4 camera files, 3 programming, 1 the cardout() instruction – Campbell Scientific NL115 Ethernet Interface and CompactFlash Module User Manual
Page 26: Cardout(stopring, size), 2 program examples, 1 ring mode, Camera files, Programming, The cardout() instruction, Program examples
NL115 Ethernet and CompactFlash
®
Module
7.2.4 Camera Files
JPEG images taken by a CC640 digital camera (retired) connected to the
datalogger can be stored to the CF card rather than CPU memory. This is done
by configuring the PakBus setting
Files Manager for the datalogger. This can
be done using Device Configuration Utility or PakBus Graph.
7.3 Programming
7.3.1 The CardOut() Instruction
The
CardOut() instruction is used to send data to a CF card. CardOut() must
be entered within each
DataTable() declaration that is to store data to the CF
card. Data is stored to the card when a call is made to the data table.
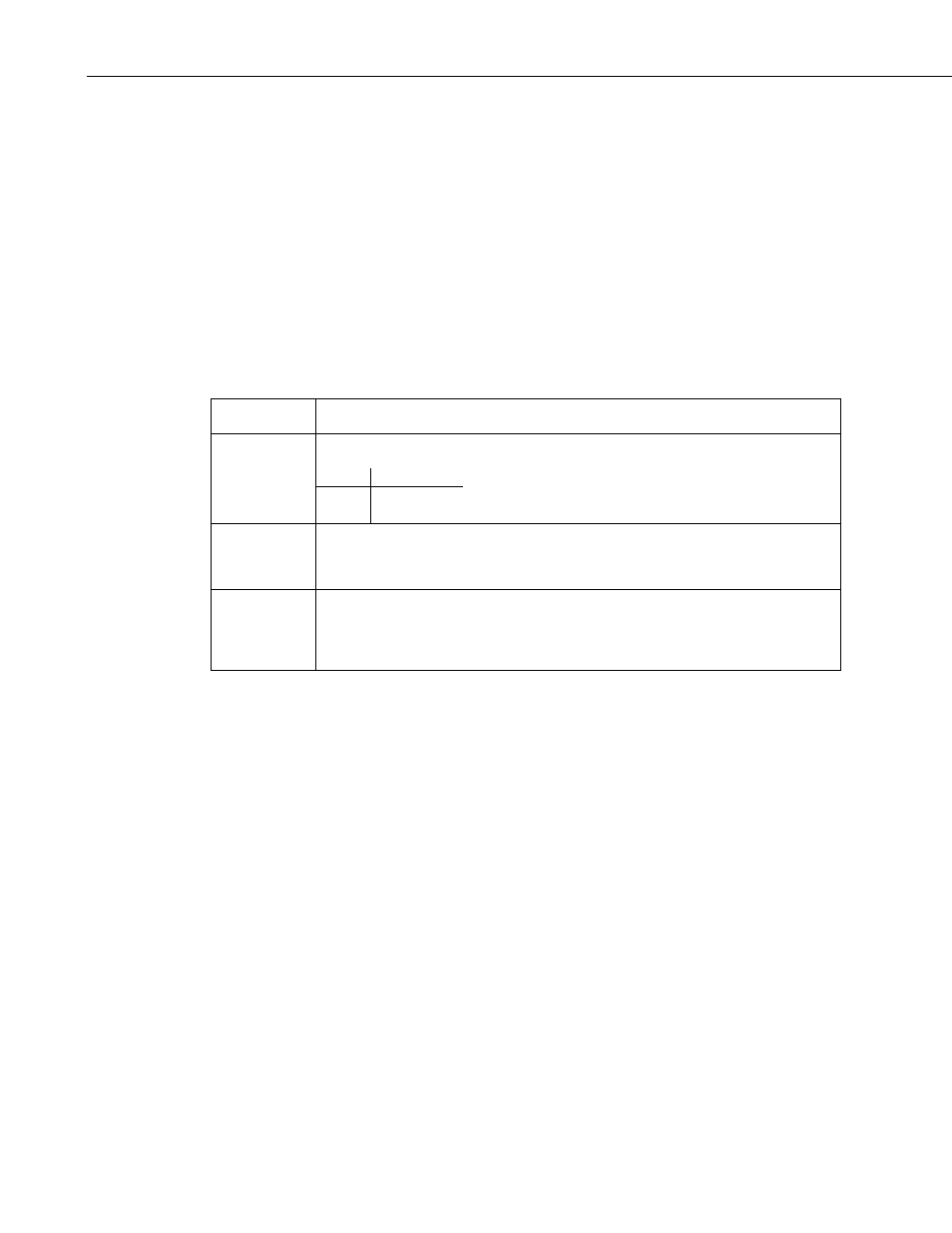
CardOut(StopRing, Size)
Parameter
Data Type
Enter
StopRing
Constant
A code to specify if the Data Table on the CF card is fill-and-stop or ring (newest data
overwrites oldest).
Value Result
0
Ring
1
Fill and stop
Size
Constant
The size to make the data table. The number of data sets (records) for which to allocate
memory in the CF card. Each time a variable or interval trigger occurs, a line (or row) of
data is output with the number of values determined by the output instructions within the
table. This data is called a record.
Note
Enter –1000 and the size of the table on the card will match the size of the
internal table on the datalogger. Enter any other negative number and all
remaining memory (after creating any fixed-size data tables) will be allocated to
the table or partitioned among all tables with a negative value for size. The
partitioning algorithm attempts to have the tables full at the same time.
7.3.2 Program Examples
7.3.2.1 Ring Mode
The following program outputs the maximum and minimum of the panel
temperature to the card once a second. The first parameter of the
CardOut()
instruction is 0, which sets the table on the card to ring mode. The second
parameter is negative, so all available memory on the card will be allocated to
the data table. Once all available memory is used, new data will begin
overwriting the oldest.
20
