An ethernet connection to the internet – Allied Telesis AlliedWare AR440S User Manual
Page 6
Page 6 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs for Corporate Networks
How to configure VPNs in typical corporate
networks
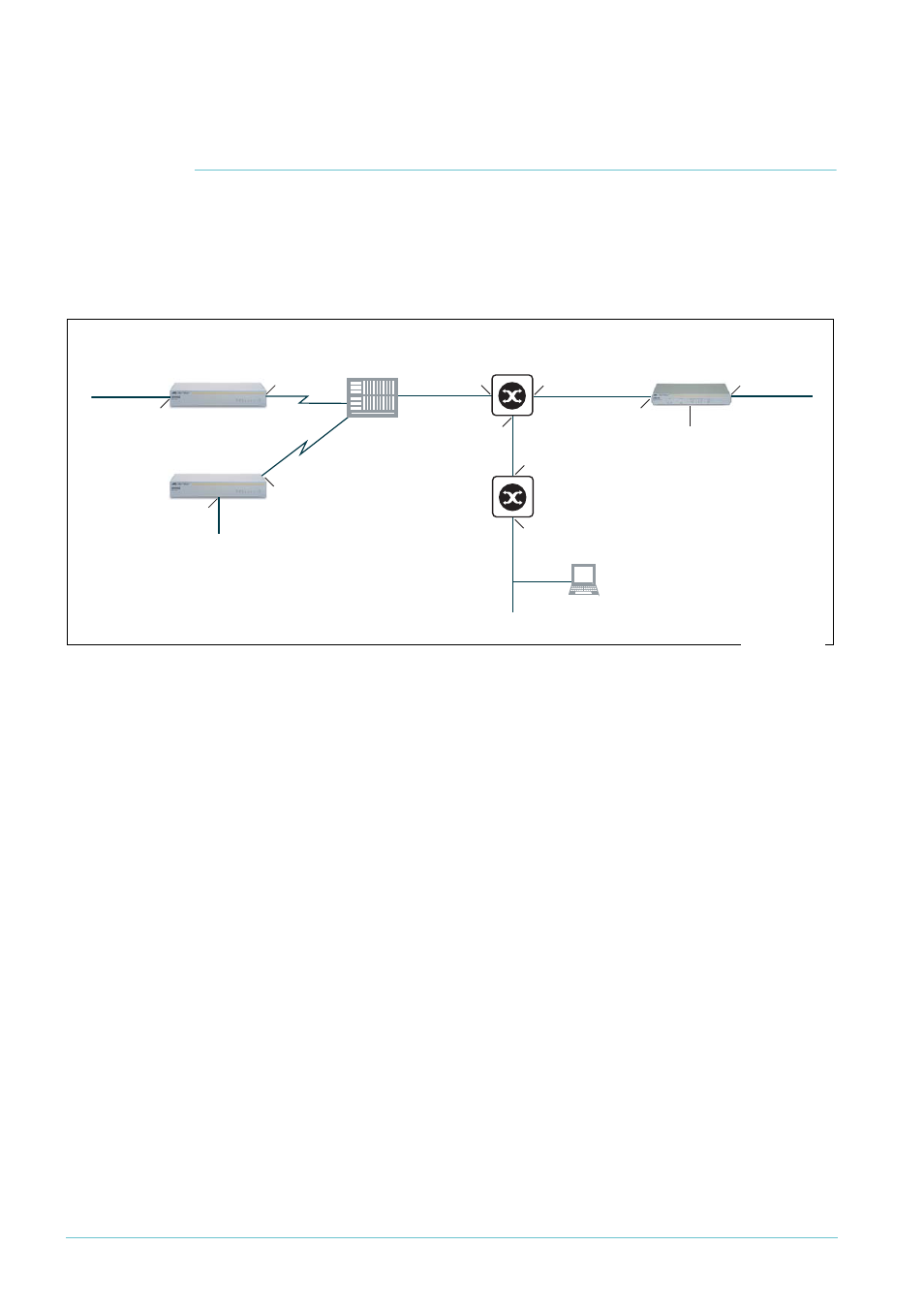
This section describes a typical corporate network using secure VPN. The network consists
of a headquarters (HQ) router and two branch office routers. The headquarters router is
acting as a VPN Access Concentrator, and allows for VPN access from either of the branch
office sites or from roaming laptop VPN clients. The network is illustrated in the following
figure.
Branch office 1 uses the PPPoA ADSL link type, and branch office 2 uses the PPPoEoA ADSL
link type. We have done this to illustrate these two commonly used ADSL link types. For
information about the ADSL link type you need, see your ADSL provider.
This How To Note gives you the commands for configuring each of the following:
1.
The headquarters VPN access concentrator router, which includes:
z
an ethernet connection to the Internet
z
a fixed Internet address. This means that the branch offices and the roaming VPN
clients have a known target for the headquarters end of the VPN
z
VPN access to and from branch office 1. This can be initiated from the headquarters
or branch office end. This is a site-to-site VPN and uses IPsec tunnel mode (see
"Background: NAT-T and policies" on page 4
z
VPN access from branch office 2. This can only be initiated from the branch office end,
because the branch office has a dynamically-assigned IP address. This also uses IPsec
tunnel mode.
z
VPN client access from roaming users on Windows 2000 and Windows XP. This is
provided by using IPsec transport mode with L2TP (see
z
optionally, prioritisation of voice (VoIP) traffic for these VPN clients by using Software
Quality of Service (SQoS). If the VPN clients use VoIP to establish voice calls via the
headquarters network, this helps maintain voice quality.
VLAN 1
192.168.141.254
222.222.222.1
222.222.222.254
200.200.200.254
192.168.140.254
211.211.211.1
192.168.200.254
physical address: 192.168.200.1
VPN tunnel address from pool: 192.168.143.1
211.211.211.254
200.200.200.1
ISP’s
router
headquarters
VPN access
concentrator
corporate
LAN
hotel’s NAT gateway
roaming VPN client
branch office 1
VPN router
branch office 2
dynamically
assigned
VLAN 1
192.168.142.254
Telco’s ADSL
exchange
Pool of addresses available
for roaming clients:
192.168.143.1-50
vpn-corporate.eps
