Port triggering – Actiontec electronic MI408 User Manual
Page 56
54
Actiontec Broadband Router User Manual
55
Chapter 5 Configuring the Router’s Security
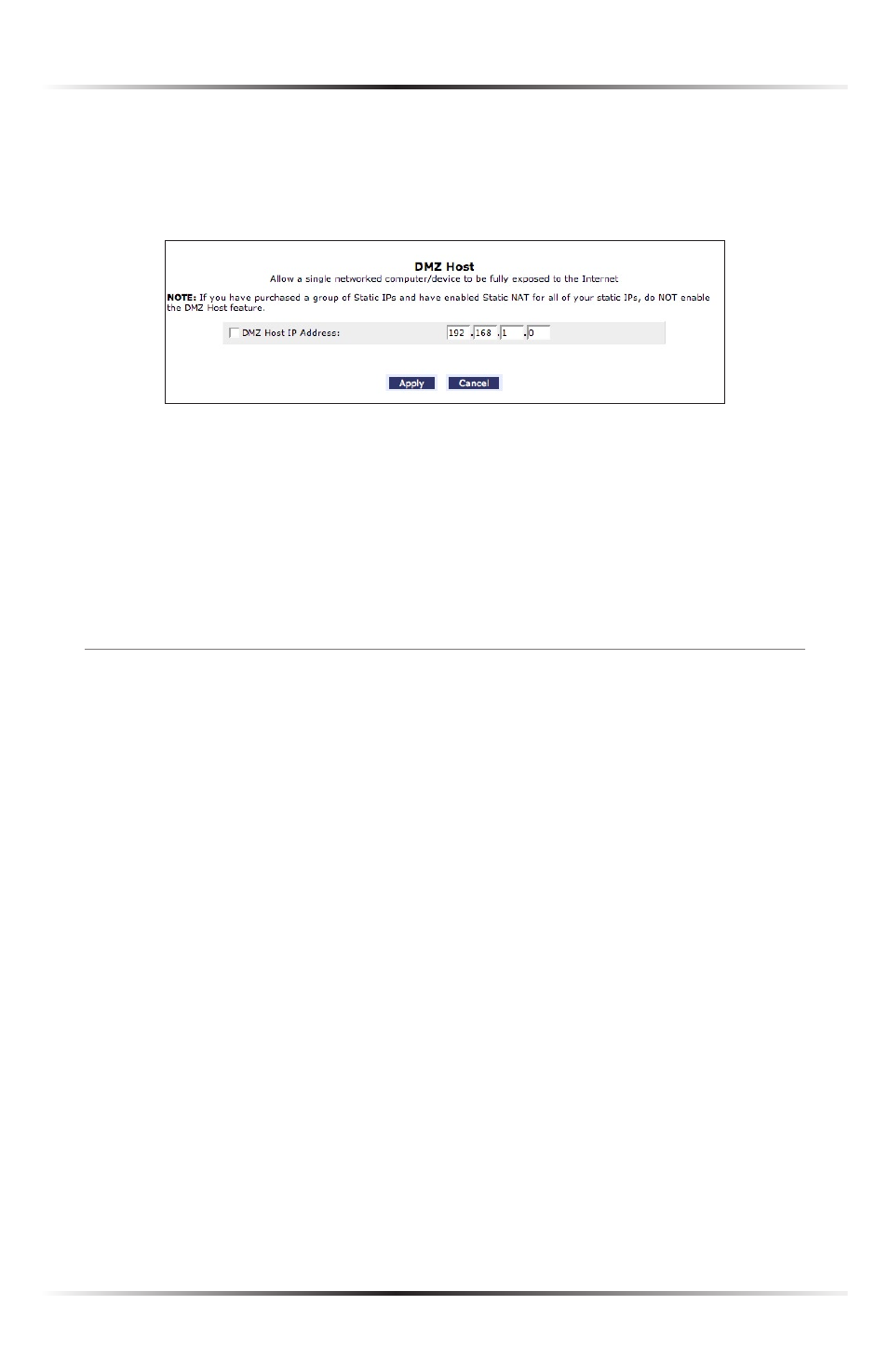
To designate a local computer as a
DMZ
host:
1. Select DMZ Host from the left side of any Security screen. The “
DMZ
Host”
screen appears.
2. Click in the “
DMZ
Host
IP
Address” check box, then enter the
IP
address of the
computer to be designated as a
DMZ
host. Note that only one network com-
puter can be a
DMZ
host at any time.
3. Click Apply.
Click in the “
DMZ
Host
IP
Address” check box again to disable the
DMZ
host.
Port Triggering
Port triggering can be used for dynamic port forwarding configuration. By setting
port triggering rules, inbound traffic is allowed to arrive at a specific network host
using ports different than those used for the outbound traffic. The outbound traf-
fic triggers which ports inbound traffic is directed.
For example, a gaming server is accessed using
UDP
protocol on port 2222. The
gaming server responds by connecting the user using
UDP
on port 3333 when
starting gaming sessions. In this case, port triggering must be used, since it con-
flicts with the following default firewall settings:
• The firewall blocks inbound traffic by default.
• The server replies to the Router’s
IP
, and the connection is not sent back to
the host, since it is not part of a session.
To resolve the conflict, a port triggering entry must be defined, which allows
inbound traffic on
UDP
port 3333, only after a network host generated traffic to
UDP
port 2222. This results in accepting the inbound traffic from the gaming
server, and sending it back to the network host which originated the outgoing traf-
fic to
UDP
port 2222.
