Max783, Design procedure – Rainbow Electronics MAX783 User Manual
Page 14
MAX783
These codes are compatible with many popular PCMCIA
digital controllers such as the Intel 82365SL. For other
interfaces, one of the inputs can be permanently wired
high or low and the other toggled to turn the supply on
and off. The truth table shows that either a “0” or “1” can
be used to turn each supply on. The two VPP outputs can
be safely connected in parallel for increased load capabil-
ity if the control inputs are also tied together (i.e., DA0 to
DB0, DA1 to DB1). If VPAA and VPPB are connected in
parallel, some devices may exhibit several milliamps of
increased quiescent supply current when enabled, due to
slightly mismatched output voltage set points.
Comparators
Two noninverting comparators can be used as preci-
sion voltage comparators or high-side drivers. The
supply for these comparators (VH) is brought out and
may be connected to any voltage between +3V and
+19V. The noninverting inputs (D1-D2) are high imped-
ance, and the inverting input is internally connected to
a 1.650V reference. Each output (Q1-Q2) sources
20µA from VH when its input is above 1.650V, and
sinks 500µA to GND when its input is below 1.650V.
The Q1-Q2 outputs can be fixed together in wired-OR
configuration since the pull-up current is only 20µA.
Connecting VH to a logic supply (5V or 3V) allows the
comparators to be used as low-battery detectors. For dri-
ving N-channel power MOSFETs to turn external loads on
and off, VH should be 6V to 12V higher than the load volt-
age. This enables the MOSFETs to be fully turned on and
results in low r
DS(ON)
. VDD is a convenient source for VH.
Internal VREF and VL Supplies
An internal linear regulator produces the 5V used by the
internal control circuits. This regulator’s output is avail-
able on pin VL and can source 5mA for external loads.
Bypass VL to GND with 4.7µF. To save power, when the
+5V switch-mode supply is above 4.5V, the VL linear
regulator is turned off and the high-efficiency +5V
switch-mode supply output is internally connected to VL.
The 3.3V precision reference (REF) is powered from the
internal 5V VL supply. It can furnish up to 5mA for exter-
nal loads. Bypass REF to GND with 0.22µF, plus 1µF/mA
of load current. The main switch-mode outputs track the
reference voltage. Loading the reference reduces the
main output voltages slightly, according to the reference
voltage load regulation error.
Both the VL and REF supplies can remain active—even
when the switch-mode regulators are turned off—to supply
memory keep-alive power (see
Shutdown Mode section).
These linear regulator outputs can be directly connected
to the corresponding switch-mode regulator outputs (i.e.,
REF to +3.3V, VL to +5V) to hold up the main supplies in
standby mode. However, to ensure start-up, standby
load currents must not exceed 5mA on each supply.
Shutdown Mode
Shutdown (S
—
H
—
D
—
N
–
= low) forces both PWMs off and dis-
ables the REF output and the auxiliary comparators
including R
—
D
—
Y
—
5
–
. Supply current in shutdown mode is
typically 25µA. The VL supply remains active and can
source 25mA for external loads. VL load capability is
higher in shutdown and standby modes than when the
PWMs are operating (25mA vs. 5mA).
Standby mode is achieved by holding ON3 and ON5
low while S
—
H
—
D
—
N
–
is high. This disables both PWMs, but
keeps VL, REF, and the precision comparators alive.
Supply current in standby mode is typically 70µA.
Other ways to shut down the MAX783 are suggested in
the applications section of the MAX782 data sheet.
__________________Design Procedure
Figure 1’s predesigned application circuit contains the
correct component values for 3A output currents and a
6V to 20V input range. Use the design procedure that
follows to optimize this basic schematic for different
voltage or current requirements.
Before beginning a design, firmly establish the following:
V
IN(MAX)
, the maximum input (battery) voltage.
This
value should include the worst-case conditions under
which the power supply is expected to function, such
as no-load (standby) operation when a battery charger
is connected but no battery is installed. V
IN(MAX)
can-
not exceed 30V.
V
IN(MIN)
, the minimum input (battery) voltage.
This
value should be taken at the full-load operating cur-
rent under the lowest battery conditions. If V
IN(MIN)
is below about 6V, the filter capacitance required to
maintain good AC load regulation increases, and the
current limit for the +5V supply has to be increased
for the same load level.
