Pressure & air flow charts – MAHLE RTI ELF-1 User Manual
Page 9
Page 6
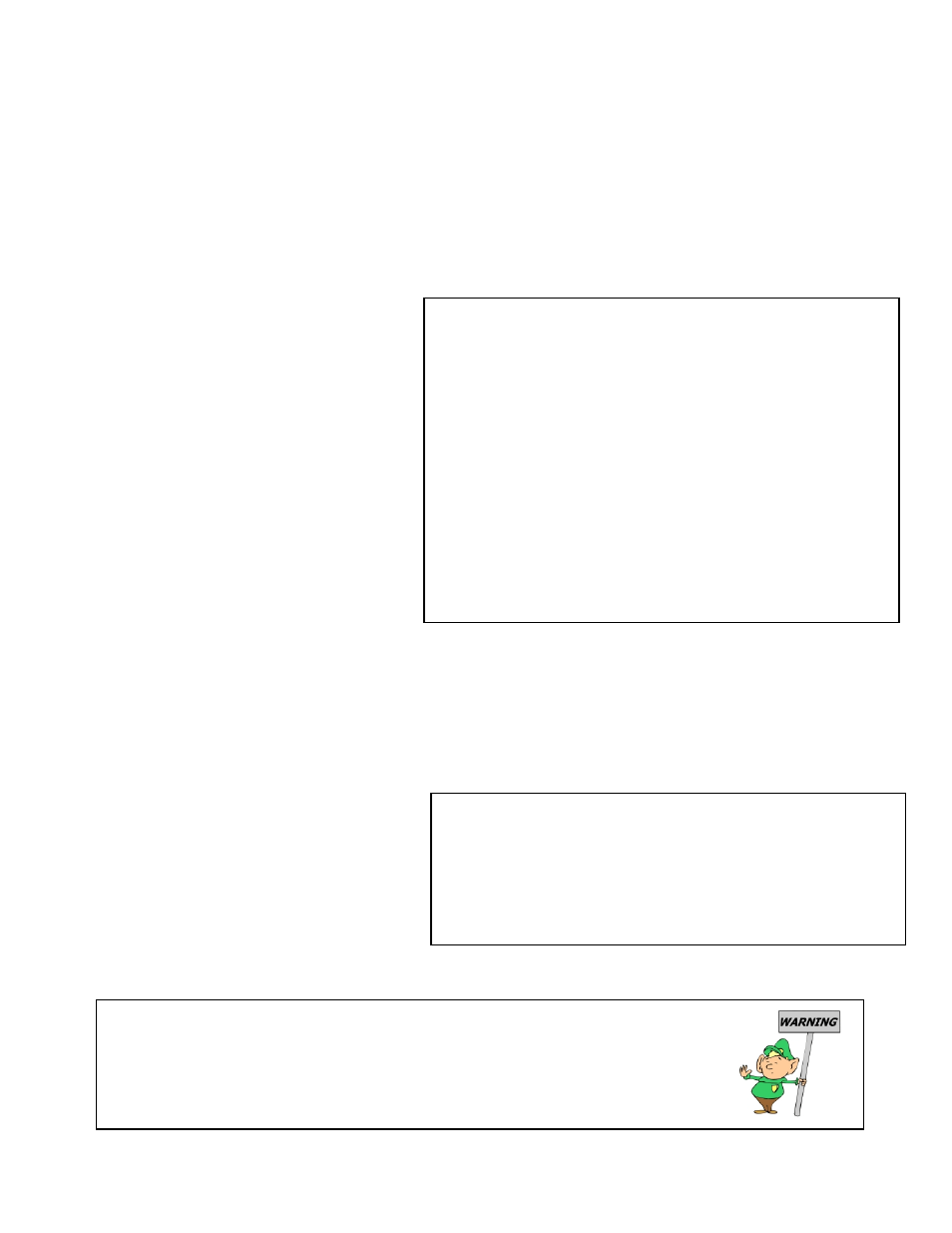
Leak Chart 1 provides a better idea of how air flow
and pressure are influenced by the size of the leak.
This chart represents a 0.020 inch diameter leak,
which is so small, it will not register on the Flow
Meter until 4 PSI is applied. At this point it registers
just 1 SCFH (Standard Cubic Feet per Hour).
As the applied pressure is increased, so does the air
flowing through the leak increase.
Unfortunately, such a leak has the effect of
dissipating fog and making it difficult to see. It’s
there, but very fine. The white light will be helpful in
this scenario.
PRESSURE & AIR FLOW CHARTS
The following information is an outline of the relationships between the flow of air, the pressure applied
and the size of a leak that influences them.
In all cases assume that any leak size described is the equivalent area of the diameter of the leak. Of
course few leaks are round, but all have an open area of leakage.
LEAK CHART 1
LEAK SIZE
PSI
SCFH
0.020
1
0
0.020
2
0
0.020
3
0
0.020
4
1
0.020
5
2
0.020
6
3
0.020
7
4
0.020
8
5
0.020
9
6
0.020
10
7
0.020
11
8
0.020
12
10
0.020
13
12
0.020
14
13
0.020
15
15
LEAK CHART 2
LEAK SIZE
PSI
SCFH
0.040
1
9
0.040
2
12
0.040
3
16
0.040
4
18
0.040
5
20
The above Leak Charts are for illustration of flow rates at different
pressures for two different sizes of leak.
Do not increase pressure beyond the maximum rated pressure of the
vehicle component being tested.
Leak Chart 2 shows the increase in air flow for a
0.040 inch leak.
Note the large difference in air flow, even though the
diameter of the leak is just doubled. The actual flow
increases dramatically.
