High availability, Scalability using cluster of brokers – HP Integrity NonStop H-Series User Manual
Page 11
is active and slave instance is on stand by. When the master instance fails, the slave instance takes
over the responsibilities of the master
Cluster I/O Protocols (CIP) subsystem:
Every broker in the cluster starts a transport connector configured for parallel I/O using the CIP
subsystem to listen on the same IP address and port. All client applications connect to this port.
This subsystem facilitates load balancing of the connections across all the brokers.
Producer:
Producers are the JMS clients that send messages.
Consumer:
Consumers are the JMS clients that receive messages.
High availability
In NSMQ, high availability is achieved using a master-slave configuration.
All the brokers in the master-slave cluster have the same configuration and compete to acquire the
lock on a data file during startup. The broker acquiring the lock starts all the network and transport
connectors and becomes the master, and the remaining instances become slave brokers. When
the master broker fails or shuts down, one of the slaves acquire the exclusive lock on the data file
and becomes the new master broker. The clients can use the failover protocol for automatic
reconnection to the new master broker.
The auto restart feature of TS/MP ensures that the failed master process is restarted again. The
auto restarted master process becomes the new slave, thus ensuring high availability is achieved.
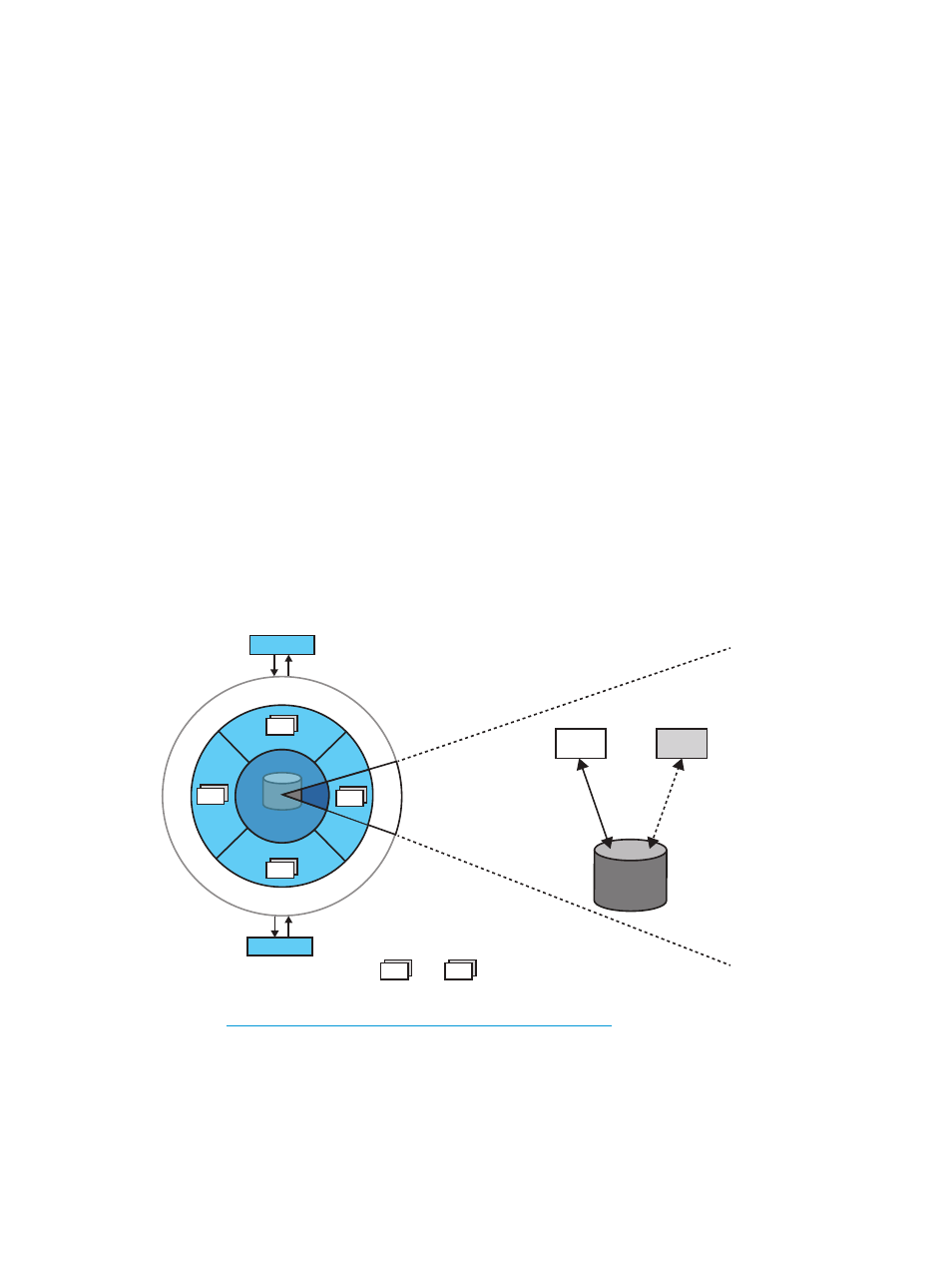
represents a master-slave configuration in NSMQ.
Figure 2 Master-slave configuration
N
onS
top C
luster I/O Proto
cols
Producer
Consumer
Bn
B1
B3
B2
SQL/MX
Database
tc
p:/
/ ostnam e IP Address> : ort N o. > B2 B2’ Master Slave SQL/MX Database B2 Bn B1 : Brokers ...... See also Scalability using cluster of brokers In NSMQ, scalability can be achieved by adding brokers to the cluster to handle additional load. High availability 11
Any number of brokers can be added or removed from the cluster without affecting the services.
Proper removal of the broker requires the cluster to be brought down. When more brokers are
added, the CIP subsystem facilitates load balancing across all brokers. Since every broker is
connected to every other broker in the cluster, all the messages are accessible to all the brokers.
If a broker shuts down or fails, the load is balanced among the remaining brokers in the cluster.
