Mechanical installation – Lenze SDSGS User Manual
Page 29
Mechanical installation
Holding brake (option)
Spring−applied holding brakes
l
29
BA 13.0011−EN 1.0
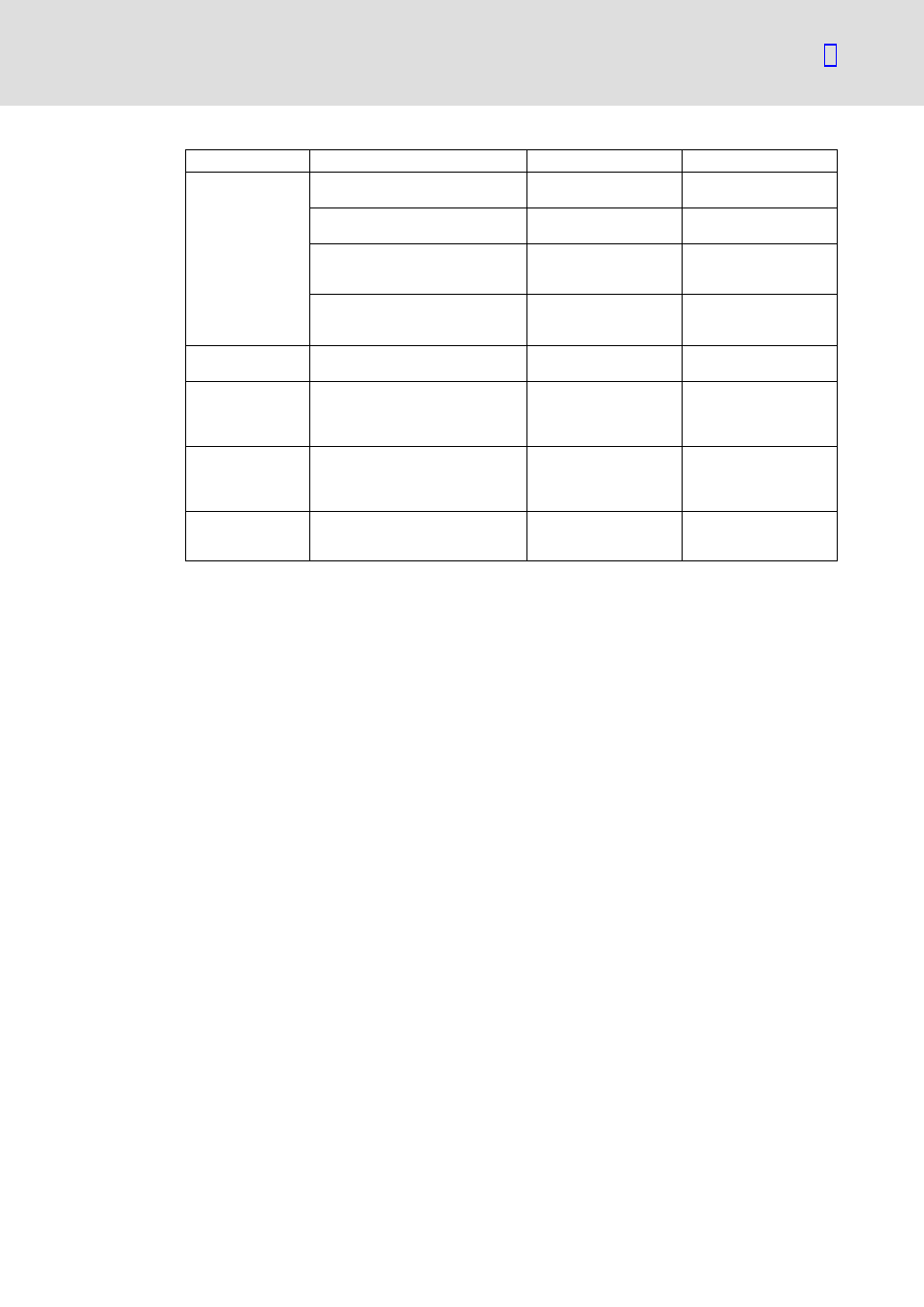
Component
Cause
Effect
Influencing factors
Friction lining
Emergency stops
Wear on the
friction lining
Applied friction energy
Overlapping wear when the drive
starts and stops
Active braking by the drive motor
with the help of the brake (quick
stop)
Starting wear if motor is mounted
in a position with the shaft vertical,
even if the brake is open
Number of start−stop
cycles
Armature plate and
flange
Rubbing of the brake lining
Running−in of armature
plate and flange
Applied friction energy
Teeth of the brake
rotor
Relative movement and impacts
between brake rotor and brake hub
Teeth wear (primarily at
the rotor end)
Number of start−stop
cycles,
level of the braking
torque
Armature plate
bracket
Load changes and impacts due to
reversal error during interaction
between armature plate, cap
screws and guide bolts
Armature plate, cap
screws and bolts are
deflected
Number of start−stop
cycles,
level of braking torque
Springs
Axial load cycle and shearing stress
on the springs due to radial
reversed error of the armature plate
Fatigue failure
of the springs
Number of switching
operations of the brake
