disk
capacity.
Data
protection is
paramount,
maximum
disk failure
protection.
3
Striping with a
dedicated
parity drive.
Efficient drive
redundancy, 1
drive used for
parity.
Loses 1 disk drive
capacity.
Well
balanced for
video
requiring
performance
and
redundancy.
5
Striping the
parity across
all drives.
Efficient drive
redundancy,
parity distributed
to all drives.
Loses 1 disk drive
capacity.
Well
balanced for
file server
requiring
performance
and
redundancy.
6
Striping with
two
dedicated
parity drives.
Double drive
redundancy, 2
drives used for
parity.
Loses 2 disk drive
capacity.
Mission
critical.
JBOD
Just a Bunch
of disks.
Each drive can
be accessed
individually from
operating system.
No redundancy.
Audio
applications.
RAID
+
Spare
A drive is set
aside as an
online hot
spare.
Automatic rebuild
of a failed drive.
Loses another
drive capacity. (In
addition to the
drive(s) needed for
the RAID level
selected.)
Minimizes
degraded
RAID level
exposure
time.
