Rs-485 enable modes – Impulse 3055 User Manual
Page 8
Card
Setup
Sealevel Systems ULTRA-485 Page
5
RS-485 Enable Modes
RS-485 is ideal for multi-drop or network environments. RS-485 requires a
tri-state driver (not dual-state) that will allow the electrical presence of the driver
to be removed from the line. The driver is in a tri-state or high impedance
condition when this occurs. Only one driver may be active at a time and the other
driver(s) must be tri-stated. The output modem control signal Request To Send
(RTS) is typically used to control the state of the driver. Some communication
software packages refer to RS-485 as RTS enable or RTS block mode transfer.
One of the unique features of the ULTRA 485 is the ability to be RS-485
compatible without the need for special software or drivers. This ability is
especially useful in Windows, Windows NT, and OS/2 environments where the
lower level I/O control is abstracted from the application program. This ability
means that the user can effectively use the ULTRA 485 in a RS-485 application
with existing (i.e. standard RS-232) software drivers.
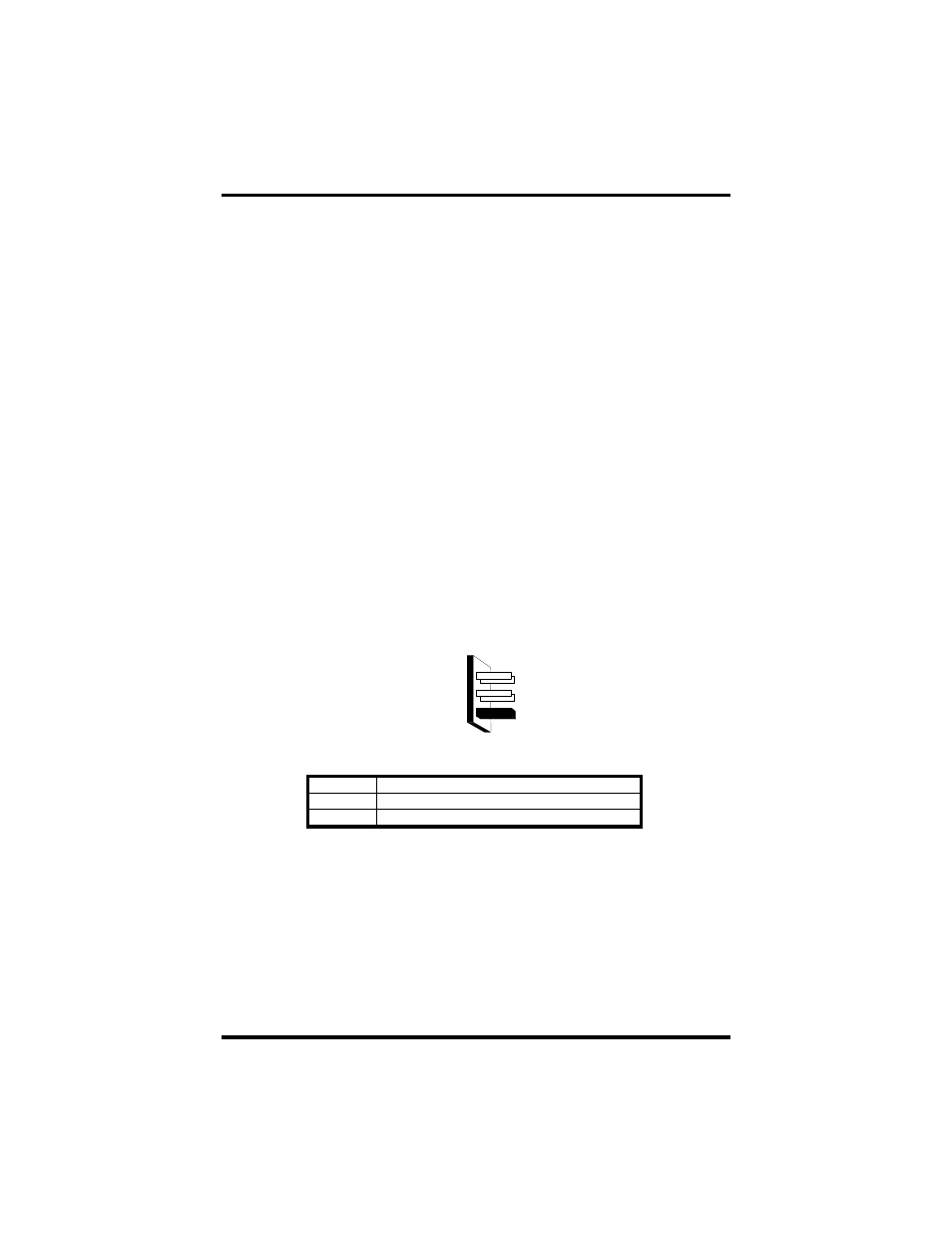
Header E5 is used to control the RS-485 mode functions for the transmitter
circuit. The selections are ‘RTS’ enable, ‘Auto’ enable, or ‘422’ which means
always enabled. The ‘Auto’ enable feature automatically enables/disables the
RS-485 transmitter circuit. The ‘RTS’ mode uses the ‘RTS’ modem control
signal to enable the RS-485 transmitter circuit and provides backward
compatibility with existing software products. The ‘422’ mode allows the port to
be used in a point to point RS-422 application where the tri-stating of the
transmitter circuit is not required.
AUTO
Driver automatically enabled/disabled
RTS
Driver enabled by UART RTS signal
422
Driver always enabled
Note: The jumper in the above example is in the ‘422’ position. This is the only
setting in which the modem control outputs (RTS, DTR) are valid.
Figure 4 - Header E5 RS-485 Transmit Mode
RTS
422
AUTO
E5
TX
