7 ac power draw and thermal dissipation – Crown Audio Macro-Tech MA-5000VZ User Manual
Page 38
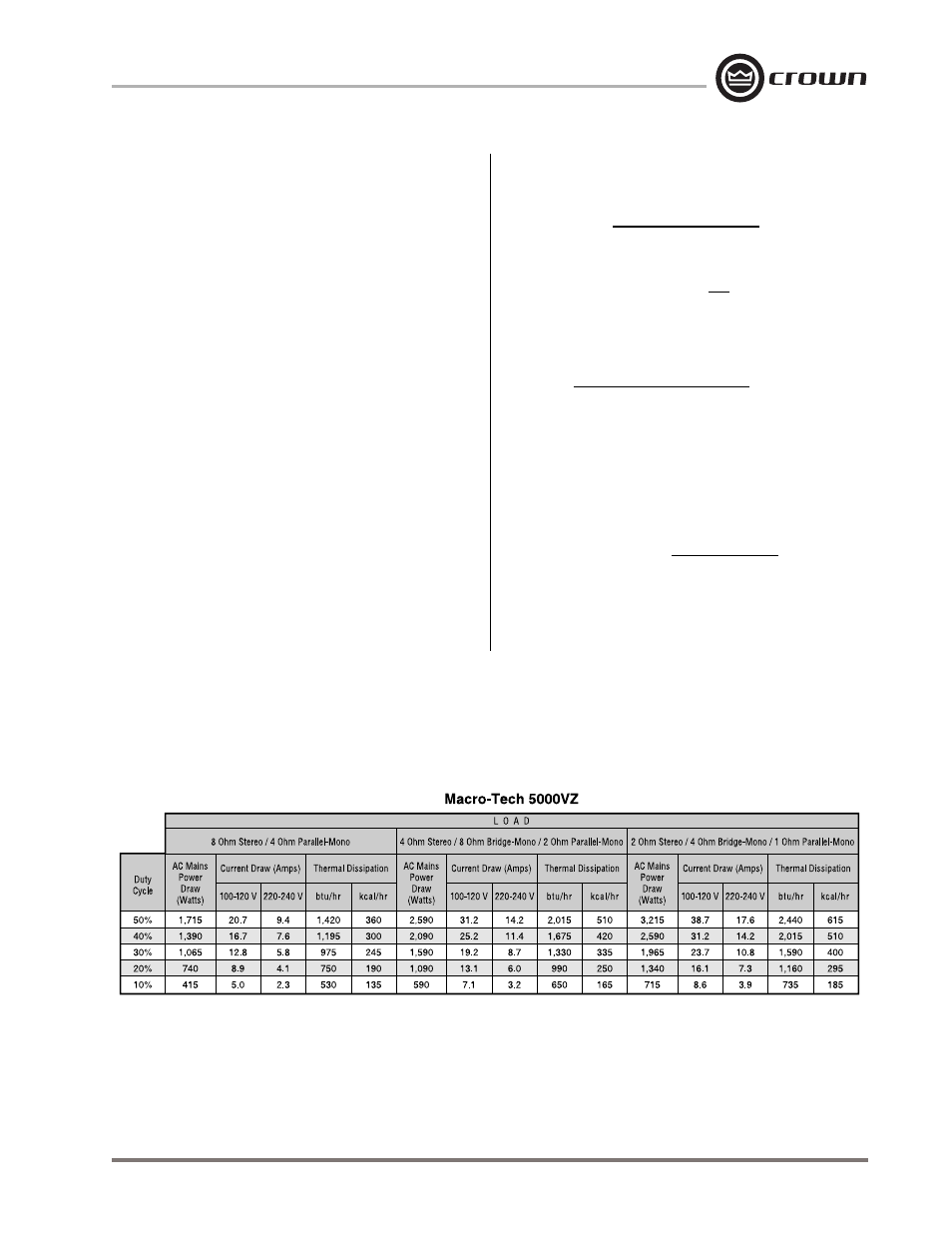
Page 39
Macro-Tech 5000VZ Power Amplifier
Reference Manual
7 AC Power Draw and
Thermal Dissipation
This section provides detailed information about the
amount of power and current drawn from the AC power
line by the
Macro-Tech 5000VZ, and the amount of heat
produced under various conditions. The calculations
presented here are intended to provide a realistic and
reliable depiction of the amplifier. The following as-
sumptions were made:
• The amplifier’s available channels are loaded, and full,
standard 1 kHz power is being delivered.
• Quiescent power draw is 90 watts (an almost
negligible amount for full-power calculations).
• Quiescent heat dissipation equals 105 btu/hr at
90 watts.
• Duty cycle of pink noise is 50%.
• Duty cycle of highly compressed rock ‘n’ roll midrange
is 40%.
• Duty cycle of rock ‘n’ roll is 30%.
• Duty cycle of background music is 20%.
• Duty cycle of continuous speech is 10%.
• Duty cycle of infrequent, short-duration paging is 1%.
Here are the equations used to calculate the data pre-
sented in Figure 7.1:
AC Mains Power
Draw (watts)
=
Total output power with all
channels driven (watts)
x Duty
Cycle
Amplifier Efficiency
+ Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
The quiescent power draw of 90 watts is typical, and
assumes the cooling fans are not running.
Thermal
Dissipation
(btu/hr)
=
Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
[
]
x 3.415
( 1 – Power to Load ) +
or
Total output power with all
channels driven (watts)
Thermal
Dissipation
(btu/hr)
=
+
Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
x Duty
Cycle
x
Amplifier Efficiency
(
)
x 3.415
Amplifier
Inefficiency
The constant 3.415 converts watts to btu/hr. Thermal
dissipation in btu is divided by the constant 3.968 to
get kcal.
To convert the power draw in watts to current draw in
amperes, use the following equation:
Current Draw
(amperes)
=
AC Mains Power
Draw (watts)
x
AC Mains
Voltage
Power
Factor (.83)
The current draw values shown in Figure 7.1 depend
on the AC mains voltage (power draw and thermal dis-
sipation are typical for any AC power voltage).
Fig. 7.1 Power Draw, Current Draw and Thermal Dissipation at Various Duty Cycles
