Allied Telesis AT-AR256E User Manual
Page 26
- 26 -
b. There are no restrictions on a host's location.
c. There are no restrictions on the number of members that may belong to a host group.
d. A host may belong to multiple host groups.
e. Non-group members may send UDP datagrams to the host group.
Multicasting is useful when data needs to be sent to more than one other device. For instance, if
one device is responsible for acquiring data that many other devices need, then multicasting is a
natural fit. Note that using multicasting as opposed to sending the same data to individual
devices uses less network bandwidth.
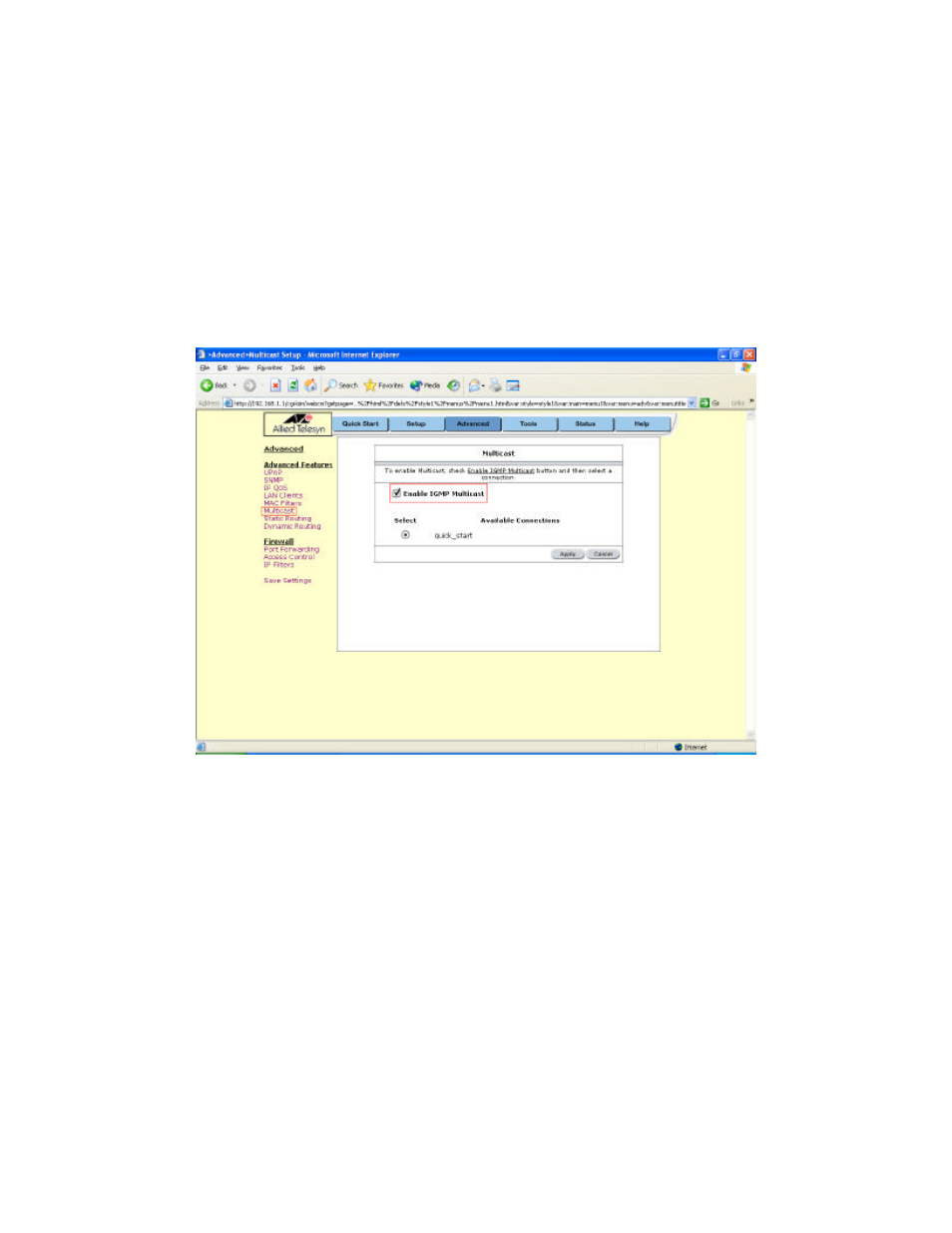
To enable Multicasting, click on Advanced and under Advanced, select Multicast. Figure 16
illustrates a typical Multicast configuration.
Figure 16 (Multicast)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.8 Static Routing
If the ADSL router is connected to more than one network, you may need to set up a static route
between them. A static route is a pre-defined pathway that network information must travel to
reach a specific host or network. You can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to
access the Internet through the ADSL router.
The New Destination IP is the address of the remote LAN or host to which you want to assign a
static route. Enter the IP address of the host for which you wish to create a static route here. For
a standard Class C IP domain, the network address is the first three fields of the New Destination
IP, while the last field should be 0. The Subnet Mask identifies which portion of an IP address is
the network portion, and which portion is the host portion. For a full Class C Subnet, the Subnet
