Cirrus Logic CDB4365 User Manual
Evaluation board for cs4365, Cdb4365, Features
Copyright
© Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2008
(All Rights Reserved)
Evaluation Board for CS4365
Features
Demonstrates recommended layout and
grounding arrangements
CS8416 receives S/PDIF, & EIAJ-340
compatible digital audio
Headers for external audio input for either PCM
or DSD
®
Requires only a digital signal source and power
supplies for a complete Digital-to-analog
converter system
Description
The CDB4365 evaluation board is an excellent means
for quickly evaluating the CS4365 24-bit, 48-pin, 6-
channel D/A converter. Evaluation requires an analog
signal analyzer, a digital signal source, a PC for control-
ling the CS4365 (only required for control port mode),
and a power supply. Analog line-level outputs are pro-
vided via RCA phono jacks.
The CS8416 digital audio receiver IC provides the sys-
tem timing necessary to operate the digital-to-analog
converter and will accept S/PDIF and EIAJ-340-com-
patible audio data. The evaluation board may also be
configured to accept external timing and data signals for
operation in a user application during system
development.
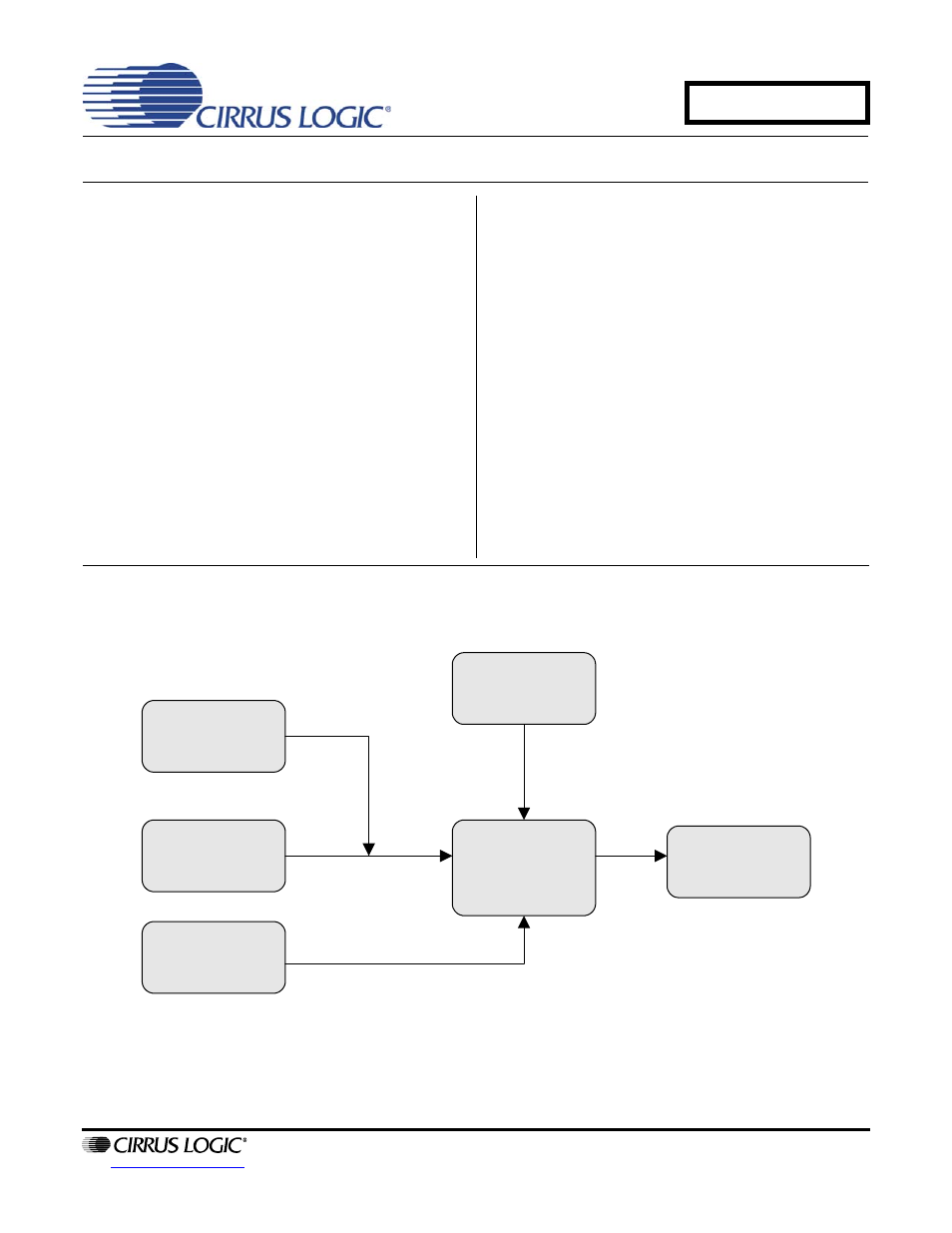
ORDERING INFORMATION
CDB4365
Evaluation Board
CS4365
Analog Outputs
and Filtering
Inputs for PCM
Clocks and Data
CS8416
Digital Audio
Interface
Hardware or
Software Board
Control
Inputs for DSD
Clocks and Data
MAY '08
DS670DB3
CDB4365
Document Outline
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- 1. CS4365 Digital-to-Analog Converter
- 2. CS8416 Digital Audio Receiver
- 3. Input for Clocks and Data
- 4. Input for Control Data
- 5. Power Supply Circuitry
- 6. Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling
- 7. Analog Output Filtering
- 8. Performance Plots
- Figure 1. FFT (48 kHz, 0 dB)
- Figure 2. FFT (48 kHz, -60 dB)
- Figure 3. FFT (48 kHz, No Input)
