3 calibration equations, Calibration equations – Campbell Scientific CS616 and CS625 Water Content Reflectometers User Manual
Page 33
CS616 and CS625 Water Content Reflectometers
7.3 Calibration Equations
TABLE 7-1 lists the calibration coefficients derived in the Campbell Scientific
soils laboratory. Both linear and quadratic forms are presented. The choice of
linear or quadratic forms depends on the expected range of water content and
accuracy requirements. These coefficients should provide accurate volumetric
water content in mineral soils with bulk electrical conductivity less than
0.5 dS m
-1
, bulk density less than 1.55 g cm
-3
, and clay content less than 30%.
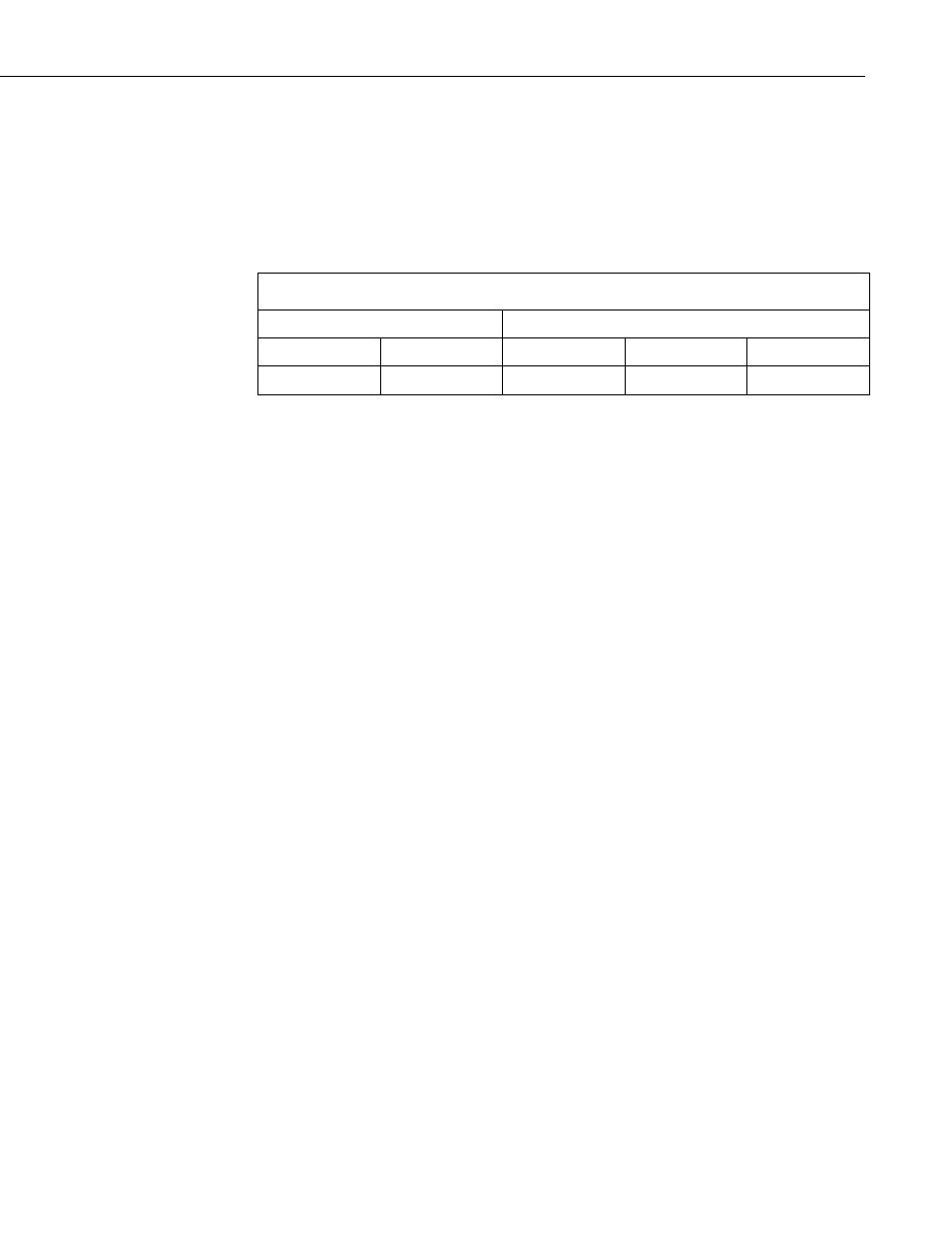
TABLE 7-1. Standard calibration coefficients for linear and quadratic forms.
Linear
Quadratic
C0
C1
C0
C1
C2
–0.4677
0.0283
–0.0663
–0.0063
0.0007
The linear equation is
VWC = -0.4677+0.0283*period .
The quadratic equation is
VWC = -0.0663 - 0.0063*period + 0.0007*period
2
.
Period is in microseconds. The result of both calibration equations is
volumetric water content on a fractional basis. Multiply by 100 to express in
percent volumetric water content.
FIGURE 7-3 shows the difference between the linear and quadratic calibration
forms over the typical range. A CS616/CS625 output period of 16
microseconds is about 1.2% VWC and 32 microseconds is 44.9%. The linear
calibration is within ± 2.7% VWC of the quadratic. The linear calibration
underestimates water content at the wet and dry ends of the range and
overestimates it by up to about 2.6 % VWC at about 20% VWC.
27
