Charging details, 1 charging algorithm, 2 maximum power point tracking – Campbell Scientific PS150/CH150 12 V Charging Regulators User Manual
Page 21: Charging algorithm, Maximum power point tracking
PS150/CH150 12 V Charging Regulators
6. Charging Details
6.1 Charging Algorithm
The PS150/CH150 offers both Continuous and Solar charging inputs. The
Continuous charging input has a maximum value of 1.1 A DC to help protect
AC/AC transformers and AC/DC converters. The 3.6 ADC typical current
limit of the PS150/CH150 Solar charging input is well suited for 70 W solar
panels. Typical Continuous charging inputs would be AC/AC transformers or
AC/DC converters in which a charge voltage is continuously applied except for
line power outages.
The PS150/CH150 uses a float charging algorithm for either the Continuous or
Solar charging inputs. This charging method can charge a battery indefinitely
without overcharging a battery.
6.2 Maximum Power Point Tracking
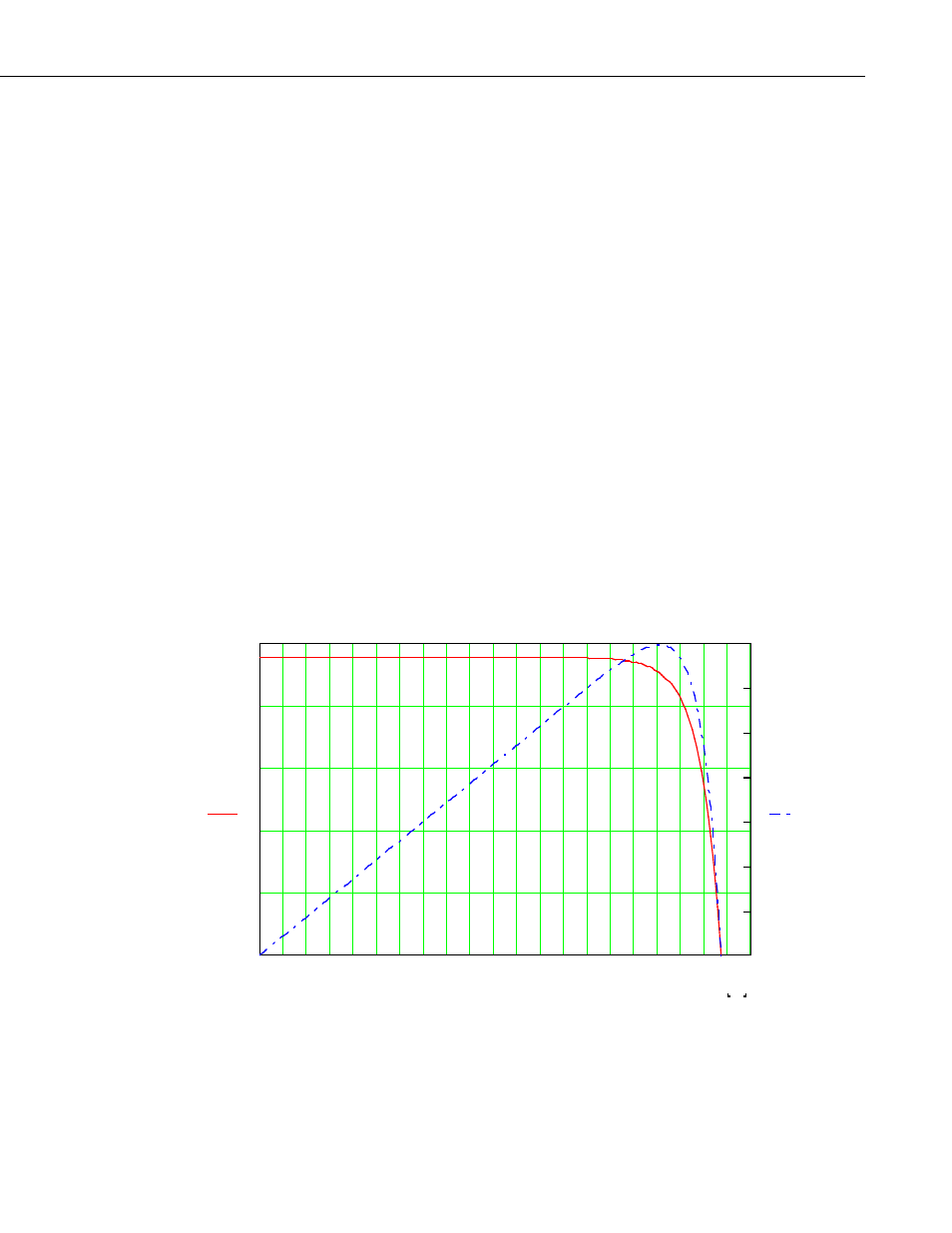
The current and power versus voltage for a 70 W solar panel are illustrated in
FIGURE 6-1. As can be seen from the figure, a Maximum Power Point of
operation exists for solar panels. Adjusting the load on the solar panel so it
operates at this Maximum Power Point is referred to as Maximum Power Point
Tracking (MPPT). MPPT is beneficial when insufficient power is available
from the charge source, which is the case during current limited charging. The
somewhat noisy charging current and voltage during the initial current limited
charging stage is due to the MPPT algorithm of the PS150/CH150 searching
for the maximum power point of the associated solar panel.
FIGURE 6-1. 70 W solar panel I – V and power characteristics
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
0
0.9
1.8
2.7
3.6
4.5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Voltage (Volts)
C
ur
re
nt
(A
m
ps
)
Po
w
er
(W
at
ts)
4.5
0
I
m
70
0
P
m
21
0
Vc
m
13