- Figure 4. FFT (48 kHz Out-of-Band, No Input)
- Figure 5. FFT (48 kHz, -60 dB Wideband)
- Figure 6. FFT (IMD 48 kHz)
- Figure 7. 48 kHz, THD+N vs. Input Freq
- Figure 8. 48 kHz, THD+N vs. Level
- Figure 9. 48 kHz, Fade-to-Noise Linearity
- Figure 10. 48 kHz, Frequency Response
- Figure 11. 48 kHz, Crosstalk
- Figure 12. 48 kHz, Impulse Response
- Figure 13. 48 kHz, Impulse Prefilter
- Figure 14. 48 kHz Dynamic Range
- Figure 15. FFT (96 kHz, 0 dB)
- Figure 16. FFT (96 kHz, -60 dB)
- Figure 17. FFT (96 kHz, No Input)
- Figure 18. FFT (96 kHz Out-of-Band, No Input)
- Figure 19. FFT (96 kHz, -60 db Wideband)
- Figure 20. FFT (IMD 96 kHz)
- Figure 21. 96 kHz, THD+N vs. Input Freq
- Figure 22. 96 kHz, THD+N vs. Level
- Figure 23. 96 kHz, Fade-to-Noise Linearity
- Figure 24. 96 kHz, Frequency Response
- Figure 25. 96 kHz, Crosstalk
- Figure 26. 96 kHz, Impulse Response
- Figure 27. 96 kHz, Impulse Prefilter
- Figure 28. Dynamic Range 96 kHz
- Figure 29. FFT (192 kHz, 0 dB)
- Figure 30. FFT (192 kHz, -60 dB)
- Figure 31. FFT (192 kHz, No Input)
- Figure 32. FFT (192 kHz Out-of-Band, No Input)
- Figure 33. FFT (192 kHz, -60 dB Wideband)
- Figure 34. FFT (IMD 192 kHz)
- Figure 35. 192 kHz, THD+N vs. Input Freq
- Figure 36. 192 kHz, THD+N vs. Level
- Figure 37. 192 kHz, Fade-to-Noise Linearity
- Figure 38. 192 kHz, Frequency Response
- Figure 39. 192 kHz, Crosstalk
- Figure 40. 192 kHz, Impulse Response
- Figure 41. 192 kHz, Impulse Prefilter
- Figure 42. Dynamic Range 192 kHz
- 9. CDB4365 Schematics
- Figure 43. System Block Diagram and SIgnal Flow
- Figure 44. CS4365
- Figure 45. Analog Outputs A1 - B1
- Figure 46. Analog Outputs A2 - B2
- Figure 47. Analog Outputs A3 - B3
- Figure 48. CS8416 S/PDIF Input
- Figure 49. PCM Input Header and Muxing
- Figure 50. DSD Input Header
- Figure 51. Control Input
- Figure 52. Power Inputs
- Figure 53. Silkscreen Top
- Figure 54. Top Side
- Figure 55. Bottom Side
- 10. Revision History
