Rainbow Electronics DS1957 User Manual
Page 5
DS1957
5 of 25
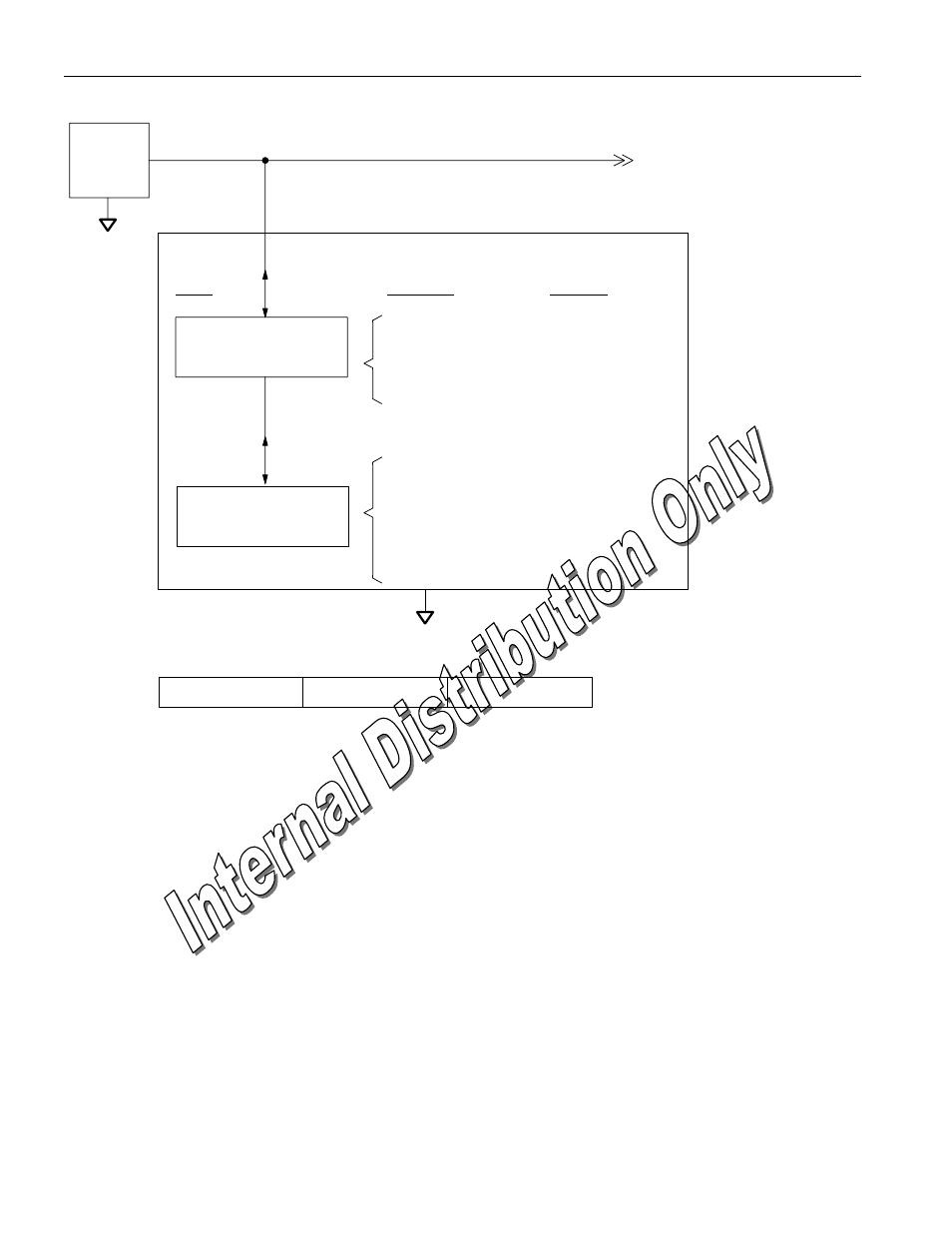
HIERARCHICAL STRUCTURE FOR 1-WIRE PROTOCOL Figure 2
64-BIT LASERED ROM Figure 3
DATA TRANSFER AND CONTROL FUNCTION COMMANDS
The “Data Transfer And Control Function Flow Chart” (Figure 4) describes the protocols necessary for
accessing the various registers within the DS1957 and to control its microcomputer. The Data Transfer
and Control Function Control section interprets the commands issued by the bus master and creates the
correct control signals within the device. The protocol issued by the bus master always starts with a
command byte which determines if the device is to be read or written or if the microcomputer is to be
activated or reset. Except for the Intermediate Product Register (IPR) and reading the Status Register,
communication with the DS1957 requires not only issuing the correct command sequence but also
providing a command-dependent 16-bit release sequence at the appropriate time. To access the IPR or
the I/O buffer for read or write, the bus master has to specify the number of bytes to be transferred.
Address information is not required since accessing the IPR and the I/O buffer always begin at address
00. Unless the bus master reads back from the IPR before the microcomputer has processed the data, all
data transferred to the DS1957 and received back by the bus master are sent least significant bit first.
8-Bit CRC Code
48-Bit Serial Number
8-Bit Family Code (16H)
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
1-WIRE ROM FUNCTION
COMMANDS (SEE FIGURE 6)
DS1957 SPECIFIC DATA
COMMAND
LEVEL:
AVAILABLE
COMMANDS:
DATA FIELD
AFFECTED:
READ ROM
MATCH ROM
SEARCH ROM
SKIP ROM
64-BIT ROM
64-BIT ROM
64-BIT ROM
N/A
BUS
MASTER
1-WIRE BUS
OTHER
DEVICES
DS1957
OVERDRIVE SKIP ROM
OVERDRIVE MATCH ROM
N/A
64-BIT ROM
WRITE IPR
READ IPR
WRITE I/O BUFFER
READ I/O BUFFER
START PROGRAM
CONTINUE PROGRAM
RESET MICRO
READ STATUS
WRITE STATUS
IP REGISTER
IP REGISTER
I/O BUFFER
I/O BUFFER
MICROCOMPUTER
MICROCOMPUTER
MICROCOMPUTER
STATUS REGISTER
STATUS REGISTER
TRANSFER AND CONTROL
FUNCTION COMMANDS
(SEE FIGURE 4)
