Elmo Rietschle S-VSA User Manual
Page 15
- 5 -
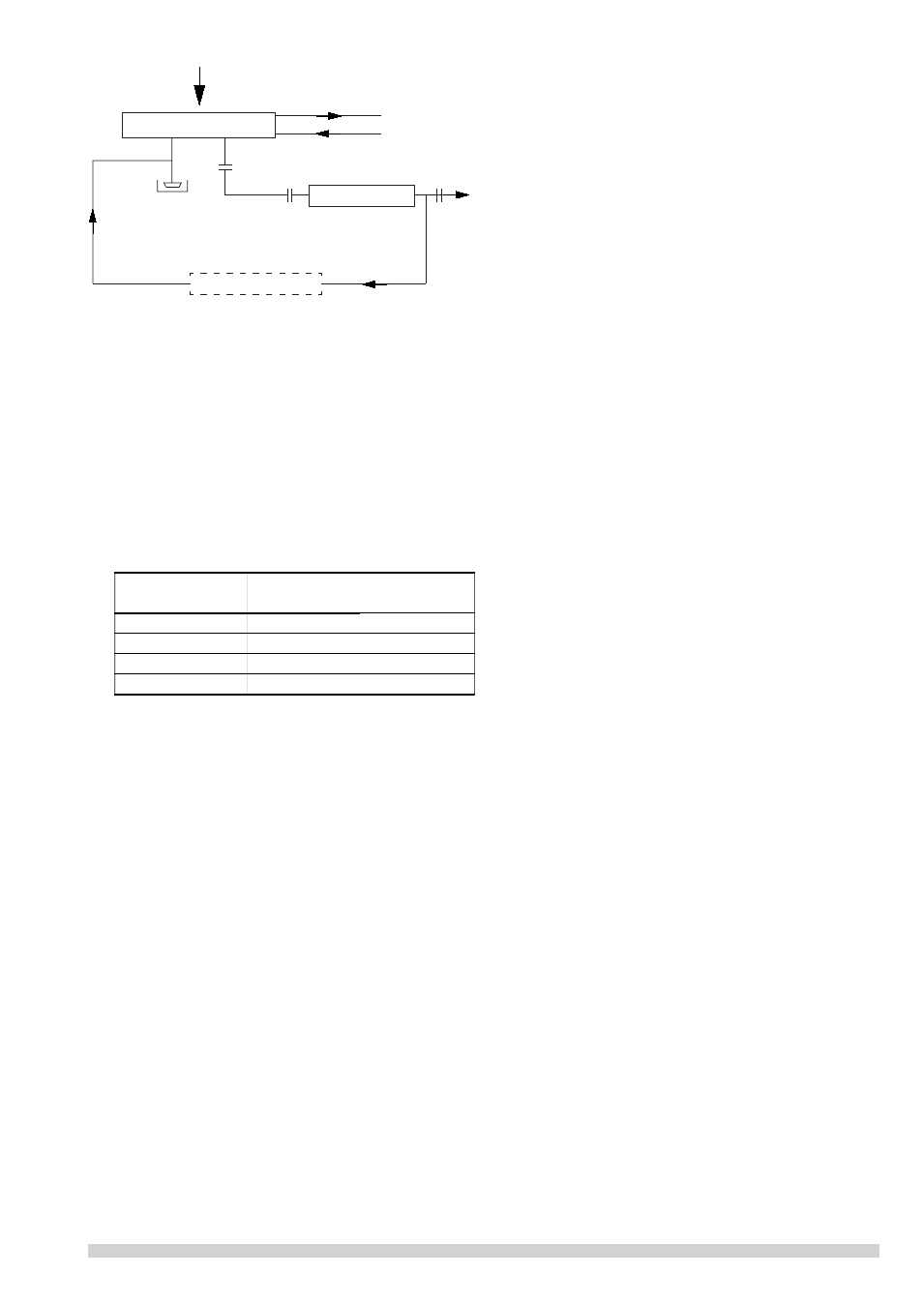
3.4 Piping diagram
! The after cooler and silencer are optional features.
3.5 Purges
3.5.1 Cooling purge
This purge is intended to cool the rotors and internals which
are heated by gas compression.. Since this compression
heat can reach above 200° C in the discharge side, a cool-
ing purge is needed to cool the gases. In most cases, an
atmospheric air cooling purge is used, this is the standard
purge.
An air filter is provided near the discharge side of the cas-
ing for this purge.
(1) Purge gas flow
This purge gas flow can vary according to operating vacuum
level
(2) Type of Cooling Purge
1. Standard: Atmosphere purge through air filter
2. Using Heat Exchanger, Recycle process gases after
cooling through the heat exchanger.
3. Using Inert gases like N
2
etc. instead of atmosphere or
cooled process gas.
3.5.2 Sealing purge
This purge is required during operation and is intended to
pressurise the front end cover with inert gas such as N
2
so
that the process gas or fluid is prevented from entering the
timing gear set and bearings. Either one of two plugs pro-
vided on the top of front end cover can be used for this
sealing purge connection.
The sealing purge gas pressure should be up to 1.5 bar
(abs.) the leak rate for the mech. seal is below 3 cm
3
/hr.
The Mech. seal can be pressurised up to 4 bar (abs.).
3.5.3 Cleaning purge
This purge is used to clean the inside the pump before
stopping. Before stopping the pump, purge with N
2
gas,
steam or cleaning agent for 20 to 30 minutes after closing
the main suction valve to clean sticky process materials or
process gases. This purge is especially important when
pumping corrosive/toxic or sticky materials like resin etc.
Model
Amount Nm
3
/h
VSA 150
18
VSA 300
18
VSA 400
25
VSA 800
above 30
VSA 2700
above 30
4. Handling procedure
4.1 Assembly of piping
4.1.1 Location
• Mount the Pump on a clean, flat & level surface of suffi-
cient rigidity. If it is to be installed outdoors, check motor,
V-belt and other parts are for outdoor service.
• There should be enough space for maintenance, disas-
sembly, reassembly and periodical inspection, etc.
4.1.2 Foundation
• The pump can be mounted on a suitable concrete plinth or
steel framework.
4.1.3 Installation
• Mount the pump horizontally and centre it in accordance
with the instruction manual. The pump should be level to
within 0.5 mm per metre.
4.2 Piping Work
4.2.1 Main Piping
• Clean the inside of suction and discharge pipework to en-
sure it is free from rust, dust and foreign matter, place a
strainer of 40 mesh on or over suction port.
• It is advisable to install an expansion joint on the suction
and discharge side of the pumps. Provide supports for pip-
ing so that no excessive load to be imposed on the pump.
• If silencer is to be fitted on the discharge side, install it as
near the discharge port as possible.
• Be sure to install a Non-return Valve adjacent to the suc-
tion port so that the pump will not turn in reverse when
switched off. If installation of the Non-return Valve is a prob-
lem for the duty of the pump, install a shut off valve, and
ensure it is closed prior to stopping the pump.
• In the event of condensate being collected at the pump
discharge, a collection tank may be installed under the
pump, and then the condensate and water will be collected
during operation and be discharged by the opening of a
drain valve.
• A drain receiver should be installed under the drain valve
to collect discharge.
4.2.2 Cooling water piping
Cooling water required to cool front end plate and casing.
The piping should be assembled with reference to the pip-
ing diagram and the outline drawing supplied.
* If Water Jacket type Silencer is installed, this Silencer also
requires cooling water.
Dry Pump Shell
Cooling water outlet
Cooling water inlet
Silencer
After cooler