Triple-Output Power-Supply Controller
for Notebook Computers
14
______________________________________________________________________________________
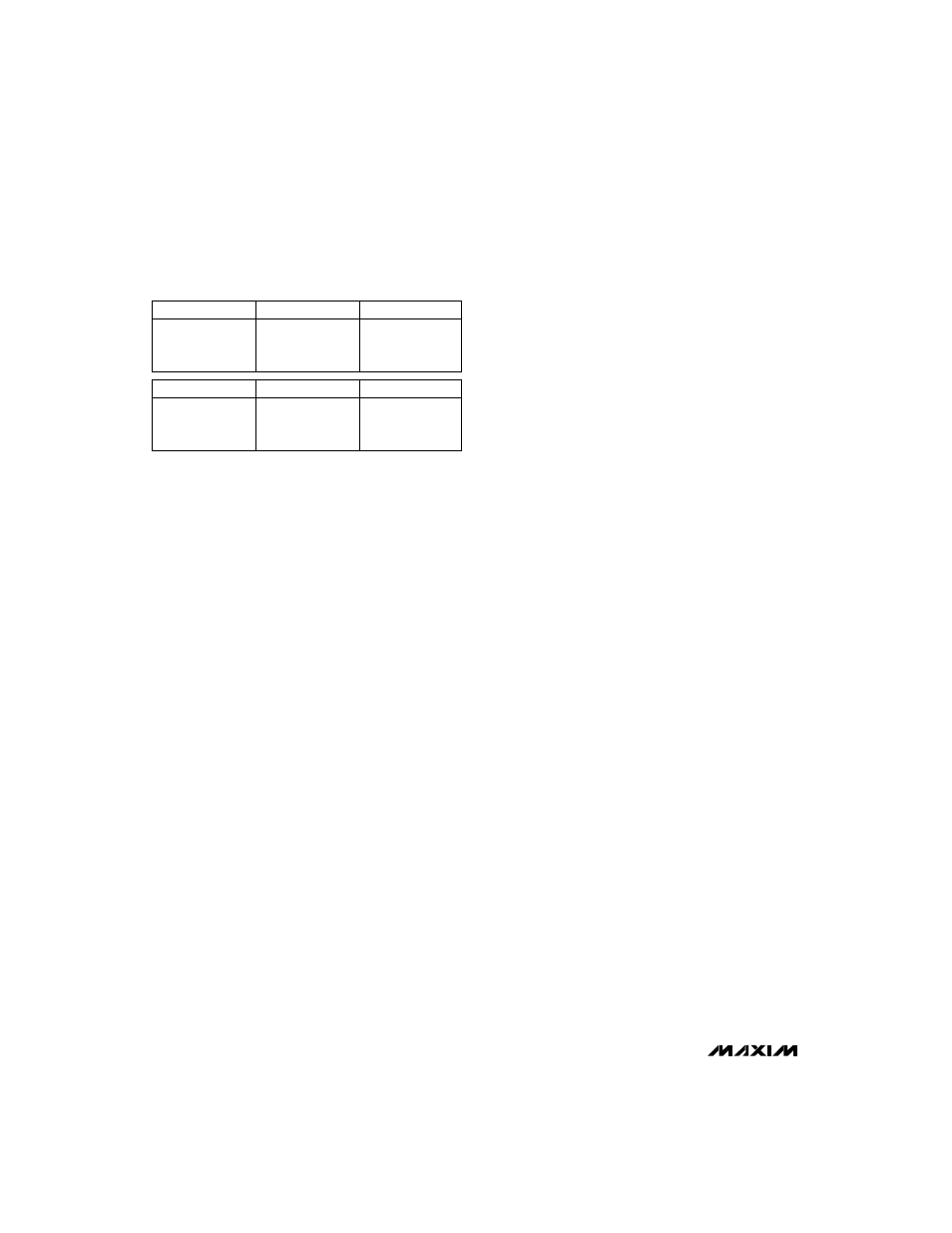
Table 2. VPP Program Codes
DA0
DA1
VPPA
0
1
0
1
0V
5V
12V
3.3V
0
0
1
1
DB0
DB1
VPPB
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0V
5V
12V
3.3V
