HP XP Racks User Manual
Page 28
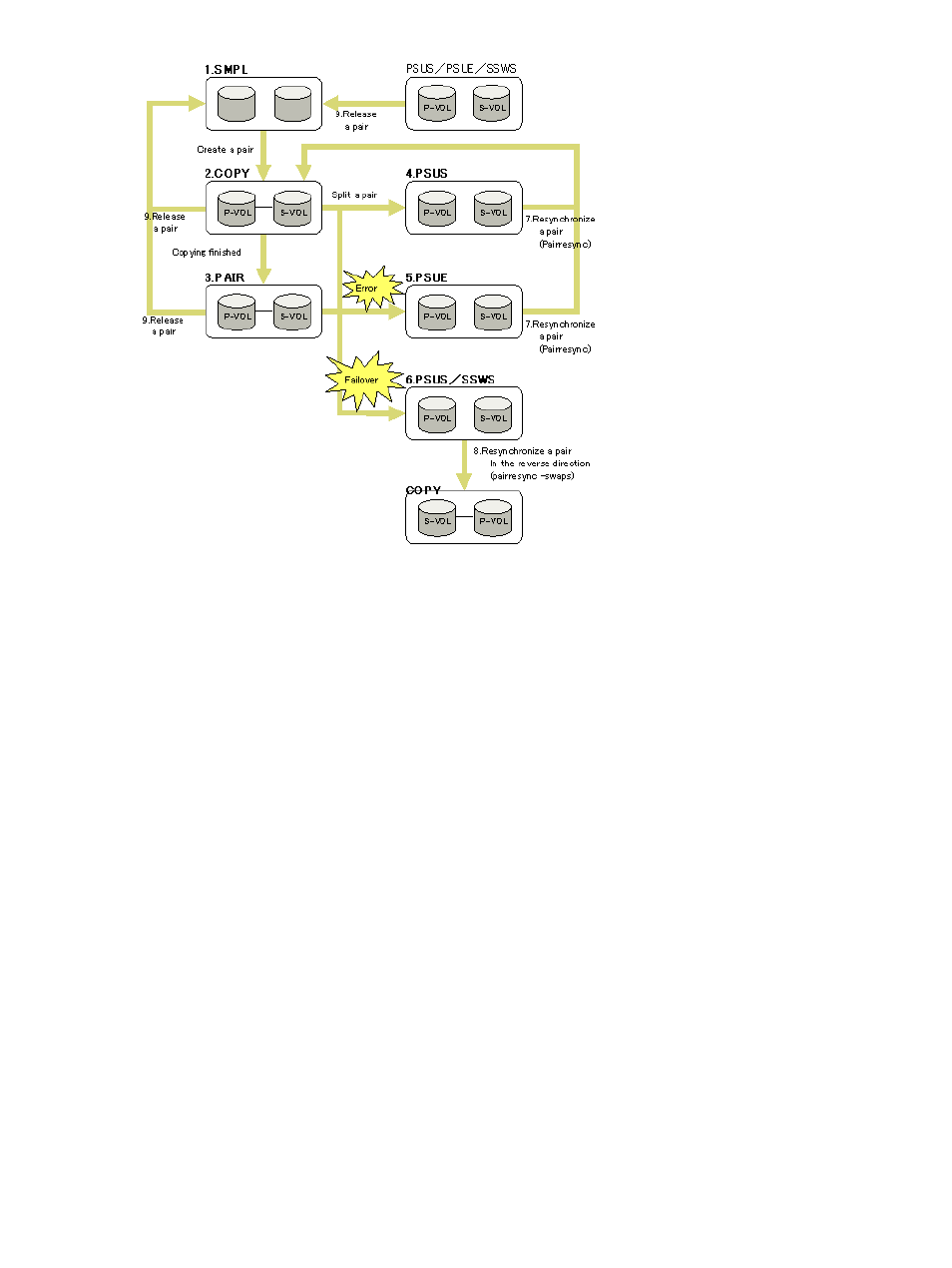
1.
When a volume is not in an ESAM pair, its status is SMPL.
2.
When you create an ESAM pair using SMPL volumes, the status of the P-VOL and the S-VOL
changes to COPY while the system copies the data.
3.
A stable synchronized pair has the status PAIR.
4.
When you split a pair, the status of the P-VOL and the S-VOL changes to PSUS (pair
suspended-split, split by command).
5.
When the MCU cannot maintain in synch the P-VOL and the S-VOL because of an error, the
status of the P-VOL and the S-VOL changes to PSUE (pair suspended-error, split due to an
error). If the MCU cannot communicate with the RCU, the status of the S-VOL stays PAIR.
6.
When a failover occurs in the storage system, the status of the S-VOL changes to SSWS, and
the status of the P-VOL changes to PSUS.
7.
When you resynchronize the pair in PSUS or PSUE status (see No.4 and No.5), the status of
the P-VOL and the S-VOL changes to COPY.
8.
When you resynchronize the pair with the S-VOL in SSWS status (see No.6), (using the RAID
Manager pairresync -swaps command on the S-VOL), the P-VOL and the S-VOL swap,
and the pair status changes to COPY.
9.
When you release a pair, the status of the P-VOL and the S-VOL changes to SMPL.
What pairs information can you view and where is it?
You can monitor the following information for pairs:
•
Percentage of synchronization (Sync. column)
•
Pair details (Detailed Information dialog box)
Pair status
◦
◦
Split types
◦
Suspend types
28
Working with volume pairs
