Real-time dust monitoring principles – SKC Limited EPAM-7500 User Manual
Page 14
1-6
Real-Time Dust Monitoring Principles
Principles
•
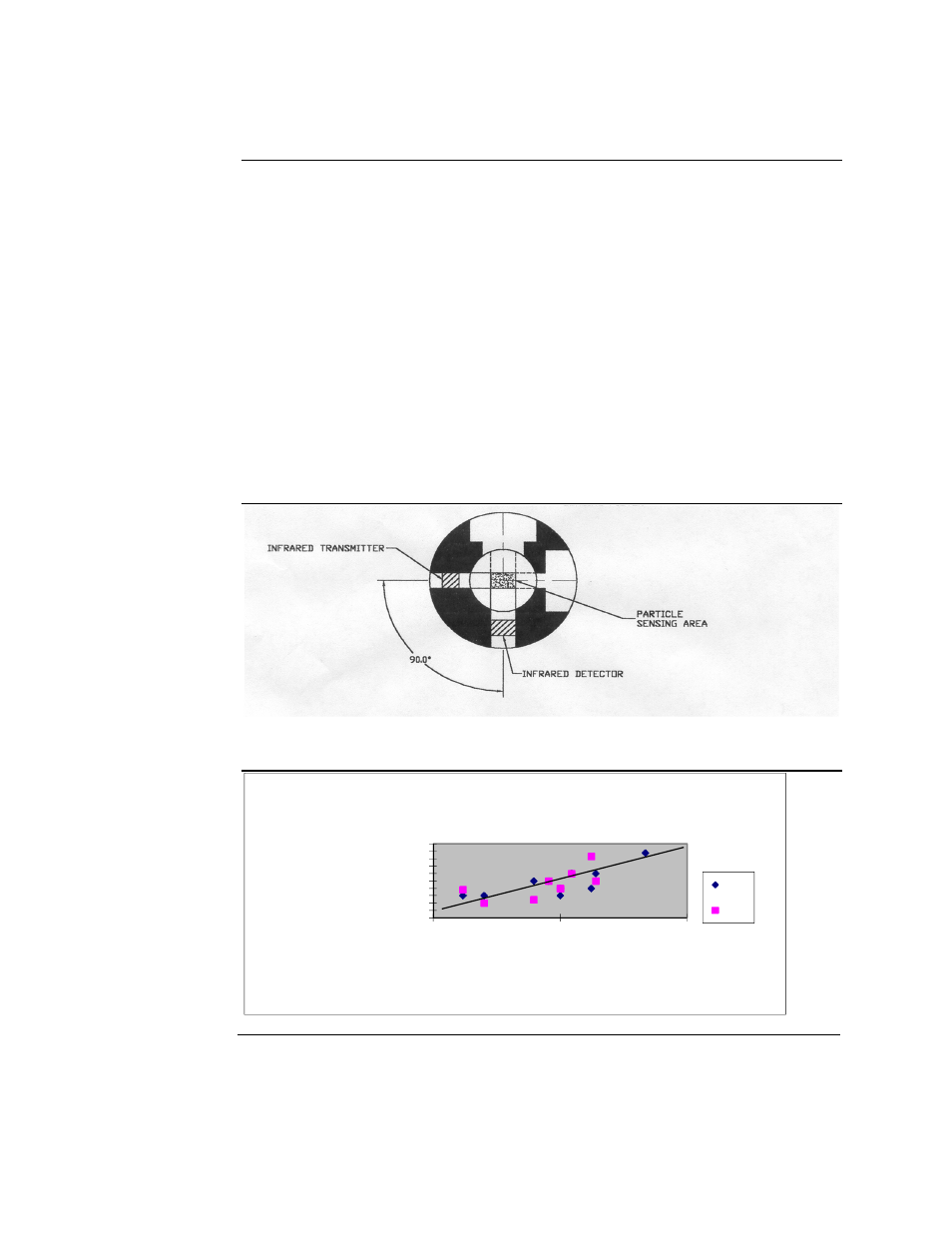
The EPAM-7500 uses the principle of near-forward light scattering of an
infrared radiation to immediately and continuously measure the
concentration in mg/m
3
of airborne dust particles.
•
This principle utilizes an infrared light source positioned at a 90-degree
angle from a photo detector.
•
As the airborne particles enter the infrared beam, they scatter the light. The
amount of light received by the photo detector is directly proportional to the
aerosol concentration.
•
A unique signal processes internally and compensates for noise and drift.
This allows high resolution, low detection limits and excellent base line
stability.
Figure 1.5. Diagram showing the principle of near-forward light scattering used in the Haz-
Dust..
Figure 1.6. Graph illustrating the principle of near-forward light scattering.
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
0
0.5
1
R
e
la
ti
v
e
O
p
ti
c
a
l
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
Gravimetric Filter Weight
Light Scattering vs. Gravimetric Filter
ARD
0.1
ARD = Arizona Road Dust
RTD = Real-Time Dust
ARD
Filter
